Standard elements of the exhaust system of a VAZ 2104 passenger car last from 30 to 50 thousand kilometers. Then the problems begin - due to wear, the preliminary and main muffler tanks burn out. Symptoms of the malfunction are noticeable without any diagnosis - the breakthrough of gases through the fistulas is accompanied by an unpleasant roaring sound. Replacing worn parts is not difficult for an experienced motorist; beginners are advised to first study the design of the Zhiguli exhaust tract.
- Exhaust tract design
- Main muffler - device and types
Video: how to make a forward flow yourself
- What tool will you need?
Video: how to replace the muffler yourself
- Video: repairing exhaust using sealant
- Video: how to replace the resonator on classic VAZ models
Functions of the VAZ 2104 exhaust system
To get maximum energy from the engine, you need to burn the fuel under optimal conditions. The required volume of air is added to the gasoline, then the mixture is sent through the inlet manifold into the cylinders, where it is compressed by pistons 8-9 times. The result is that after the flash, the fuel burns at a certain speed and pushes the pistons in the opposite direction, the motor performs mechanical work.
In addition to the energy that rotates the engine crankshaft, by-products are released when the air-fuel mixture is burned:
- exhaust harmful gases - carbon dioxide CO2, nitrogen oxide NO, carbon monoxide CO and other chemical compounds in smaller volumes;
- a large amount of heat;
- a loud sound similar to a rumble that is formed with each flash of fuel in the cylinders of the power unit.
A significant portion of the released thermal energy is dissipated into the environment thanks to the water cooling system. The rest of the heat is taken up by combustion products that escape through the exhaust manifold and exhaust pipe.
The exhaust pipe of the “four” is located closer to the right side of the car - as on all classic Zhiguli models.
What problems does the VAZ 2104 exhaust system solve:
- Removal of flue gases from the cylinders during the exhaust stroke - combustion products are pushed out of the chambers by pistons.
- Cooling of gases by heat exchange with ambient air.
- Suppression of sound vibrations and reduction of noise levels from engine operation.
The latest modifications of the “fours” - VAZ 21041 and 21043 were equipped with an electronically controlled fuel supply system - an injector. Accordingly, the exhaust tract was supplemented with a section of a catalytic converter that neutralizes toxic gases through chemical reduction (afterburning).
VAZ 2114 exhaust system diagram
The VAZ 2114 exhaust system is practically no different from other VAZ mufflers, although there are some minor differences from later systems with a more complex catalytic converter design. The system diagram is shown in the photo below, and we will talk about the features of its elements right now.
As in the VAZ 2109 of later modifications with an injection engine, the system consists of:
- intake pipe;
- catalytic converter;
- oxygen sensor;
- intermediate resonator;
- muffler.
The design of the late exhaust system used a corrugated hose, which made it possible to reduce the transmission of vibrations from the engine to the exhaust system. Its resource was much shorter than that of other elements of the system, so it must be replaced more often. In the process of refinement, which we will talk about later, the corrugated hose could be replaced with a more advanced multilayer hose with reinforced braid made imported.
Exhaust tract design
On all classic VAZ models, including the Four, the exhaust is designed the same and consists of three parts:
- a receiving section in the form of a double pipe is screwed to the exhaust manifold flange - the so-called pants;
- the middle part of the tract is a single pipe equipped with a resonator tank (on cars with 1.5 and 1.6 liter engines there are 2 such tanks);
- at the end of the tract the main muffler is located.
In the carburetor version of the “four” the exhaust tract consists of 3 parts
In the injection modifications of the “four”, a neutralizer tank is added, installed between the “pants” and the resonator section. The efficiency of the element is controlled by an oxygen sensor (otherwise known as a lambda probe), which sends signals to the electronic control unit.
Each part of the system performs its function. The receiving pipe dampens the primary noise, collects gases into a single channel and removes the lion's share of the heat. The resonator and the main muffler absorb sound waves and finally cool the combustion products. The entire structure is supported by 5 fasteners:
- The intake pipe is connected to the motor via a flange connection, fasteners are 4 nuts with M8 threads, made of heat-resistant bronze.
- The second end of the “pants” is screwed to a bracket located on the gearbox housing.
- The barrel of the main muffler is suspended from the bottom by 2 rubber struts.
- The rear end of the exhaust pipe is attached to the body using a rubber cushion.
