When the time comes for a planned replacement of the cardan crosspiece or (more likely) vibration, beating, noise and crackling begin in the area of the cardan, car owners are prepared to pay a significant amount for repairing the cardan. Most often the cardan crosspiece requires replacement. This part cannot be restored, it can only be replaced. It is not expensive, but replacement work will require removing the cardan, so be prepared to spend a whole day at the service station. If you are not afraid of difficulties, then you can change the cardan cross with your own hands.
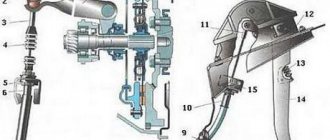
The cardan serves to connect the gearbox and the rear (in a rear-wheel drive car) or front (in all-wheel drive) axle. Its task is to transmit rotation from the engine to the bridge or bridges. The connection point for these elements is the hinge, the main part of which is the cross. It has the shape of a cross, at the ends of which there are cups with needle bearings. The bearing is separated from the housing by a sealing ring made of rubber or plastic. For each car model, the dimensions of the crosspieces differ from each other.
Possible crosspiece malfunctions:
- Cross play
- Needle bearing wear
- Wear of the cross itself
- Leakage and lack of lubrication
- O-ring failure
- Metallic ringing when moving
- Noise and crackling in the cardan area
Theoretically, the crosspiece is a very reliable part, the service life of which should be about 500,000 kilometers. But in practice, replacing the universal joint cross occurs after a mileage of 50-100 thousand kilometers. This is influenced by factors such as operating conditions, the manufacturer of the part, and the quality of the materials used in the manufacture of the part. If your car is often used in rural areas, then dirt and various bumps will shorten the life of your cross by several times. A common reason for crosspiece failure is simple inattention during routine maintenance. Often, no attention is paid to the lack of lubrication until the crosspiece makes itself known by vibration, noise or ringing.
Brand tour
So, there are a couple of suitable crosses to choose from. Or even a whole set. Which one should you prefer? One that is original, or one that was produced by a company with a good reputation. Despite the relative simplicity of the design, the crosspieces of some companies may differ significantly from those of other manufacturers. Some parts quickly rust, while others begin to vibrate after 50 thousand kilometers . Always good crosspieces can be found under the names of the following companies:
- GKN (Germany) - perhaps the best replacement for the original part;
- GMB (Japan) is a famous Japanese manufacturer whose crosspieces can also boast a low price;
- Trialli (Italy) - in fact, these are consolidated OEM companies, so the high quality of the crosspieces they produce is guaranteed;
- Kraft (Poland) - offers budget crosspieces with an oiler. Quality is above average;
- LSA (Czech Republic) is a company little known outside the Czech Republic and several neighboring countries. And it’s in vain - the crosspieces of this company, although more expensive than their popular Polish counterparts, often surpass them in quality;
- Weber (USA) is a manufacturer of parts whose quality is almost equal to GKN, that is, the leader of our selection;
- Herzog (Germany) - the company offers good spare parts, which, alas, are often counterfeited. We'll talk about the features of fakes later.
If your budget is limited, pay attention to Polish and Japanese crosspieces. Unfortunately, bad domestic roads quickly “kill” even the most reliable parts. GKN, Herzog and Weber crosspieces are much more durable. Which is also good, these spare parts always pass the mirror test, so you can safely order them in online stores . Less well-known manufacturers offer spare parts of “depending on luck” quality, so we recommend putting their products last on the list of priorities.
Troubleshooting
Before carrying out repairs, you need to find the cause of the problem. To do this, you will need to drive the car onto a pit or a lift. We put the transmission in neutral and climb under the car. We inspect the cardan, special attention should be paid to the condition of the crosspiece seals. Next, holding the crosspiece, we rotate the cardan itself. If the crosspiece requires replacement, the play can be noticed immediately. If there is no play, but various noises and squeaks are heard during rotation, then the crosspiece may not need to be changed. You just need to replace the lubricant. There are two crosspieces in the cardan and both need to be diagnosed. The rear universal joint crosspiece fails most quickly, since it bears heavy loads. When moving, dirt and moisture also fall more onto the rear crosspiece.
This is interesting: Rear driveshaft device
Conclusion
Finding a new cross is very easy. You can be guided by codes, vehicle data, vehicle identification number and even the geometry of the part. There are plenty of manufacturers of crosspieces - you can find both American and domestic analogues in the store. It’s easy to get confused in such a wide assortment, so we strongly advise you to write down the names of the companies listed in the tour of brands and go to the store with this list. If the part being considered in the store is even slightly loose, you cannot buy it - after installation on the car it will begin to vibrate strongly, which will reduce driving comfort and may cause the driveline transmission to fail.
