Purpose of the radiator
Contrary to popular belief, a car cooling radiator performs several functions at once. His tasks include:
- Heat removal from product elements and its transfer to the atmosphere.
- Providing the possibility of adding and removing coolant (antifreeze, water, antifreeze) using special holes at the bottom and top.
- Creation of optimal pressure inside the system, thanks to the presence of a relief valve.
The main function of the radiator is to exchange heat and reduce the coolant temperature to a safe level.
Depending on the situation, cooling occurs by blowing with counter air or a fan, which starts when a certain temperature is reached. Depending on the make/model of the vehicle, the fan may be mechanical, electric, or hydraulic. The second option is considered the most popular.
How does the engine cooling system work?
When considering a radiator, it is important to know the features of the car's cooling system, which is designed to reduce engine temperature to a safe level. In addition, its functions include heating the air, cooling the exhaust gases, the flow in the turbocharged system, as well as the oil in the automatic transmission. Structurally, the cooling system can be liquid, air or mixed. The most popular is the first option. Structurally, it consists of the following elements:
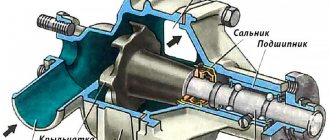
- Radiator. The main unit through which coolant passes to reduce the temperature.
- Water pump. Guarantees the circulation of working coolant throughout the system. It can be belt, gear or other types.
- Thermostat. Necessary to regulate the process of antifreeze passing through the radiator. It can have three positions - closed, partially / fully open.
- Fan. Triggered to increase airflow efficiency. Most often necessary when the car is moving at low speed and the air flow is not enough for cooling.
- Temperature sensor. Controls the temperature regime and gives a command when it is necessary to start additional cooling.
- ECU. The main unit that receives signals and regulates the operation of the car’s engine cooling system.
Depending on the car, other components may also take part in the operation, for example, an engine cooling relay, a heater, a thermostat, a fan control unit, etc.
Important
All elements interact closely with each other. So, after starting the engine, the coolant circulates using a pump in a minimal circle - through the block and cylinder head without passing through the radiator.
This is done for faster heating. As soon as the temperature reaches 80-90 degrees Celsius, the sensor is triggered and sends a command to open the thermostat.
In this case, antifreeze is directed through the radiator to maintain normal temperatures. If the engine continues to heat up, a signal is sent to turn on the fan, providing additional airflow.
Purpose and varieties
Heat removal is far from the only purpose of an engine cooling system. She is additionally responsible for performing a number of other tasks:
- heating the air mass for heating the vehicle interior;
- reducing the waiting time required to bring the engine to operating temperature;
- reducing the temperature of lubricants used for internal combustion engines;
- if recirculation is used, the temperature of the exhaust gases from the internal combustion engine decreases;
- if there is an automatic transmission, the lubricant located inside is cooled.
The design of the engine cooling system directly depends on its mode of operation and operating principle. Accordingly, it is customary to classify a node into several categories:
- liquid - heat is removed due to the constant circulation of the technical fluid;
- air - when using the considered scheme of engine cooling systems, heat will be removed by circulated air;
- combined - includes the use of the 1st and 2nd options simultaneously.
Practice shows that the combined option is the most effective, ensuring stable operation of the motor as a whole.
Types of radiators
Structurally, the devices under consideration differ in several criteria: assembly method, case material and additional elements. Taking into account the features, the price of a car radiator also differs. By design they are:
- Tubular-plate. They consist of tubes, inside of which so-called turbulators are mounted. This is done to lengthen the coolant path through the radiator and, accordingly, improve cooling. Such devices have greater rigidity and a minimal percentage of defects.
- Tubular-tape (soldered). Unlike the previous version, all elements are connected by soldering, which complicates the maintenance process. Such radiators have higher heat output and lower price.
There are two options based on the number of moves:
- One-way. Fluid flows in one direction.