VAZ 2104 injection models are equipped with an additional gas purification section and oxygen sensors
The middle resonator part is not attached to the bottom in any way and is held in place only by the adjacent sections - the muffler and the exhaust pipe. This point must be taken into account when disassembling the exhaust. Being an inexperienced car enthusiast, I changed the muffler myself and, in the process of disconnecting the pipes, I broke off the clamp securing the “pants”. I had to look for and buy a new clamp.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
This section contains products for tuning and modification of the Stinger exhaust system for VAZ and foreign cars. Having its own production and extensive experience, Stinger Sport LLC manufactures both products for VAZ tuning and exhaust systems for individual projects for motorsports. And also, with the spread of foreign cars in Russia, exhaust systems for foreign-made cars began to appear in our assortment. Refinement of the exhaust system is one of the first, so to speak, operations with which the modification of a tuning car begins, since the costs of spare parts and labor are relatively small, and the resulting effect is quite noticeable.
The VAZ tuning exhaust system consists of the following main elements: an exhaust manifold (the so-called spider) “Stinger”, which has two main schemes 4-1 and 4-2-1, a direct-flow resonator “Stinger” with a flow area of 51 mm or 60 mm (standard the exhaust of a VAZ car has a diameter of 46 mm), and the main muffler “Stinger” with a bore section of 51 mm and 60 mm, which also has a direct-flow design.
Stinger Spider: The 4-2-1 design is the most widespread, as Stinger spiders of this design provide an increase in power over a wider range of operating speeds. Of all three elements of the exhaust system, the spider plays the most important role.
Direct-flow resonators Stinger: replacing a standard resonator with a direct-flow resonator of increased diameter occurs in the case when the engine is subject to modification; when installed on a standard motor, it practically does not increase power, but often buyers install it after the failure of the standard one for the future.
The main muffler Stinger: on standard engines it gives virtually no increase in power, but it has an attractive appearance, thanks to various types of attachments, and a bass sound, so many car owners begin modifying the exhaust system with it.
This section presents sports exhaust systems and components from both Stinger’s own production and products from other manufacturers, as we try to offer our customers the maximum choice.
In addition to the production of sports exhaust systems, we are also trying to expand the geography of sales of our products. Now you can buy Stinger exhaust for VAZ in Togliatti , Samara, Yekaterinburg, Volgograd. And if you use the services of our online store, then the VAZ exhaust from Stinger can be purchased anywhere in Russia.
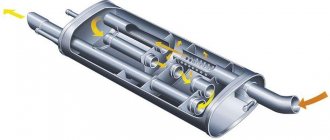
Main muffler - device and types
The factory-made element is made of refractory “black” steel and coated with a layer of anti-corrosion paint. The part consists of 3 parts:
- front pipe, curved to bypass the rear axle;
- three-chamber muffler tank with a system of partitions and pipes inside;
- outlet pipe with a bracket for mounting a rubber cushion.
The original Zhiguli mufflers are made of refractory steel with anti-corrosion protection
At the end of the front pipe there are slots for connection to the resonator. The connection is fixed from the outside with a clamp, a tightening bolt and an M8 nut.
The mufflers for “classics” sold today are not reliable - spare parts are often made from second-rate metal and burn out after 15-25 thousand kilometers. It is quite difficult to identify a low-quality part when purchasing; the only way is to visually check the quality of the welds.
In addition to the factory version, other types of mufflers can be installed on the VAZ 2104:
- element completely welded from stainless steel;
- sports (direct-flow) option;
- a homemade section with a round cistern made from a thin-walled iron pipe.
Factory forward flow is externally distinguished by the shape of the body, heat-resistant black coating and a decorative nozzle instead of a regular pipe
A stainless steel exhaust element will cost 2-3 times more than a factory part, but can last up to 100 thousand km. I was convinced of this personally when I bought and installed a stainless exhaust system on my VAZ 2106 - the design is identical to the exhaust tract of the V4. I happily forgot about the pipe burnouts for several years.
The direct-flow type of muffler differs from the standard part in its operating principle. Gases pass through the perforated pipe and do not change the direction of movement, the resistance of the section is zero. Result: it is easier for the engine to “breathe”, but the noise is suppressed less well - the operation of the motor is accompanied by a rumbling sound.
The main difference between forward flow is the minimal resistance to the passage of gases, which gives an increase of 3-5 liters. With. to engine power
If you are “friendly” with a welding machine, the factory version of the muffler can be modified or the element can be made from scratch. In home-made products, the principle of direct flow is implemented, since welding a flat tank with partitions is much more difficult - it is easier to buy a ready-made part. How to make a main muffler with your own hands:
- Select pipes for the outer casing and direct-flow channel. As a tank, you can use a round muffler from a Tavria, or take a curved front pipe from an old section from a Zhiguli.
- Make an internal perforated pipe by drilling holes Ø5-6 mm and making through slots with a thin circle on the metal.
Perforation in the form of holes and slits is performed to allow the passage and further absorption of sound vibrations - Insert the pipe into the casing, weld the end caps and external connecting pipes.
- Fill the cavity between the tank body and the direct-flow channel with non-flammable kaolin wool or basalt fiber.
