A hybrid engine has several energy sources: gasoline and electric motors. Both units drive the car individually or together. Several types of hybrid designs have been developed, and each realizes the main advantage over “conventional” engines - fuel efficiency. This means it is possible to achieve high environmental requirements for transport.
History of hybrid engines
Hybrid power plants were known back in the 19th century. The inventor of the first hybrid powered by electricity was Robert Anderson. However, Henry Piper received a patent for the system in 1905. Ferdinand Porsche worked in the same direction. Serial producers of hybrid engines were the French company Parisienne des Voitures Electriques, the American corporation General Electric, and the Belgian Pieper.
Hybrid technology did not rapidly develop at the beginning of the 20th century for several reasons:
- low fuel cost;
- unprofitable compared to gasoline internal combustion engines.
By the end of the 20th century, rising energy costs and stricter environmental standards forced automakers to return to developing efficient engines. Initially, VW, Mercedes, GM, Audi joined the race, but they never reached the point of serial production of hybrid cars, moving on to other areas of development. The first successful car with a hybrid engine was the 1997 Toyota Prius. Within a year, the company was able to sell 25,000 models. The second popular hybrid on the market is the Honda Insight.
After the Prius, Toyota launched serial production of the following models: Hybrid Harrier, Highlander, Estima Hybrid, Crown, Camry Hybrid, Lexus RX. Among Honda's developments with a hybrid installation, the Accord Hybrid and Civic Hybrid are famous. Single cars are found in Ford, Audi, Mazda, Renault, BMW, Nissan, Hyundai.
Let's talk in more detail about what a hybrid car means. Let's look at the device, operating principle, and what are the pros and cons of hybrid installations.
Operation of hybrids: destroying myths
- Hybrid cars are a new product that have not been fully improved and have many shortcomings. This is a myth, since the Toyota brand has been engaged in full-scale mass production of hybrid models for almost 20 years.
- Hybrids run out of battery power, which leads to problems. This is true, but only partially. In the initial stages of technology development, similar cases occurred, but today high-precision electronics do not allow the battery to be deeply discharged.
- Hybrid cars break down more often and are expensive and difficult to repair. This is a myth, since hybrid cars are no less reliable in operation than conventional diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines. Most service stations comprehensively service hybrids on a par with conventional cars. Moreover, the gearbox in hybrids eliminates the presence of friction clutches, which makes such a transmission simple and reliable, which cannot be said about various types of automatic transmissions. As for internal combustion engines, the engine in hybrids often operates at low speeds and does not reach peak loads. If we also take into account the Atkinson cycle, then the engine life of a hybrid engine is much greater than that of a conventional engine.
- The internal combustion engine of a hybrid has less power; such cars lose dynamics compared to their analogues. Yes, the power of internal combustion engines in hybrids is less, but due to the addition of an electric motor, the total power of the units significantly exceeds the power of conventional analogues with one gasoline engine.
- The consumption of a hybrid car in practice is not much different from a conventional car. This is partly true, since the consumption rate of hybrid cars directly depends on the driving modes. To achieve maximum efficiency, you need to change your driving style to slow, calm and smooth, avoiding acceleration, active throttling, etc. In other words, pressing the gas pedal hard will command the control system to start the internal combustion engine.
The idea of saving fuel in hybrid cars is to drive on electric power for as long as possible with a charged battery at speeds of up to 60 km/h, which is often enough in dense city traffic. It is also necessary to add that the system takes into account a large number of factors: outside temperature, degree of heating of the internal combustion engine and, battery charge, movement downhill or uphill, etc. In different conditions, a hybrid can use an internal combustion engine, or can move only on electric energy.
- The battery for a hybrid is difficult to find on the market, and the battery takes up a lot of space in the trunk of the car. This is a myth, since batteries for hybrids are always available for order in auto stores, and there is also a wide selection on various Internet resources. In terms of space, the battery takes up virtually no usable space in the luggage compartment.
- You cannot put gas on a hybrid car. This is a myth, since global gas equipment manufacturers produce equipment compatible with the electronic control unit of a hybrid car.
Operating principle and design of hybrid engines
The operating principle of hybrid engines is based on combining the capabilities of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The gasoline unit develops maximum torque at high speeds, while the electric engine develops maximum torque at low speeds. Combining installations makes it possible to exclude mechanical energy conversion mechanisms from the design, increase the efficiency of the power unit and reduce fuel consumption.
Complete design
A car with a hybrid engine is designed differently than conventional cars with an internal combustion engine. Here under the bottom are:
- internal combustion engine;
- one or more electric motors;
- battery pack.
