Engine device
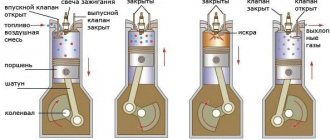
All daewoo nexia engines installed on the car were a classic gasoline 4-cylinder, in-line, four-stroke unit. Structurally, the engines were identical, had the same lubrication system, cooling system, and cylinder block. The engine marked G15MF also had a number of significant differences from the Opel Kadett E
The gas distribution system used a scheme with an overhead arrangement of one camshaft. The catalytic converter and lambda probe were missing.
In the newer modification, labeled A15MF, minor design changes were applied. The gas distribution mechanism was driven by two overhead camshafts. The number of valves was increased to 4 per cylinder, and the ignition system was significantly changed. A lambda probe and a catalytic converter were installed on the power plant.
The engine control system consists of an electronic control unit (ECU), sensors for engine and vehicle operating parameters, as well as actuators. The ECU is a special-purpose mini-computer. It consists of random access memory (RAM) and programmable read-only memory (PROM). RAM is used by the microprocessor to temporarily store current information about engine operation (measured parameters) and calculated data. From RAM, the engine control unit takes programs and initial data for processing. Codes of any faults that occur are also recorded in RAM.
General description of power units
All daewoo nexia engines installed on the car were a classic gasoline 4-cylinder, in-line, four-stroke unit. Structurally, the engines were identical, had the same lubrication system, cooling system, and cylinder block.
The engine marked G15MF also had a number of significant differences from the Opel Kadett E.
The gas distribution system used a scheme with an overhead arrangement of one camshaft. The catalytic converter and lambda probe were missing.
In the newer modification, labeled A15MF, minor design changes were applied. The gas distribution mechanism was driven by two overhead camshafts. The number of valves was increased to 4 per cylinder, and the ignition system was significantly changed. A lambda probe and a catalytic converter were installed on the power plant.
In 2008, both G15MF and A15MF engines were discontinued. They were replaced by more advanced models labeled A15SMS and F16D3.
G15MF powerplant
This is the first engine that began to be installed on a car.
Characteristics of daewoo nexia engine G15MF:
The Daewoo Nexia engine reaches a speed of 175 km/h to hundreds, accelerating in 12.5 seconds. Fuel consumption in city mode is 9.3 liters per hundred, on the highway - 7 liters per hundred. The engine has proven itself well; with proper care, the engine life without major repairs is more than 200,000 km.
Powerplant A15MF
In 2002, some changes were made to the Daewoo Nexia engine, thanks to which the power of the unit was increased to 85 hp, without reducing the engine life. The most significant change was the use of 16 valves, 4 valves per cylinder.
The main difference from the engine with 8 valves was the use of a new cylinder head. Now it had two camshafts installed, and the ignition was controlled by an electronic unit, thanks to which it was possible to reduce fuel consumption (city - 9.3 liters per hundred, highway - 6.5 liters per hundred). The cylinder diameter was not changed, as for the pistons - grooves for the valves appeared on the bottom.
Powerplant A15SMS
The motor embodies all the best properties of the older predecessor G15MF, in addition, quite significant innovations were introduced to improve environmental performance.
The engine control system received a large number of sensors, which made it possible to more finely control engine settings in automatic mode. An ignition module has been installed. The intake manifold has a new geometry. Two catalytic exhaust gas converters and two oxygen concentration sensors are installed.
The engine power increased to 89 hp, the engine life did not change, thanks to the improvements it began to comply with EURO-3 standards.
Powerplant F16D3
The motor is an improved version of its predecessor F14D3; enough innovations have been introduced into it to improve performance.
Characteristics of daewoo nexia engine F16D3:
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Volume, cm³. | 1598 |
| Valves, pcs. | 16 |
| Valves per cylinder, pcs. | 4 |
| Cylinder, diameter, mm. | 79 |
| Piston, stroke, mm. | 81,5 |
| Fuel system | Distributive injection |
| Location | Transverse |
| Power, hp | 109 |
| Compression ratio | 9,5 |
| Torque, Nm at rev. per minute | 142 at 4000 |
| Gas distribution mechanism | DOHC 16V |
| Fuel | gasoline AI-95 |
| Consumption, l per hundred km (city) | 7,3 |
| Coolant | Base: ethylene glycol |
| Cooling system | Closed, forced |
| Lubrication system | Combined |
| Engine oil volume, l. | 3,75 |
| Engine oil type | 5W-30/10W-40/15w-40 |
| Environmental standards | EURO-3 |
Engine diagram
Elements of the F16D3 electronic engine control system:
1* — phase sensor; 2 — engine intake air temperature sensor; 3* — throttle position sensor; 4* — diagnostic block; 5* — coolant temperature sensor; b* — knock sensor; 7 — intake air absolute pressure sensor; 8* — speed sensor; 9* — warning lamp for control system malfunction; 10* — mounting block of fuses and relays; 11 - battery; 12 — electronic control unit; 13zh — wheel speed sensor; 14 — ignition coils; 15* — crankshaft position sensor; 16* — control oxygen concentration sensor; 17* — spark plugs; 18
— diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor
This memory is volatile, i.e. When the electrical power is interrupted (the battery is disconnected or the wiring harness block is disconnected from the ECU), its contents are erased. The PROM stores the engine control program, which contains a sequence of operating commands (algorithms) and calibration data - settings. The PROM is non-volatile, i.e. The contents of the memory do not change when the power is turned off.