How to change the crosspiece on the cardan
To repair the crosspiece, it is necessary to remove the cardan. Before you disassemble, you need to know some nuances:
- Fill the nuts with waterproofing agent to make the fasteners easier to unscrew.
- Use a chisel to mark the cardan flanges and rear axle flanges. If this is not done, vibration may occur on the cardan.
- To avoid damaging the threads of the nuts, it is advisable to use a curved spanner.
- If the cardan bolts rotate, you need to fix them with a screwdriver.
First, unscrew the four bolts on the propeller shaft, then remove the suspension bearing mount. After these procedures, we remove the cardan; it needs to be removed from the gearbox splined connection. Before removing the crosspiece, it is advisable to wrap the spline part with material to prevent sand from getting in there. Before removing the crosspiece, you need to prepare a tool: a hammer, pliers, a thick screwdriver and a round tube of suitable diameter. Clamping the shaft in a vice will make your work much easier. There are special pullers for removing crosspieces, but they are often not used even at service stations. However, many garage craftsmen are able to make such a device for themselves in 10-15 minutes. Next we get the retaining rings. Often, to remove them, you need to tap them with a hammer using a spacer. After this operation, the stoppers can be easily removed with pliers. Next, the cups are knocked out of the eyes. This is done with a hammer and the same spacer that was used when removing the retaining rings. Sometimes the cups fall out on their own; most often you will have to remove them with improvised objects.
What are turnouts used for?
Such devices are widely used for track connections. Designed for transferring trains and other rail transport from one railway line to another.
These are elements of special length, laid on wooden or reinforced concrete sleepers, which are needed to solve the following problems:
- combining two or three tracks running side by side;
- branching one line into several neighboring ones;
- joining parallel or intersecting paths.
Their practical role is difficult to overestimate, since they minimize the costs of constructing railways, and also reduce their total length, plus, with them there is no need to lay circular routes. The key to moving railway transport as quickly as possible from point A to point B is what a turnout is: a definition of this kind may not be the most scientific, but it very accurately reflects the importance of these structures.
Preparing the lugs and forks and installing a new spider
The repair will be carried out poorly if the eyes and fork are not cleaned of dirt and rust. This is done with a metal brush or sandpaper. All internal surfaces also need to be cleaned and lubricated before installing a new cross. Do not forget about the grooves of the retaining rings; they need to be cleaned with an awl or a thin screwdriver. Next, the cups are removed from the new cross, and the cross itself is inserted between the eyes. When removing the cups, you need to make sure that the bearing needles do not fall apart. If there is no lubricant under the new cups, the part should be changed, or lubricated yourself. The cups are placed on the crosspiece, then they need to be pressed in with a hammer until the locking grooves open. The repair of the cross is completed by replacing the retaining rings.
This is interesting: Preparing for repairs
How to spot a fake
The focus of counterfeit distributors is on spare parts from well-known companies. This is due to the popularity of their brands. So a test on a mirror alone is not enough - you will need to study the packaging, average market prices, and the quality of the metal. But first things first. When purchasing a crosspiece, be sure to check:
- Packaging. Firstly, today spare parts are placed in packages made of thick cardboard, usually corrugated. Secondly, the packaging must have trademarks, markings, and stickers. Important information on the packaging: codes, country of production. Counterfeit packages may not have codes and may not indicate the country of production. Often the font is blurry, too small and completely unreadable;
- Price. Refer to information from online stores. It is worth displaying the conditionally average price for a new crosspiece. The price of a fake will always be lower. This does not apply to discount periods, when prices drop by 25-30 percent;
- Part quality. Check the crosspiece on the mirror, turn the cups. Carefully examine the metal of the cross - there should be no scratches, abrasions, chips, etc. Pay attention to the retaining rings.
You should only buy a crosspiece from a trusted store. There are several known cases when, instead of the ordered original crosspiece, a fake was received. Roughly speaking, this spare part is not worth buying without an external inspection - there are a lot of pitfalls that need to be identified at the stage of external inspection of the part. When ordering from online stores, make sure that its customers do not have problems returning the goods to the seller.
Installing a cardan on a car
When installing the cardan, you need to follow several rules:
- All connections must be thoroughly lubricated
- Avoid getting sand and dirt on moving joints
- Check the condition of the crosspiece seals. If they are worn out, replace them
- Achieve a complete match of the marks made when removing the marks. If they do not match, there is a high probability of vibration of the cardan and you will have to do balancing
First we insert the splined part, then tighten the four bolts on the cardan. Don't forget about attaching the outboard bearing. All bolts must be tightened well, and then checked again. If the driveshaft comes loose while driving, the car may be thrown off the road.