- Two-way. The coolant path is more complex. First, the antifreeze passes through part of the tubes in one direction, and then in the second compartment it changes direction.
According to the material:
- Copper. More expensive. They are characterized by increased strength and better heat transfer. Easily repaired by soldering.
- Brass. They are rarely found in their pure form. Copper-brass structures are most often used.
- Aluminum car radiators. Appeared against the backdrop of rising copper prices. In production, modern welding methods are used, providing increased reliability and strength. Despite the worse heat transfer, such products cope with this task.
Today, all car engine radiators are made of aluminum. They have a lower price, but require a special approach to repair. For restoration, conventional soldering is not enough, because it usually has low efficiency. Argon welding is most often used.
Coolants
A coolant (liquid) moves inside the system, which, when passing through the radiator, is cooled and returned to the engine. Conventionally, all coolants are divided into several types:
- Distilled water. The most economical option that does not require the purchase of additional funds. It is used in the warm season, when there is no risk of the system freezing.
- Antifreeze is the old name for coolant used in the USSR. Previously, such compositions were poured into Zhiguli, but today they are almost never used.
- Antifreezes are modern coolants that contain special additives. They differ in terms of service life, corrosion protection features, the presence of additives and other features.
Conventionally, antifreezes are ethylene glycol, carboxyl, hybrid, lobrid and propylene glycol. They differ in characteristics, composition, set of additives and characteristics. For example, inorganic corrosion inhibitors are used in ethylene glycol compositions, and organic ones are used in carboxyl compositions. Hybrid and lobrid ones contain organic and inorganic components. As for propylene glycol coolants, they use safer propylene glycol.
The task of modern antifreezes is to remove heat, protect against corrosion and clean the car radiator from contaminants accumulated inside.
At the same time, the anti-corrosion function is considered the most important, and the effectiveness of this option directly affects the price. When choosing a coolant, you need to focus on the manufacturer’s recommendations in relation to the car brand.
Damage, malfunctions and repairs
The radiator cannot be called the most reliable component of a car. During operation, it is affected by many negative factors, including mechanical ones. The most common damages include:
- Contamination of pipes and central part. In this case, flushing may be required.
- Fan damage.
- The accumulation of dirt and leaves on the outside of the product, which reduces heat transfer.
- Damage to the pipes or the radiator itself with subsequent leakage of coolant from the system.
- Corrosion of internal elements.
If any of the problems discussed above occur, there is a high risk of engine overheating, so the car’s radiator needs to be repaired. A sign of a breakdown may be the appearance of an antifreeze leak or rapid overheating of the engine during moderate operation.
The most difficult case is when the engine “boils” and steam starts coming out from under the hood. In this case, you need to stop and wait for the system to cool down. Only after this can you begin to troubleshoot the problem. If the problem occurs on the road, do the following:
- Check the tightness of the connections of all tubes.
- Make sure the cooling fan operates.
- Check relay wiring and temperature sensor.
- Add the required amount of coolant. Be careful as there is a high risk of hot liquid splashing.
It is better to entrust repairs to professionals. If it is not possible to go to a service station, you can use epoxy resin or “cold welding”. You must first drain the coolant from the system and remove the device from the car for easier access. There are other repair methods:
- Welding. Used when there is minor damage. Suitable for copper or brass devices. Requires a gas torch and degreaser. When performing argon welding on an aluminum “cooler”, aluminum wire is needed.
- Replacement. In a situation where the tube is damaged along its entire length, it will not be possible to solder the car radiator or weld the hole. The only way to solve the problem is to replace the old tube with a new one.
When deciding on the need and method of repair, it is necessary to assess the damage. In the most severe cases, the entire radiator may need to be replaced.
Radiator damage: causes, prevention
A sign of a radiator failure is the appearance of leaks: a puddle of antifreeze under the car will alert any driver and force him to seek diagnostics. The second warning sign is engine overheating, which can lead to expensive major repairs. In these cases, the culprit of the problem may be not only the radiator, but also other components of the cooling system.