The ECU receives information from system sensors and controls actuators such as the fuel pump and injectors, ignition coil, idle speed control, oxygen concentration sensor heating element, canister purge valve, exhaust gas recirculation valve, intake tract length variable valve (on the F16D3 engine ), air conditioning compressor clutch, cooling fan.
Basic engine malfunctions
Daewoo power units have a number of characteristic disadvantages:
The Nexia engine with 8 valves and a volume of 1.5 liters has become one of the most popular on Daewoo Nexia in recent years. Today there are quite a few cars on the secondary market with this engine. 80 hp unit (A15 SMS), this is a naturally aspirated gasoline engine with distributed multipoint fuel injection with an ignition coil, which replaced the 1.5-liter G15 MF engine developing 75 hp. with an unreliable distributor.
Daewoo Nexia engine 8 valves timing device, technical characteristics of Daewoo Nexia 1.5 l.
The Daewoo Nexia engine 8 valves with a volume of 1.5 liters has become one of the most popular in Daewoo Nexia in recent years. Today there are quite a few cars on the secondary market with this engine. 80 hp unit (A15 SMS, the same engine is in the Chevrolet Lanos), this is a naturally aspirated gasoline engine with distributed multipoint fuel injection with an ignition coil, which replaced the G15 MF developing 75 hp. with an unreliable distributor.
Nexia engine design 8 valves
The Nexia engine is a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, overhead camshaft. The location in the engine compartment is transverse. The operating order of the cylinders is: 1-3-4-2, counting from the auxiliary drive pulley. The power supply system is phased distributed fuel injection (Euro-3 toxicity standards). The engine has a cast iron cylinder block.
The engine, gearbox and clutch form the power unit - a single unit mounted in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal supports. The right support is attached to a bracket located on the front wall of the cylinder block, and the left and rear ones are attached to the gearbox housing.
Technical characteristics of Daewoo Nexia N150
The Nexia car of the South Korean concern Daewoo was created on the basis of the German Opel Cadet car, produced from 1984 to 1992. The Korean version of the car was called Daewoo Racer. In 1994, the Daewoo company carried out a restyling, after which the model received the final name “Nexia”. In 1996, production of the model began in Uzbekistan (JSC UzDaewoo Auto) and in the city of Aksai near Rostov-on-Don. Since 2000, production of the model (except for engines) has been transferred to Uzbekistan. In 2008, the car underwent restyling, during which some body panels and lighting equipment were changed, and new engines began to be installed. The information is relevant for models 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2021.
| Parameter | Engine A15SMS | Engine F16D3 |
| Body type | Sedan | |
| Layout diagram | Front transverse engine arrangement; front wheel drive | |
| Number of seats | 5 | |
| Number of doors | 4 | |
| Curb weight, kg | 969 | 1025 |
| Gross weight in basic configuration, kg | 1404 | 1460 |
| Total weight of the towed trailer, kg: | ||
| not equipped with brakes | 430 | 400 |
| equipped with brakes | 860 | 860 |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 163 | 175 |
| Minimum turning radius, m | 4,9 | |
| Trunk volume, l | 5,3 | |
| Ground clearance, mm | 160 | |
| Engine | ||
| Parameter | Engine A15SMS | Engine F16D3 |
| Type | Gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line | |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 | 4 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 | |
| Cylinder diameter/piston stroke, mm | 76,5/81,5 | 79/81,5 |
| Working volume, cm3 | 1498 | 1598 |
| Compression ratio | 9,5 | 9,5 |
| Rated power, kW (hp) | 58,9 (80) | 80 (108) |
| Crankshaft rotation speed at rated power, min - 1 | 5600 | 5800 |
| Maximum torque, Nm | 123 | 153 |
| Crankshaft rotation speed at maximum torque, min1 | 3200 | 4000 |
| Ignition system | Electronic | |
| Gap between spark plug electrodes, mm | 0,7-0,8 | 1,0-1,1 |
| Power system type | Distributed (phased) fuel injection | |
| Transmission | ||
| Parameter | Engine A15SMS | Engine F16D3 |
| Clutch | Single disc, dry, with diaphragm pressure spring | |
| Clutch release drive | Hydraulic | |
| Transmission | Mechanical, with synchronizers in all forward gears | |
| Number of forward gears | 5 | |
| Gearbox ratios: | ||