Sometimes repairs may not be necessary, you just need to inject. If you don’t know how to syringe the crosspiece, then you will need a large syringe and special lubricant. If you can't find lubricant, use lithol. The rear crosspiece especially needs to be sprayed, since the bulk of the dirt gets there. Many crosses have a special hole for injection. They must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt before the process. You need to syringe until the lubricant begins to pour out. Be prepared that most of the grease will be on the ground. It is better to collect a new portion of lubricant, but do not collect it from the ground.
Cardan joint: device, purpose
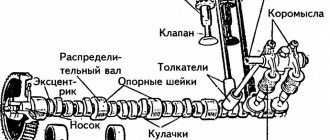
The device with two forks is made in the form of a universal joint, which performs the main function in the gearbox. It is divided according to the type of transmitted rotation:
- transmitting rotation of equal angular velocities (CV joint);
- transmitting rotation of unequal angular velocities;
- with a semi-cardan elastic and rigid hinge.
Mechanisms are single-shaft, double-shaft and multi-shaft; based on the number of hinges, they can be divided into single-, double- and multi-hinge.
In front-wheel drive cars, CV joints are installed that do not use crosspieces.
The mechanism is mounted on vehicles with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive. When transmitting unequal angular velocities, one and sometimes two cardans are used, it all depends on the distance over which the rotation needs to be transmitted.
The first shaft, located from the gearbox to the support, is called the intermediate shaft, and the second is called the rear shaft. They are connected using a support, rigidly fixed with a clamp on the bottom of the car. This is the so-called suspension bearing.
This device is designed to properly maintain HF. This design uses an additional hinge with a cross. In addition to this gearbox, a compensating device is used, which is called a sliding clutch. It is designed to lengthen or shorten the cardan while the machine is moving and is a splined connection between the cardan and the fork tip. When overcoming obstacles, a mutual change occurs between the rear axle and the car body. As a result, the cardan is compressed or stretched. These changes are compensated by a sliding clutch. If it is necessary to transmit rotation to two shafts at an angle, a mechanism with a semi-elastic hinge is used.
This is interesting: How much does the VAZ 21083 engine weigh?
How to check your work
You can check your work immediately after replacing the crosspiece and installing the cardan on the car. The verification process includes the same manipulations as when searching for cross play. The cardan should also be inspected for oil or grease leaks. Pay special attention to the seals. The second stage of testing is testing in motion. During a test drive, you can immediately hear vibration, noise or beating of the cardan.
The job of replacing the universal joint is complete, and you did it yourself, spending money only on spare parts. In addition, you have completely removed and installed the cardan, now if any unit of the cardan fails, it will not be difficult for you to replace it.
Crosspieces with movable guard rails.
The main difference between crosses and a movable guardrail (Fig. 3) and conventional crosspieces is the presence of a movable guardrail, instead of one of the fixed guardrails, and a spring to return it to its place after the wheels pass along its groove. Supporting bridges are essential for crosspieces with a movable guard, and a carriage is often part of the structure in addition to the double pads. Various details, such as anti-lift devices and a retaining shoe, are intended to keep the guard in place in relation to the costal parts of the cross. Recently, crosspieces with spring guards have begun to attract more attention. Recent projects have eliminated many wasteful parts and now produce a cross that is more powerful and requires less maintenance. AREA has developed designs for 1/9, 1/10, 1/11 and 1/12 grade crosspieces. These designs have short spring rails and replace all the rivets in the reinforcing strips with bolts. In addition, clamping brackets attached to the main bolts and bolted to the carriage or pads replaced the former rivet connections. The carriages provide the crosspiece with the correct direction in profile and plan, and rivet joints, on the contrary, give unsteadiness and play due to corrosion or vibration under the composition. Although these new designs require greater articulation at the joint due to the short spring length of the rail, they have been used successfully on busy roads for several years. The short guard at the front of the cross allows the use of a shorter counter rail in a straight path, and this is its advantage. Crosspieces with a movable guardrail are used almost exclusively on main lines - at transfers and exits, where traffic occurs primarily along the main track. Properly designed shock absorbers ensure that the spring rail remains open as the train passes and closes with a slight click after the last wheel of the train has passed, without damaging the crosspiece.