- An electronic unit with an inverter is installed to control and convert energy.
The source of energy in a hybrid engine is an internal combustion engine running on gasoline or diesel. The power converted by the generator starts the traction motor and charges the batteries. It is from the battery pack that the electric motor receives additional power if there is not enough generator energy.
Similar article Problems and reviews of the Mercedes M274 engine
The inverter converts the high-voltage battery's DC current into higher-voltage 3-phase alternating current. Energy is used for:
- electric motor control;
- reverse conversion of current from the generator to recharge the battery;
- on-board power supply.
Structurally, the inverter is a housing with a set of electronic boards and transistor assemblies.
We will consider the general principle of operation of a hybrid car below.
Engine operation
The mode of joint operation of the internal combustion engine and the electric motor depends on the design of the hybrid power unit and the driving mode of the vehicle. So, when starting to move, the gasoline engine does not always need to be started. The car will move due to the operation of an electric motor powered by a battery.
A large battery capacity with the possibility of external recharging can reduce gasoline consumption to zero if the vehicle's daily mileage is short.
The electric motor keeps the car running at idle speed: when parked at a traffic light or at a temporary stop. At this time, the internal combustion engine is turned off as long as there is enough electric power. Usually the gasoline engine is connected at a speed of 60 km/h. Under heavy loads, for example, driving up a hill, you will need double effort from both units. In this mode, the car can travel more than 500 km.
What's distinctive is how the hybrid engine operates during braking. The braking system of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle converts kinetic energy into thermal energy, dissipating it in the air. Hybrids are equipped with a recuperation system, i.e. return. When the vehicle slows down, the electric motor switches to generator mode, supplying electrical energy to the battery.
general description
Improvements in internal combustion engines (ICEs) are barely keeping pace with the requirements placed on them. On the one hand, there are consumers with dreams of both a powerful and economical engine, and on the other, there are environmentalists who are tightening toxicity standards. And in conclusion - geologists, increasingly insistently reminding us of the depletion of “black gold” reserves. One of the options for solving this problem is hybrid power plants, consisting of a conventional internal combustion engine and an electric motor. Unlike electric vehicles and fuel cell vehicles, which are still the “cars of the future,” hybrids have been in mass production since 1997.
Let's compare a car with a conventional combustion engine and an electric car. An ordinary car can travel four to five hundred kilometers without refueling and at the same time poison the atmosphere with a certain amount of harmful substances . There are plenty of gas stations in any region, and you can replenish your fuel supplies in a matter of minutes. An electric car can travel about 80-160 km on a single battery charge. It is environmentally friendly, silent and practically flawless until the moment it comes to recharging the batteries. For the “electric” machines that exist today, this process lasts several hours.
Hybrid cars take the best from both engines: internal combustion engine and electric. The advantage of the first is its convenient energy carrier, liquid fuel, and the second is its outstanding torque characteristics. Unlike an internal combustion engine, an electric motor is not needed. It can “stand and wait” without consuming energy. But as soon as the current was turned on, we immediately got maximum traction on the wheels. An electric motor is more efficient than an internal combustion engine in frequent starts and stops (i.e., when driving in the urban cycle). An internal combustion engine, on the contrary, is more efficient at constant, optimal speeds for a given engine.
In a hybrid, both engines work for each other. The internal combustion engine turns the generator and supplies energy to the electric motor. This, in turn, allows the internal combustion engine to operate without sudden acceleration loads, in the most favorable modes. Almost all modern hybrids have a recovery system or, in Russian, “energy return”. Its essence is that when braking or when the car is coasting, the electric motors begin to spin from the wheels and work as generators, charging the battery. Hence – less wear, environmental friendliness and efficiency (especially in the urban cycle.)
So, before us is a technologically advanced car, which eliminates the shortcomings and combines the advantages of two engines. But.., it’s too early to clap your hands, and let’s listen to what the skeptics say.
Hybrid cars are more complex and more expensive than traditional internal combustion engine cars. Rechargeable batteries have a small operating temperature range, do not like frost, are subject to self-discharge, and their service life is limited to several years. And the “efficiency” of a hybrid is directly related to the condition of the battery. In addition, there is the problem of recycling used batteries. Hybrids are more expensive to repair, and not everyone will undertake the repair itself. In addition, many also question the high environmental friendliness and efficiency of hybrids. Thus, a number of tests conducted by reputable automotive publications have shown that hybrids provide noticeable fuel savings only in the city, while driving in the mixed cycle they are insignificant, and outside the city they are significantly inferior to modern diesel engines. The honorary title “The most environmentally friendly car of the year” in 2007 and 2008 was also awarded to cars with diesel engines.