| 1st gear | 3,818 | 3,818 |
| 2nd gear | 2,158 | 2,158 |
| III gear | 1,478 | 1,478 |
| IV gear | 1,129 | 1,121 |
| V gear | 0,886 | 0,886 |
| reverse | 3,333 | 3,333 |
| main gear | Cylindrical, helical | |
| Final drive ratio | 3,722 | 3,55 |
| Differential | Conical, two-satellite | |
| Wheel drive | Shafts with constant velocity joints | |
| Chassis | |
| Front suspension | Independent, lever-telescopic, with hydraulic shock absorber struts, made integral with the steering knuckles, with coil springs, lower wishbones and anti-roll bar |
| Front wheel bearings | Ball, angular contact, double row |
| Front wheel alignment angles: | |
| longitudinal to the tilt of the wheel steering axis | 1°45’±1° |
| camber angle | -25’±45′ |
| wheel alignment | 0°±10′(0±1 mm) |
| Rear suspension | Semi-independent, with coil springs, hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers, anti-roll bar and trailing arms elastically connected by a U-shaped transverse beam |
| Rear wheel alignment angles: | |
| wheel camber | from -2°10′ to -1°10′ |
| wheel alignment | -10′ to 40′ (-1 to 4 mm) |
| Rear wheel bearings | Conical, roller |
| Wheels | Disc, steel, stamped or light alloy |
| Wheel rim size | 5.5 JX14 |
| Tires | Radial, low profile, tubeless |
| Tire size | 185/60R14 |
| Steering | |
| Steering gear | Rack and pinion |
| Gear ratio: | |
| without amplifier | 24,5 |
| with hydraulic booster | 18,4 |
| Steering gear | Two steering rods connected to the rack by rubber-metal, and to the swing arms by ball joints |
| Brake system | |
| Service brake system | The front brakes are disc brakes with movable calipers and automatic adjustment of the gaps between the discs and pads. The rear brakes are drum brakes with automatic adjustment of the gaps between the shoes and drums. Drive - hydraulic, two-circuit with diagonal separation of circuits, vacuum booster and pressure regulators in the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels |
| Parking brake | With manual cable drive on the brake pads of the rear wheels |
| Electrical equipment | |
| Electrical diagram | Single-wire, negative terminals of power supplies and consumers are connected to ground (the body and components of the car) |
| Rated voltage, V | 12 |
| Battery capacity, Ah | 55 |
| Generator | AC, three-phase, with built-in rectifier unit and electronic voltage regulator |
| Maximum current supplied by the generator, A | 85 |
| Starter | Excited by permanent magnets, with planetary gearbox |
| Starter power, kW | 0,8 |
Nexia engine cylinder head 8 valves
The Nexia 8 valve cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy, common to all four cylinders. The head is centered on the block with two bushings and secured with ten bolts. A sealing gasket is installed between the block and the cylinder head.
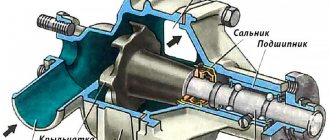
The intake and exhaust ports are located on opposite sides of the cylinder head. Valve seats and guides are pressed into the cylinder head. The valve closes under the action of a single spring. Its lower end rests on the washer, and its upper end rests on a plate held by two crackers. The crackers folded together have the shape of a truncated cone, and on their inner surface there are beads that fit into the grooves on the valve stem. The valves are driven by the camshaft. The camshaft is cast iron and rotates on five supports (bearings) in an aluminum bearing housing, which is attached to the top of the cylinder head.
Timing drive of Nexia engine 8 valves
The camshaft of the Nexia's 8-valve engine is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. The valves are actuated by the camshaft cams through pressure levers, which rest on the hydraulic lash compensators with one shoulder, and on the valve stems with the other shoulder through guide washers. The engine has hydraulic compensators , which are self-adjusting supports for the pressure levers. Under the influence of oil filling the internal cavity of the compensator under pressure, the compensator plunger selects a gap in the valve drive. The use of hydraulic compensators in the valve drive reduces the noise of the gas distribution mechanism and also eliminates its maintenance.
If the belt breaks, the valve bends! Among other features, it can be noted that the timing belt rotates the pump (water pump). The belt is replaced every 60 thousand kilometers, the pump must be changed every 120 thousand kilometers. Please note that on the old 8-valve engine with 75 hp. The timing belt generally changes every 40 thousand kilometers.