It is better to use non-flammable kaolin wool or basalt fiber as a noise absorber - Seal the casing cover by welding and install 3 eyes for rubber hangers.
The final stage of manufacturing is painting the part with a heat-resistant composition. After installing any muffler - factory or homemade - the protruding end of the pipe can be refined using a decorative nozzle, fixed from the outside with a locking screw.
Video: how to make a forward flow yourself
Repair of the exhaust system of VAZ 2114
The most common breakdowns of the VAZ 2114 exhaust system were burnouts, mechanical damage, and ruptures of the suspensions that hold pipes and resonators under the bottom of the car. Most often, the culprit of burnout was corrosion, and it appeared due to poor system protection. The factory anti-corrosion protection of mufflers and pipes was rather nominal, and at high temperatures and constant moisture that accumulated in the pipes in the form of condensation, the system rusted quite quickly.
Also, the causes of burnouts were late ignition and failures or disconnection of the catalyst, when fuel that did not have time to burn in the engine got into the muffler and burned out there under the influence of high temperatures. And this temperature is about 600-800 degrees. As a result of the fire, fuel explosions often occurred, which led to burnouts of the system. They also complained about the ineffective operation of mufflers and resonators, which gave car enthusiasts a reason to modify the exhaust system.
Troubleshooting
The first problems with the gas exhaust system may begin after 20 thousand kilometers. How do muffler malfunctions manifest on the VAZ 2104 model:
- the main symptom is an increase in noise level from the exhaust pipe due to gas breakthrough; the volume of the sound depends on the size of the defect;
- the fastenings of the sound-absorbing section wear out, the tank begins to wobble and hit the body elements, while driving, a dull knock is heard from under the bottom;
Rubber products stretch over time, the muffler body begins to dangle in a horizontal plane and touch the bottom of the car. - in rare cases, the pipe becomes clogged with soot, preventing the flow of gases, the engine stalls and will no longer start;
- Failure of lambda probes on cars with an injector leads to over-enrichment of the fuel mixture, a sharp increase in gasoline consumption and malfunctions during the operation of the power unit in all modes.
Receiving signals from the lambda probes, the electronic control unit regulates the supply of fuel to the cylinders. When the oxygen sensor does not show signs of “life”, the controller goes into emergency mode and dispenses fuel “blindly”, following the programmed program. Hence the excessive enrichment of the mixture, jerking while driving and other troubles.
The catalyst is an expensive element, so owners of “fours” replace it with a straight piece of pipe
A clogged muffler or catalyst leads to complete failure - the engine refuses to start. My friend searched for a long time for the reason when he encountered this problem on his “four”. I changed spark plugs, high-voltage wires, measured the pressure in the fuel rail... and the culprit turned out to be a clogged converter - the ceramic honeycombs were completely clogged with soot. The solution turned out to be simple - instead of an expensive element, a straight section of pipe was installed.
The lower burnout of the housing indicates condensation that has accumulated at the bottom of the tank
The most common problem with a muffler is burnout of the tank or pipe connection secured with a clamp. Causes of malfunction:
- Aggressive condensate accumulates in the muffler can, gradually corroding the metal. Due to the effects of chemical corrosion, many small holes are formed in the bottom wall of the tank, where smoke breaks through.
- Natural wear of the section. From constant contact with hot combustion products, the metal becomes thinner and breaks through in a weak spot. Usually the defect appears near the welded joint of the pipe and the tank.
- Mechanical damage to the can from an external impact or as a result of fuel burning out inside the exhaust manifold. In the latter case, a loud bang is heard from the pipe; sometimes the shock wave can tear the muffler body at the seams.
A burst muffler is a consequence of problems in the ignition or gas distribution system - the remaining fuel burns in the exhaust tract
The most harmless malfunction is the breakthrough of gases at the junction of the muffler and resonator pipes. The exhaust noise increases slightly, but if no action is taken, the volume gradually increases. The fastening of the joint weakens, the resonator section begins to sag and touch the protrusions of the road surface.
A clear sign of gases escaping at the junction of the exhaust pipes is the flow of condensate that breaks through along with the smoke when the car’s engine has not yet warmed up to operating temperature.
A fistula at the junction of the pipes can be identified by wet traces of condensation
Exhaust system malfunctions and their elimination
Due to increased pressure and very high temperatures due to intense fuel combustion, the muffler quite often fails. The level of performance of individual elements and the entire exhaust gas system of the VAZ 2114 is significantly affected by the following unfavorable technological factors:
- rapid heating to very high temperatures and possible overheating of the exhaust system;
- frequent sharp fluctuations in temperature - from heating to rapid cooling;
- permanent vibration during engine operation;
- frequent impacts and mechanical damage to the VAZ muffler;
- frequent pollution;
- scratches and chips caused by small hard particles of the road surface;
- development of internal and external corrosion;
- lack of means that effectively protect the metal surfaces of the VAZ 2114 exhaust system.