Let's take a closer look at what hybrids are and how they work.
According to the degree of hybridization, they are divided into “moderate” , “full” and plug-in . “Full” is able to move only on electricity, without consuming fuel. “Moderate” always uses the internal combustion engine, and the electric motor is connected if additional power is required. Plug-in hybrid - this hybrid can be plugged into an outlet for recharging. As a result, the owner of such a hybrid gets all the benefits of an electric car, without the biggest drawback: limited mileage on a single charge. When the electric charge runs out, the internal combustion engine is connected and the car turns into a regular hybrid.
Based on the principle of interaction between the electrical and fuel components of a car, hybrid drives are usually divided into three types: serial, parallel and series-parallel .
Types of hybrid units
Hybrid engines vary in type of application and layout. According to the first criterion, hybrids are divided into microhybrids, moderate hybrids and complete hybrids. We'll talk about them in more detail below.
The use of different layout systems of hybrid engines reflects the level of development of hybridization, the essence of which is the desire of manufacturers to convert the car to an alternative energy source. The most progressive companies in terms of development are Toyota, BMW, Hyundai, and Volvo.
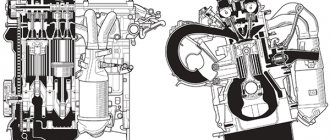
Interaction diagrams between motor and internal combustion engine
The design of the hybrid engine is selected based on the design characteristics of the vehicle: required power, acceleration speed, fuel consumption, etc. There are sequential, parallel and combined circuits.
Series circuit
The sequential hybrid vehicle system was invented by Porsche in 1899. The circuit includes an internal combustion engine with a generator, a traction motor and batteries. In this scheme, the internal combustion engine starts a generator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, powering the electric motor. In turn, the electric motor acts on the drive wheels, setting the car in motion.
The large capacity of the batteries allows the car in some modes to operate only on electrical energy, with the internal combustion engine turned off. The batteries are charged from the generator when the power consumption of the electric motor is low, for example, during measured driving. However, in acceleration mode, the generator power may not be enough, and then the battery compensates for the lack of energy.
The sequential design of a hybrid engine is good because the capacious battery allows the installation of an internal combustion engine of smaller dimensions and lighter weight. A simpler design uses less fuel and requires less maintenance.
The electric motor rotates in any direction, allowing the car to be simplified by removing the clutch and gearbox. And when installing electric motors with gearboxes in the drive wheels, you can do without a differential. A similar scheme is found on BelAZ mining dump trucks and ZIL city buses. Rarely found in passenger cars.
Similar article Technical characteristics of the Mercedes OM 364 engine
Parallel circuit
Hybrid engines with a parallel system can drive a vehicle using an internal combustion engine, a traction electric motor, or a combination of both. Often an electric motor is installed instead of a flywheel, using the electric motor as a generator and starter to start and stop the car. The batteries are recharged during regenerative braking.
The parallel circuit is suitable for low-power vehicles. Due to the use of low-capacity batteries, the weight and initial cost of the machine are reduced. A similar design is found in the Honda Insight and BMW 7 ActiveHybrid models.
Series-parallel circuit
In essence, this scheme is a modification of the parallel one. A special feature of hybrid engines with a series-parallel system is the presence of a power divider in the transmission. The energy of the internal combustion engine is divided into 2 streams in accordance with the vehicle’s driving mode. Part of the power goes to the drive wheels, the other goes to the electrical energy storage device.
To implement such an arrangement, a less powerful internal combustion engine is required, but with high efficiency. For example, an Atkinson cycle engine with a short compression stroke. Toyota Prius and Lexus RX are built according to this scheme.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k1nG8PkP28E&feature=youtu.be
Advantages of cars with a hybrid installation
Economical operation
Economical operation is the main advantage of hybrids. To achieve it, it was necessary to seek a balance, that is, to balance all the technical indicators of the car, but at the same time preserve all the useful parameters of an ordinary car: its power, speed, ability to accelerate quickly, and many other very important characteristics inherent in modern cars. Moreover, the ability to accumulate energy, including not wasting the kinetic energy of movement during braking, but to charge batteries, in addition to the main obvious advantages, has brought some side “small joys” to car enthusiasts, for example, less wear on brake pads.
How the savings were achieved: — By reducing engine volume and power; — Engine operation in an optimal and uniform mode, much less dependent on driving conditions; — Complete engine stop when necessary; — Possibility of movement only on electric motors; — Regenerative braking with battery charging.