Technical characteristics of the Nexia engine 8 valves 80 hp.
- Working volume – 1498 cm3
- Number of cylinders – 4
- Number of valves – 8
- Cylinder diameter – 76.5 mm
- Piston stroke – 81.5 mm
- Timing drive - belt
- Power hp – 80 at 5600 rpm. per minute
- Torque – 123 Nm at 3200 rpm. per minute
- Maximum speed – 175 km/h
- Acceleration to the first hundred – 12.5 seconds
- Fuel type – gasoline AI-92
- Fuel consumption in the city – 8.5 liters
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle – 8 liters
- Fuel consumption on the highway – 7.7 liters
A fairly reliable and unpretentious engine, the main thing is to change the oil, timing belt, and pump on time. A completely repairable power unit.
Reading time: 2 minutes
The Daewoo Nexia engine 8 valves with a volume of 1.5 liters has become one of the most popular in Daewoo Nexia in recent years. Today there are quite a few cars on the secondary market with this engine. 80 hp unit (A15 SMS, the same engine is in the Chevrolet Lanos), this is a naturally aspirated gasoline engine with distributed multipoint fuel injection with an ignition coil, which replaced the G15 MF developing 75 hp. with an unreliable distributor.
Technical characteristics of the Nexia engine
Below are brief technical characteristics of engines, such as volume, power, number of valves, torque, compression ratio.
| Engine | Volume (l) | Power (hp) | Number of valves (pcs) | Torque (Hm) | Compression ratio |
| Engine G15MF | 1.5 | 75 | 8 | 100 | 8.1 |
| Engine A15MF | 1.5 | 88 | 16 | 130 | 8.3 |
| Engine A155MS | 1.5 | 85 | 8 | 130 | 9.5 |
| Engine F16D3 | 1.6 | 109 | 16 | 150 | 9.5 |
As can be seen from the table above, the most energy-intensive was the last engine, which, by the way, was installed on the Chevrolet Aveo, Cruze and Lacetti.
Daewoo Nexia engine design 8 valves
Engine Nexia 1.5 l. gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, overhead camshaft. The location in the engine compartment is transverse. The operating order of the cylinders is: 1-3-4-2, counting from the auxiliary drive pulley. The power supply system is phased distributed fuel injection (Euro-3 toxicity standards). The engine has a cast iron cylinder block.
The engine, gearbox and clutch form the power unit - a single unit mounted in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal supports. The right support is attached to a bracket located on the front wall of the cylinder block, and the left and rear ones are attached to the gearbox housing.
Cylinder head for Daewoo Nexia 8 cl.
The Nexia 8 valve cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy, common to all four cylinders. The head is centered on the block with two bushings and secured with ten bolts. A sealing gasket is installed between the block and the cylinder head.
The intake and exhaust ports are located on opposite sides of the cylinder head. Valve seats and guides are pressed into the cylinder head. The valve closes under the action of a single spring. Its lower end rests on the washer, and its upper end rests on a plate held by two crackers. The crackers folded together have the shape of a truncated cone, and on their inner surface there are beads that fit into the grooves on the valve stem. The valves are driven by the camshaft. The camshaft is cast iron and rotates on five supports (bearings) in an aluminum bearing housing, which is attached to the top of the cylinder head.
Timing drive of Nexia 1.5 l engine.
The camshaft of the Nexia's 8-valve engine is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. The valves are actuated by the camshaft cams through pressure levers, which rest on the hydraulic lash compensators with one shoulder, and on the valve stems with the other shoulder through guide washers. The engine has hydraulic compensators , which are self-adjusting supports for the pressure levers. Under the influence of oil filling the internal cavity of the compensator under pressure, the compensator plunger selects a gap in the valve drive. The use of hydraulic compensators in the valve drive reduces the noise of the gas distribution mechanism and also eliminates its maintenance.
If the belt breaks, the valve bends! Among other features, it can be noted that the timing belt rotates the pump (water pump). The belt is replaced every 60 thousand kilometers, the pump must be changed every 120 thousand kilometers. Please note that on the old 8-valve engine with 75 hp. The timing belt generally changes every 40 thousand kilometers.
Engine characteristics Nexia 8 valves 80 hp
- Working volume – 1498 cm3
- Number of cylinders – 4
- Number of valves – 8
- Cylinder diameter – 76.5 mm
- Piston stroke – 81.5 mm
- Timing drive - belt
- Power hp – 80 at 5600 rpm. per minute
- Torque – 123 Nm at 3200 rpm. per minute
- Maximum speed – 175 km/h
- Acceleration to the first hundred – 12.5 seconds
- Fuel type – gasoline AI-92
- Fuel consumption in the city – 8.5 liters
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle – 8 liters
- Fuel consumption on the highway – 7.7 liters
Resource of 1.6-liter engine
As mentioned above, only in the N150 version of Daewoo Nexia an engine with a displacement of 1.6 liters appeared. They were also equipped with the Chevrolet Lacetti, where the engine performed quite well. The usual designation for the F16D3 power unit. Another marking of it is LXT. Assembled in South Korea from 2002 to 2013. In terms of design, it is a modernized version of the Daewoo A16DMS engine.