All of these factors, to one degree or another, affect the safety and performance of the exhaust unit. If the integrity is broken in any place, a gas flow immediately rushes into the resulting fracture or fistula. Due to its speed and pressure, it quickly expands the emergency hole. And then the malfunction makes itself felt - the system begins to loudly “growl” and clap, exhaust gases come out at the wrong point, and the muffler knocks. In such conditions, it becomes almost impossible to operate the car.
It should be borne in mind that in addition to loud and sharp bangs, defects in the exhaust system of the VAZ 2114 can also affect the operating mode of the engine itself. Therefore, in some cases it will be necessary to carry out repairs of system elements, thanks to which you can temporarily do without completely replacing the entire assembly.
Diagnosis of breakdowns, which precedes restoration operations, is facilitated by the fact that the occurrence of defects is usually accompanied by an unpleasant strong grinding and roaring sound under the car bottom. The owner of the car remains to carefully examine the entire chain and determine the location and nature of the malfunction. Most often, breakdowns occur in the following components.
- Lambda probe. It is an electronic sensor that analyzes the composition of emitted gases in order to ensure optimal combustion of automobile fuel. As a rule, after 100 thousand kilometers of the car, the metal analyzers included in the sensor lose their working properties. Usually in this case, the exhausted lambda probe is not repaired, but replaced with a new one.
- Corrugation. Its elastic hose, taking on engine vibration, stretches over time due to such mechanical vibrations, which negatively affects the mitigation of shaking. If the old corrugation fails, simply replace it with a new one.
- Resonator. This element of the VAZ 2114 exhaust system can periodically burn out under the influence of high temperatures of fuel combustion. Most often this is the result of using a product made of low-quality thin stainless steel. The best way to fix the problem is to replace the burnt element with a new one. However, as a temporary measure, it is also possible to weld the burnout area with a special electrode.
- Connecting gaskets. A sign of their failure is the appearance of strong vibration in the exhaust system area when the engine is running. To eliminate loud rattling, most often it is enough to simply replace the gaskets.
Purpose and design of the resonator
The structure of the resonator is similar to a direct-flow muffler - a perforated pipe is laid inside the cylindrical body without any partitions. The difference lies in the jumper that divides the jar into 2 resonator chambers. The element performs 3 functions:
- perceives and pre-damps sound waves;
- dissipates part of the heat coming from combustion products;
- Extends the service life of the main muffler.
Unlike direct flow, the resonator does not absorb, but repeatedly reflects sound vibrations
When operating, a two-chamber tank uses the principle of resonance - sound vibrations are repeatedly reflected from the walls, collide with oncoming waves and cancel each other out. The VAZ 2104 was equipped with 3 types of sections:
- Cars with a carburetor power system were equipped with a long resonator for 2 tanks. For the modification with a 1.3 liter VAZ 2105 engine, an element with 1 can was installed.
The number of cans in the resonator section depends on the engine displacement - Models with an injector, produced under Euro 2 environmental standards, were equipped with a shorter resonator with 1 tank. The inlet pipe began with a flange, which was fastened with two bolts to the mating part of the neutralizer.
- On modifications of VAZ 21043 and 21041, “tailored” to Euro 3 requirements, the shortest resonator was used, equipped with a mounting flange for 3 studs.
On the “four” with an injector, shorter resonator sections Euro 2 and Euro 3 are installed
Damage and malfunction of the resonator cans are similar to the main muffler section. During operation, housings and pipes burn out, rust or break due to external influences. The repair methods are identical - welding, temporary bandage or complete replacement of the part.
Tuning the exhaust system of VAZ 2114
Those who planned to modify the exhaust system in order to increase power were deeply mistaken. Since even the simplest calculations show that the increase in power due to forward flow or any other modernization is completely imperceptible even on a special stand, and even more so in the conditions of real vehicle operation. Sports direct-flow engines could make beautiful and impressive noise and frighten young children with menacing pipes of huge diameter, but this has nothing to do with the technical tuning of the car.
Another thing is preparing a new exhaust system to increase service life and reliability. In this case, completely different circuits, completely different pipe materials and completely different resonator designs were used. The undoubted advantage of this modification was the use of stainless steel, which could outlive the car itself. Also, the reliability of the system was affected by the corrugation, which was also often replaced with a more reliable one from third-party manufacturers.
In general, you don’t have to want much from the exhaust system of the VAZ 2114; you just have to monitor its condition, check the rubber suspensions from time to time and periodically replace the mufflers and exhaust pipes with new ones. Don't drive the exhaust pipes into holes, and good luck to everyone!