This entire system is so complex that it has become fully possible only in modern conditions, using rather complex algorithms for the operation of the on-board computer. Even correct and effective (from a safety point of view) braking is controlled by the on-board computer.
Ecological cleanliness
Reducing carbon fuel consumption had an immediate impact on environmental cleanliness. A complete stop of engines in places where cars accumulate on city roads, and above all in traffic jams, is of paramount importance. The use of rechargeable batteries, which have a much smaller capacity than in electric vehicles, has reduced the problem of recycling used batteries. The development of hybrid technology in public transport and for trucks will further improve the environmental situation of cities.
Good driving characteristics
Now there is no need to install the engine based on peak operating loads. At the moment when a sharp increase in traction load is necessary, both the electric and conventional motors are switched on simultaneously (and in some models, an additional electric motor). This allows you to save on installing a less powerful internal combustion engine, which operates most of the time in the most favorable mode. This uniform redistribution and accumulation of power, followed by rapid use, allows the use of hybrid installations in sports cars and SUVs. Despite the fact that electric motors have a fairly strong torque in terms of the weight and dimensions of the engine, compared to other engines, developers still install not very powerful electric motors in a number of models, reducing their dimensions. At the same time, in order to sum up the power, combined torque transmission schemes are used, with direct transmission of mechanical torque directly from the engine. This scheme is called “hybrid-shared drive”.
Increased driving range
Time is the most valuable resource for a person. Eliminating half of the trips to gas stations, and even more of these trips when driving around the city, frees up some time for the car owner for other big and important matters.
Energy Conservation and Reuse
The main disadvantage of a carbon fuel engine has been eliminated - the inability to return energy back to carbon fuel. Transportation engineers have long tried to capture braking energy in order to reuse it. For example, special designs with a large flywheel were used. But only electrical energy can be saved with minimal losses and as cheaply as possible. Both batteries and special capacitors are used as storage.
Regular fueling
Electric vehicles still have one big drawback - the need to charge the battery. The process is long, and requires some specially equipped charging point. Thus, it becomes unsuitable for long and long trips. But technologies have already been developed that make it possible to charge lithium-ion batteries with electrodes made of nanomaterials to 80% capacity in 5-15 minutes.
In a hybrid car, this drawback is eliminated. Refueling is carried out according to the usual scheme, with ordinary carbon fuel, when necessary, and further movement can be continued immediately.
In the urban operating cycle, a hybrid car operates in electric mode 80% of the time. In February 2006, car enthusiasts from the United States were able to hack the electronic control system of a Toyota Prius, and learned how to force the car to switch to electric vehicle mode. The French company PSA Peugeot Citroen will begin mass production of hybrid versions of the Peugeot 307 and Citroen C4 by 2010. The cars have an electric mode at speeds below 50 km/h. The driver can switch to EV mode at will.
Classification by degree of electrification
Understanding the features of hybrid engines, we will also talk about the various applications of electric motors. The degree of electrification of a machine indicates the capabilities of the electrical installation. In one case, it comes as an app, in another it allows you to fully move on electric power. To understand how much progress has gone forward, let’s consider the stages of electrification sequentially.
Microhybrid
The microhybrid engine is the simplest form of hybridization. The car is equipped with a Start-Stop system, in which the electrical installation is used as a starter and generator, but does not transmit energy to the wheels. When the car is idling, the control unit turns off the gasoline engine, allowing you to save fuel. On average, consumption in the city is reduced by 10%.
The energy saved from regenerative braking powers the start-stop system and on-board devices.
A standard gearbox with a pulse oil pump is installed in the microhybrid power plant. In the "Start-Stop" mode, while the engine is not running, it is necessary to keep the switching elements turned on. The pump maintains oil pressure in the transmission channels so that after starting the engine, the car is ready to drive within 0.3 seconds.
Mild hybrid
The term “mild” or “moderate” hybrid means that the electric motor is used in cars as a light “support” for the internal combustion engine. The main work in acceleration and normal driving mode is performed by the gasoline engine. The essence of using an electric installation is to help when starting and accelerating the car, as well as to recharge the battery during braking. The electric motor power does not exceed 50 kW.
Similar article Brief description of ZMZ engines
Hybrids of this type include: BMW 7 ActiveHybrid, Honda Civic Hybrid, Suzuki Smart Hybrid, Mercedes S 400 Hybrid.
Full hybrid
A full-fledged hybrid car is capable of running on one traction electric motor when the internal combustion engine is turned off. The electric motor replaces the clutch and works as a generator to charge the batteries, including in regenerative braking mode. Unlike a moderate hybrid, an electric motor with a power of 60 - 250 kW is used here.