F16D3
Serial production of the engine began in 2002. The new engine replaced the F14D3, which by that time no longer met current environmental standards. Further environmental tightening and changes in the principles of engine construction contributed to the emergence of other engines that replaced the F16D3 - F16D4 and F18D4. In terms of its layout, it is a regular in-line “four” with two shafts of a DOHC gas distribution mechanism. The block is cast from high-strength material, and its cylinders are bored directly into the body itself.
The cylinder head design is designed to ensure the best cooling and effectively blow through the internal components of the internal combustion engine. The 16-valve cylinder head is improved with hydraulic compensators. The F16D3 engine has an insufficiently high-quality timing belt: it requires replacement after 60-80 thousand km. The most problematic areas are the pump, high-voltage wires, spark plugs, and thermostat. All these engine components will have to be replaced within the first 80-100,000 kilometers.
It is very important during operation of the Daewoo Nexia 1.6 F16D3 to regularly check the condition of the timing belt, since if it breaks, the valves are guaranteed to bend. One of the strengths of the engine is the interchangeability of parts with other modifications of the power unit (previous and subsequent)
Problems with finding components and consumables should not arise in a large, medium-sized or even small city. There are enough specialists who sort out this power unit. As for the shortcomings of the F16D3, we can note periodic drops in traction, power, early failure of the timing belt, oil leakage and unstable idle speed.
Car owners often complain about the increased “appetite” of the engine, not only for motor oil, but also for fuel during the operation of the vehicle in an urban environment. But the simple design and the absence of complex systems makes it possible to capitalize on a 1.6-liter installation even in ordinary garage conditions. As for the potential resource of the Daewoo Nexia 1.6 engine, the manufacturer assures that the engine will last 250,000 kilometers. Reviews from car owners indicate a much greater potential of the engine - 300,000 kilometers.
Technical specifications G15MF 1.5 l/75 l. With.
Initially, the engine did not have a lambda probe and a catalytic converter, so as requirements became stricter, it was replaced with more progressive modifications. The engine diagram is copied from the German Opel Kaddet E in 1994:
- inline four for transverse arrangement under the hood;
- SOHC gas distribution scheme with one camshaft;
- adjusting the mixture with a potentiometer similar to the VAZ 2110.
It is possible to boost it using classical methods to increase power, and do it yourself in a garage without involving specialists.
For its time, the G15MF engine had progressive technical characteristics:
| Manufacturer | Daewoo |
| Engine brand | G15MF |
| Years of production | 1994 – 2008 |
| Volume | 1498 cm3 (1.5 l) |
| Power | 55.4 kW (75 hp) |
| Torque moment | 120 Nm (at 3400 rpm) |
| Weight | 117 kg |
| Compression ratio | 8,5 |
| Nutrition | injector |
| Motor type | in-line petrol |
| Ignition | switching, contactless |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE |
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 2 |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy |
| Intake manifold | duralumin, channels of different lengths |
| An exhaust manifold | cast iron |
| Camshaft | original cam profile |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | 76.5 mm |
| Pistons | original |
| Crankshaft | AA-DW000 |
| Piston stroke | 81.5 mm |
| Fuel | AI-92 |
| Environmental standards | Euro-1/2 |
| Fuel consumption | highway – 7 l/100 km mixed cycle 8.8 l/100 km city – 10.5 l/100 km |
| Oil consumption | maximum 0.6 l/1000 km |
| What kind of oil to pour into the engine by viscosity | 5W30, 5W40, 0W30, 0W40 |
| Which engine oil is best by manufacturer | Liqui Moly, LukOil, Rosneft |
| Oil for G15MF by composition | synthetic in winter, semi-synthetic in summer |
| Engine oil volume | 3.75 l |
| Operating temperature | 95° |
| ICE resource | declared 200,000 km actual 250,000 km |
| Adjustment of valves | screws |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze |
| Coolant volume | 7 l |
| water pump | with plastic impeller GVG-90A |
| Spark plugs for G15MF | BPR6E from NGK or domestic AU17DVR |
| Spark plug gap | 0.8 mm |
| Timing belt | original Goodyear G1116H 111H9.5P170, replacement Gates K15310XS |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst |
| Oil filter | with check valve |
| Flywheel | 6 holes, one offset |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | M12x1.25 mm, length 26 mm |
| Valve stem seals | manufacturer Goetze |
| Compression | from 10 bar, difference in adjacent cylinders maximum 1 bar |
| XX speed | 800 – 850 min-1 |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm clutch bolt – 19 – 30 Nm bearing cap – 68 – 84 Nm (main) and 43 – 53 Nm (connecting rod) cylinder head – three stages 20 Nm +65° + 65° + 65° |
The factory manual must contain both a description of the engine parameters and step-by-step operations for repairing/maintenance of the internal combustion engine in order to maintain the warranty and the service life declared from the factory.