Rice. 3. Crosspiece with a movable guardrail: 1 — length of the crosspiece; Lpp - front part; Lnm is the theoretical length of the front part; Lxn - tail section; L xm - theoretical length of the tail section; 1 — front liner; 2 - movable guardrail; 3 - fixed guardrail; 4 — guards for legs; 5—carriage; 6 — main liner; 7 — place of insertion of the short core rail; 8 — core liner; 9— theoretical tip; 10 - practical tip; 11 — guide bracket; 12 — spring cup; 13 — fuse for legs; 14— tail liner; 15 - long core rail; 16 — corner of the cross; 17 - short core rail; 18 — paired linings; 19 — front liner; 20 - fixed rail; 21— straight butt plate; 22 — movable guardrail; 23 - stepped bolt; 24 — curved butt plate; 25 — external spiral spring; 26 — internal spiral spring; 27 — rod; 28 — rod guide bushing; 29 — recess in the rail head; 30— spring cup bracket; 31— spring cup; 32 — movable guardrail; 33 - amplification band; 34- guide bracket; 35 — guide bracket bracket; 36 — cushion of the guide bracket; 37 — support for the bolt head; 38 — clamping bracket; 39 — main liner; 40— core liner
The guardrail spring rail is sharply bent to provide sufficient space for the guardrail spring rail to be able to open when the wheels of the train pass. A triangular recess is cut into the head of the spring guardrail to allow the flanges of the wheels of the train passing along the main track to pass through. The notch is 12.7 mm deep at the tip and disappears at the point of the core where the bandage completely covers both rails. This prevents impacts from worn flanges and unnecessary opening of the spring guard during the passage of rolling stock.
Removing the driveshaft crosspiece - check its condition visually
In order to prolong the life of the crosspiece and, of course, the cardan itself, it is necessary to regularly carry out visual inspections, with which you can assess its serviceability. It also wouldn’t hurt to use high-quality lubricant for the driveshaft crosspieces, especially since purchasing it is not difficult at all. Moreover, it is recommended to lubricate its elements at least every ten thousand kilometers.
You can carry out diagnostics as follows: grab the flange with one hand, and the shaft with the other, and rotate them in different directions. If play is formed, this indicates severe wear of the part, and therefore the need for urgent repairs or its complete replacement. In order to understand whether it is possible to limit ourselves to just replacing worn elements, you will need to completely remove the driveshaft crosspiece.
This is done according to the following scheme. First, you should unscrew the cardan mounting bolts, and then it can be easily dismantled. Next, unscrew the nuts with which the shaft is attached to the rear axle shank. Using pliers, you need to loosen the locking ring and dismantle the cross itself. Then turn the shaft so that it hangs and knock out its cups with a hammer. Now remove them, given the dimensions of the driveshaft crosspiece, this is not difficult to do.
Cardan shaft crosspiece - how to find out about a breakdown?
This part can rightfully be called the central link of the entire cardan, since it performs the most important function in its operation - transmitting torque from the gearbox to all the necessary units . Thus, it is she who makes the shaft itself rotate. Therefore, every motorist should know how to replace the driveshaft crosspiece and how to properly monitor it so as not to get into a very unpleasant situation, especially when it comes to an unexpected breakdown during travel. Also, to extend its service life, information on how to lubricate the driveshaft crosspieces will be useful.
The very first harbinger of a crosspiece failure is a characteristic knock that occurs in the cardan box while driving. In addition, you can also hear creaking, grinding and even crackling sounds. Remember that the repair of the driveshaft crosspiece cannot be postponed until later, since even a small malfunction will affect the quality of the trip and the operation of the entire mechanism, and therefore can cause an accident.
The main reason for such a malfunction, as a rule, is the gap in the cardan joint, as well as wear of the bearings of the cross itself.
Of course, their serviceability is affected by both driving style and the quality of the road surface, but if the first completely depends on the driver, then we are unable to influence the second factor. Cross-country trips, which cause heavy stress, have a particularly negative impact. In addition, the location of the cross is not the most favorable (very close to the road surface), so it is constantly exposed to dust, dirt and water.
Strelochnaya street
This is the name for a large number of transfers on a relatively small section of the main route.
They are different, depending on the nature of the location in relation to the main track. But in the general case, this is a set of sequentially arranged transfers to a side path that have a single purpose. The following varieties are distinguished:
- Simple - usually very extended, with significant distances between the axes. Among the advantages is that it is extremely easy to maintain and is perfectly visible. The main disadvantage is the dimensions: it turns out to be long and takes up a relatively large amount of space. Areas of application: sending and receiving parks.
- Shortened - minimizes transition areas, but reduces maneuverability. I found my niche at large bases and cargo yards, warehouses and similar sites.
- Non-concentric fan - characterized by a constant radius of laying all curves. It is laid to increase the track spacing of the main track (when necessary), but its installation involves a large amount of excavation work.
- At a double angle of the cross - minimizes the length of the zone, allows you to perform various maneuvers. Relevant for sorting hubs, the necks of receiving and dispatching parks and other objects with more than 5 lines.