Radiator leaks can occur for several reasons:
- mechanical damage due to an accident;
- hitting the radiator with pebbles and branches that have a high enough acceleration to pierce the connecting tubes;
- corrosion of metal parts resulting from the use of low-quality antifreeze or plain water;
- leakage of pipes due to loosening of connecting clamps;
- divergence of seams due to vibration and natural wear;
- cracks in radiator tanks are one of the “diseases” of plastic parts;
- scale and deposits in the radiator, clogging the pipes;
- freezing of coolant inside the radiator.
Modern aluminum radiators are practically irreparable: sealing them will cost the same amount as buying a new one, which means that repairs only make sense on rare or very expensive models. In other cases, it is better to follow preventive measures so that the radiator lasts as long as possible:
- purchasing quality products from European manufacturers;
- using good antifreeze that does not leave deposits on the honeycombs and other parts of the cooling system;
- timely topping up of antifreeze and replacement if necessary (like other technical fluids, it evaporates and degrades over time);
- selection of a radiator in accordance with the technical characteristics of the car, so that during installation there are no distortions, areas of stress and unnecessary vibration;
- installing protection on the car’s radiator grille, which significantly reduces the likelihood of stones and insects getting inside;
- periodic maintenance of the radiator and the entire cooling system.
Prevention and care
To extend the life of the product, proper care and regular maintenance are required. It is important to understand that the radiator absorbs all the dirt and dust and therefore needs to be flushed periodically. If nothing is done, the device quickly becomes clogged and stops performing its functions.
The main means of prevention is periodic flushing and cleaning of the car’s cooling system. You can do this yourself or entrust the work to a specialist.
| Stages of flushing a car's cooling system |
| 1. Allow the engine to cool, secure the hood and put on special gloves that do not allow water to pass through. |
| 2. Drain the antifreeze from the cooling system and fill it with distilled water |
| 3. Start the engine and leave it for 20-25 minutes |
| 4. Drain the liquid and repeat this procedure several times to completely clean the system. It is necessary to act until clean water begins to come out of the system. |
| 5. At one stage, add cleaning agent to the water to better clean the system. You can find special formulations on sale, for example, Winns Radiator Flush |
During operation, we must not forget that the radiator can become clogged from the outside. The pollutants are leaves, dirt, dust, etc. To solve the problem, you need to dismantle the product and blow it with air pressure or rinse it with a stream of water under high pressure. The main thing is not to overuse the pressure to avoid damaging the device’s cells.
After this, it is necessary to fill the system with high-quality antifreeze with a set of necessary anti-corrosion additives. To eliminate air locks, open the cap on the radiator and start the engine. After some time, the air will come out on its own, and all that remains is to add coolant to the system.
Current system
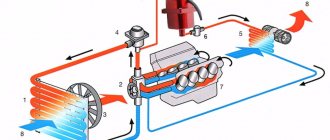
Domestic and foreign cooling systems are overwhelmingly closed, where liquids are forced to move. Their main elements are:
- cooling radiator;
- pipes and connecting hoses;
- jacket (technological channels of the block);
- water pump;
- multi-blade fan;
- thermostat.
When the power plant is operating, the antifreeze located in the channels of the jacket receives heat from the engine. Then it moves through the existing channels to the radiator to cool, and returns back through other channels. The movement is aided by a pump located in the system, and cooling is facilitated by a large fan located behind the radiator. The work intensity is adjusted by a built-in thermostat and timely auto-start/auto-stop of the fan.
Topping up the required volume of antifreeze is carried out through a special neck in the radiator. This can also be done using an expansion tank. As a rule, modern systems fit about 6-12 liters of antifreeze. It can be replaced after it has been completely drained by unscrewing the cap on the block or at the bottom of the radiator tank .