Engine 1.5 l, P4 SOHC, 8 valve (one overhead camshaft)
Top of the engine
| 1. ENGINE LIFTING EYE 2. FILLER CAP 3. CAP SEAL 4. HEAD BOLT 5. WASHER 6. CAMSHAFT HOUSING COVER 7. GASKET 8. CAMSHAFT HOUSING 9. CAM HOUSING BOLT 10. BOLT 11. CAMSHAFT THRUST PLATE 12. BOLT 13. NUT 14. IGNITION DISTRIBUTOR 15. HIGH VOLTAGE WIRE BUNCH 16. BYPASS VALVE 17. ADAPTER 16. CAP 19. COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR 20. SPARK PLUG 21. PIN KA 22. EXHAUST MANIFOLD GASKET 23. EXHAUST MANIFOLD 24. HEAT PROTECTIVE CASING 25. NUT 26. CYLINDER HEAD GASKET 27. EXHAUST VALVE 28. INTAKE VALVE 29. CYLINDER HEAD | 30. GUIDE BUSHING 31. VALVE SPRING SUPPORT PLATE 32. VALVE SPRING 33. UPPER SPRING PLATE 34. VALVE ROD RUNNERS 35. STOP 36. VALVE DRIVE LEVER 37. ZAZ HYDRAULIC COMPENSATOR ORA 38. VALVE SEAL 39. OUTLET VALVE CAP 40. THERMOSTAT 41. SEAL 42. BOLT 43. THERMOSTAT HOUSING 44. TIMING BELT 45. GEAR BOLT 46. WASHER 47. CAMSHAFT GEAR 48 BALL 49 SEAL 50 SPINAL 51. CAMSHAFT 52. PRO INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET 53. INTAKE MANIFOLD 54. NUT 55. GASKET THROTTLE BODY 56. THROTTLE BODY |
Lower part of the engine (1.5 l, P4 SOHC)
| 101. OIL DIPstick 102. GUIDE TUBE 103. BUSHING 104. CYLINDER BLOCK 105. BUSHING 106. PLUG 107. OIL FILTER 108. BUSHING PLUG 109. BUSHING 110. BUSHING 111. BOLT 112. BOLT 113. WASHER 114. CLUTCH COVER 115. CLUTCH DISC 116. FLYWHEEL 117. CRANKSHAFT REAR SEAL 118. BEARING 119. CRANKSHAFT 120. MAIN BEARING INSERT 121. MIDDLE THRUST MAIN BEARING INSERT 122. K MAIN BEARING CAP 123. BOLT 124. OIL PAN GASKET 125. OIL PAN 126. DRAIN PLUG 127. PLUG GASKET 128. BOLT 129. KEY 130. OIL PUMP RECEIPT PIPE | 131. SEAL 132. BRACKET 133. REDUCING VALVE BOLT 134. SEAL 135. REDUCING VALVE SPRING 136. REDUCING VALVE PLUNGER 137. OIL PUMP 138. PUMP BYPASS VALVE CA 139. CRANKSHAFT FRONT SEAL 140. WASHER 141. GEAR 142. MOUNTING WASHER PULLEY 143. GEAR WHEEL BOLT 144. PULLEY 145. PULLEY 146. SCREW 147. COVER 148. BOLT 149. OIL PUMP HOUSING GASKET 150. PLUG 151. WATER PUMP BOLT 152. DRIVE PUMP 153. SEAL 154. MANIFOLD 155. MANIFOLD Crankcase VENTILATION 156. CONNECTING ROD BOLT 157. CONNECTING ROD CAP 158. CONNECTING ROD INSERTS 159. CONNECTING ROD 160. PISTON AND PISTON PIN 161. PISTON RINGS 162. BELT TENSIONER |
Specifications
| engine's type | In-line, 4-cylinder |
| Working volume | 1.5 l |
| Engine code in vehicle identification number | 1 |
| Cylinder diameter | 76.5 mm |
| Piston stroke | 81.5 mm |
| Compression ratio | 8,6 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1–3–4–2 |
| Valve chamfer angle (intake and exhaust) | 46° |
| Valve stem diameter (intake and exhaust) | 7 mm |
| Exhaust valve disc diameter | 31 mm |
| Seat chamfer angle (intake and exhaust valves) | 45° |
| Allowable misalignment: | |
| – seats and bushings | 0.05 mm |
| – valve discs | 0.03 mm |
Valve springs
| free length | 40.9 mm |
| length with valve closed | 31.5 mm |
| closed valve force | 275 N (31.5 mm) |
| valve open force | 618 N (21.6 mm) |
Camshaft journal diameters
| Camshaft journal diameters: | |
| – 1st | 39.435 – 39.455 mm |
| – 2nd | 39.685 – 39.705 mm |
| – 3rd | 39.935 – 39.955 mm |
| – 4th | 40.185 – 40.205 mm |
| – 5th | 40.435 – 40.455 mm |
| Bearing clearance | 40 – 50 µm |
Valve lift
| Valve lift: | |
| – inlet | 5.61 mm |
| – graduation | 6.12 mm |
| Shaft axial clearance | 0.04 – 0.16 mm |
Crankshaft
| Root necks | |
| Diameter | 55 mm |
| Allowable taper | 5 µm |
| Allowable ovality | 4 µm |