The full hybrid principle is implemented in the Audi A1 and BMW X6 ActiveHybrid. Such hybrids are equipped with powerful lithium-ion batteries. However, with a capacity of 12 kW/h, the electricity storage device can provide a vehicle range of no more than 60 km. When the charge level is low, the internal combustion engine switches on automatically, but to reduce fuel consumption and increase the range of the electric motor, engineers developed Plung-In.
Hybrid plugins
Plung-In or hybrid plugin is similar in principle to a full hybrid. The difference lies in the ability to recharge the battery from an external network. The distance that a car can travel on electric power alone is characterized by the PHEV indicator.
To turn a hybrid engine into a Plung-In, additional equipment must be supplied: a charger, an additional control unit and a battery pack. The charging socket is located near the fuel tank filling flap. To recharge the battery, you can use your home power supply, taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations.
Type medium hybrids
Intermediate transmission device
The classification of hybrid parallel transmissions begins with determining the role of the electric motor in the entire power unit of the car. If the electric motor is used only as an assistant to the internal combustion engine, for example, as in the Honda Insight, the transmission is classified as a “moderate hybrid”. The power of the electric motor in a middle-class hybrid transmission does not exceed 60 kW.
BMW Corporation used one of its latest innovations in the field of hybrid transmissions when creating the BMW ActiveHybrid 7 model. The sedan is equipped with a single gearbox – an 8-speed automatic transmission.
Full hybrid system
Lexus RX 400h is equipped with a “full hybrid” system
When an electric motor is used to transfer power to the wheels, the term "full hybrid" is used - this is the powertrain used in the Lexus RX 400h. The car can move using both the internal combustion engine and the energy of the electric motor. The gearbox does not have a torque converter. For the first time in Europe, a full parallel hybrid scheme was installed in 1998 on the Audi Duo package.
Microhybrid
A car transmission where the generator has additional functions is often called the “microhybrid” class. These are cars that have a start/stop system; the electric motor does not transfer its energy to move the wheels. The micro-hybrid circuit only allows you to turn off the engine sharply during short stops. The system is started by the starter; the car uses a standard gearbox with a built-in pulse pump to quickly supply pressure to the oil channels of the gearbox.
Series-parallel circuit
The mixed type of hybrid transmission eliminates the use of a traditional gearbox. The joint operation of the electric motor and internal combustion engine occurs through the use of a planetary gear. The fuel motor transmits torque to the wheels together with the electric motor, and the generator operates at the same time. Automatic speed control is carried out through an electronic control unit.
Planetary gear
This type of ECVT is widely used by Toyota in the latest Toyota Prius range. The company's engineers have created their own unique HSD hybrid transmission scheme. The device circuit included a power divider (planetary gear) and a separate generator.
With this type of hybrid, the electric motor runs most of the time, the fuel motor uses the Atkinson cycle to operate, while most internal combustion engines operate on the Otto principle. The know-how of Japanese engineers was acquired by Ford and Nissan for installation on their full-hybrid models.
Advantages and disadvantages of hybrid cars
Having figured out how a hybrid car works, let’s summarize it in the form of an objective assessment. Let's summarize the pros and cons of a hybrid engine in a table.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. High efficiency due to the use of torque from the internal combustion engine at any load | 1. There are few specialists in the repair and maintenance of hybrids |
| 2. Gasoline savings in the city 10 - 30% | 2. High cost of batteries. If one element fails, the entire assembly must be replaced. Disposal problem |
| 3. Braking energy is recovered into electrical energy | 3. Availability of a large number of electronics. Difficulty with spare parts. Expensive repairs. |
| 4. Use of internal combustion engines of lower power and dimensions. Possibility to dispense with clutch and gearbox | 4. Insufficient number of stations for recharging batteries. Low mileage on electric power alone |
| 5. Reliable start in winter | 5. Poor maneuverability |
| 6. Reduced toxic emissions | 6. Cold weather causes batteries to fail faster. |
| 7. Quiet operation | 7. Silent operation leads to accidents |
Mechanics
Any complex unit has in its “arsenal” the principle of its operation or action. In the case of hybrid engines, you need to know that, formally, there are two engines in such a car: gasoline and electric. These “twin brothers” change in their work depending on the operating mode of the power plant, and sometimes they work in pairs. An electronic system controls this change of engines, determining which engine should be turned on at the moment. For example, on the highways you need a gasoline one, because the battery capacity may not be enough, but in traffic jams you can just “roll” on electric power. If we delve deeper into the mechanics, there are three operating principles for such “hybrids”.