| Bearing clearance | 15 – 53 µm |
| Shaft axial clearance | 0.12 – 0.352 mm |
| Crankpins | |
| Diameter | 43 mm |
| Allowable taper | 5 µm |
| Bearing clearance | 19 – 71 µm |
| Lateral clearance in connecting rod bearing | 0.07 – 0.242 mm |
Cylinders and pistons
| Cylinder diameter | 76.5 mm |
| Clearance between piston and cylinder | 0.02 mm |
| Piston stroke | 81.5 mm |
| Allowable taper | 6.5 µm |
| Piston pin diameter | 18 mm |
| Gaps in the piston ring lock: | |
| – upper compression ring | 0.3 – 0.5 mm |
| – lower compression ring | 0.3 – 0.5 mm |
| – oil scraper ring | 0.4 – 1.4 mm |
Tightening torques for threaded connections
| Camshaft housing cover bolts | 8 Nm |
| Cylinder head (and camshaft housing) bolts | 25 Nm (+60″, +60″, +30″) |
| Camshaft Gear Bolt | 45 Nm |
| Camshaft thrust plate bolts | 8 Nm |
| Crankshaft pulley bolts | 55 Nm |
| Connecting Rod Cover Bolts | 25 Nm (+30°) |
| Nuts securing the exhaust pipe to the cylinder block | 22 Nm |
| Flywheel bolts | 35 Nm (+30°) |
| Nuts securing the intake manifold to the cylinder block | 22 Nm |
| Main bearing cap bolts | 50 Nm (+45°) |
| Oil drain plug | 45 Nm |
| Oil pan bolts | 5 Nm |
| Pump pressure reducing valve plug | 30 Nm |
| Oil pump bolts | 7 Nm |
| Bolts securing the oil intake pipe to the cylinder block | 7 Nm |
| Bolts securing the oil inlet pipe to the pump | 7 Nm |
| Water pump bolts | 8 Nm |
| Belt tensioner bolts | 20 Nm |
Engine lubrication system filling capacity
| Including oil filter | 3.75l |
| Oil filter type | PF47 |
Engine maintenance and repair
To eliminate the possibility of engine damage and reduced engine reliability, you must carefully study and follow the recommendations below. Do not lift or support a raised engine on the oil pan. In this case, the pan may be deformed and the intake filter of the oil pump of the engine lubrication system may be damaged.
When working on the engine, to avoid short circuits, the negative cable of the battery should be disconnected.
After dismantling the air cleaner or the MSVT unit, it is necessary to close the inlet pipes. This will protect the engine from accidental entry of foreign objects and dirt. For example, a small nut or washer can get into the cylinder through the intake air tract and seriously damage the engine during startup.
In this section of the manual, when describing engine repairs, as a rule, preparatory operations for removing additional equipment are not mentioned: power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, etc.
Design Features
The one and a half liter single-shaft in-line petrol engine G15MF was created before the advent of Euro-2 standards, so the design feature is an extremely simple exhaust tract design without a catalyst and CO probe. The remaining nuances of the internal combustion engine are:
- modernization of the injection system - injection here is distributed, but simultaneous, regulated by a potentiometer, as on domestic Ladas;
- modification of the combustion chambers - these engines have a smaller cylinder diameter compared to the prototype, and a dome-shaped chamber, partially extended into the piston;
- according to the manufacturer, oil consumption is within 300 g/1000 km, and gasoline consumption is 8.8 l/100 km in the combined cycle;
- flat tooth timing belt from the leading brand Geitz with a service life of 200,000 km, although the safety of the valves is already ensured here, they cannot meet the pistons.
The gas distribution system is made according to the SOHC scheme with one camshaft. Compared to the sample, the volumes of the combustion chambers are reduced; power will be increased only in the next series of Daewoo engines - A15MF.
To increase the resource, the attachment is driven by a separate belt, the condition of which is recommended to be monitored every 20 thousand km, and changed after 50 thousand.
After the introduction of Euro-3 and even Euro-4 regulations, Daewoo management continued to install these obsolete power drives on Nexia and Espero until 2008. Compactly located attachments do not interfere with major repairs, including on your own.
Advantages and disadvantages
The strength of the Daewoo concern has always been caring for the user, so the motor has an octane number switch - from the four proposed options 95, 92, 87 and 83, the user can choose any one simply by switching the wires. For example, the octane number of A-76 is approximately 82, so the engine “digested” even 76 gasoline.
The next advantage was the resource of more than 250 thousand km between capitals. Currently, even with improved designs and component diagrams, such a resource is rare for power drives.
The main disadvantage of the G15MF is the magnetoelectric sensor of the ignition distribution system. The wires are constantly being unsoldered, the repair does not help for long. When replacing the sensor, you should focus on a mileage of 10 thousand km. If the device does not fail during this time, it will last a long time. If the problem recurs, it is better to replace the sensor with a new one.
The original cylinder head is suitable for tuning - a camshaft with increased phases can be placed inside.
List of car models in which it was installed
The G15MF engine was used for several versions of cars manufactured by Daewoo:
- Lemans 5i sedan 1C4 – 1994 – 1995;
- Cielo sedan – 1995 – 2000;
- Cielo LoadRunner – 1996 – 1997;
- Nexia KLETN – 1995 – 1997;
- Espero sedan KLEJ – 1997 – 1999.
Since Daewoo Nexia was produced in Korea, Uzbekistan, Romania, Egypt and Vietnam, different manufacturers assigned the car different names - Pointer, Racer, Lemans, Cielo and Chevrolet Nexia. In addition to sedans, the characteristics of the G15MF engine made it possible to install it on three-door and five-door hatchbacks, similar to the Opel Kaddet E.
Maintenance schedule G15MF 1.5 l/75 l. With.
Despite the declared service life of 250,000 km, the manufacturer recommends servicing the G15MF engine during maintenance according to the following schedule:
| Consumable item or service step | Time (year) or mileage (1000 km), whichever comes first |
| Timing drive | 7/100 |
| Battery | 2,5/40 |
| Adjusting the thermal clearance of valves | 2/15 |
| Checking and cleaning the crankcase ventilation | 2/35 |
| Attachment belts | 4/50 |
| Inspection and cleaning of the fuel line | 2/40 |
| Motor oil | 1/10 |
| Oil filter | 2/20 |
| Air filter cartridge | 2/40 |
| Fuel filter | 4/40 |
| Checking and replacing heating/cooling hoses | 3/30 |
| Antifreeze | 2/40 |
| CO and oxygen sensor | 10/100 |
| Spark plug | 1 – 2/20 |
| Exhaust tract | 1/20 |
The classic internal combustion engine design allows you to reduce operating costs and the cost of overhauls.
Review of faults and methods for repairing them
Thanks to the concave shape of the piston and the hole inside it, the G15MF motor does not bend the valve when the timing belt breaks. It has several problems:
| Underheating or overheating | thermostat failure | thermostat replacement |
| Knock during operation | 1) development of hydraulic compensators 2) axial play of the crankshaft has appeared 3) main bearing wear 4) the attachment belt is tightened | 1) replacement of consumables 2) support bearing for replacement 3) installation of new liners 4) adjusting the tension or replacing the belt |
| "Maslozhor" | 1) stuck or worn oil scraper rings | 1) decarbonization or replacement of rings |
Other breakdowns inherent in all in-line engines with an overhead camshaft should be repaired in working order.
Main malfunctions of power plants
Daewoo power units have a number of characteristic disadvantages:
| Characteristic disadvantages | Causes | Solution |
| Increased oil consumption | Wear of piston rings Wear of oil pump | Replace rings Replace oil pump Replace sealing elements, tighten bolts |
| Strong knocking sound (engine is warm) | The clearances in the main bearings are larger than required. The tension of the drive belts is increased. The torque converter is loosened. | Replace liners Adjust tension, replace if necessary |
| Knock in the engine after starting | Front main bearing - increased clearance Crankshaft - increased end clearance Hydraulic valve lifters faulty | Replace Shaft support bearing - replace Check, replace if necessary |
| Engine heats up quickly | Thermostat is faulty | Check, replace if necessary |
| The motor takes a long time to warm up | Thermostat is faulty | Check, replace if necessary |
Most such work may require special tools, equipment, and knowledge.