The tachometer does not work on the VAZ 2115
Determining the rotation of the crankshaft on VAZ-2115 passenger cars with injection engines is assigned to a device called a tachometer. It is based on a stepper motor, on an armature shaft, which is mounted on a pointer. This is what will move along the tachometer scale, indicating the speed of the crankshaft when the engine is running. The angle of rotation of the arrow will depend on the signals received at the terminals of the stepper motor from the electronic control unit, and voltage pulses from the primary circuit of the ignition system.
If the tachometer begins to “grumble” at the readings, then works normally, and then freezes in some position, then the driver first needs to perform a bar test (2115-3801010), which consists of checking the correct operation of all his devices. This test is very simple: simply press the reset button and, without releasing it, turn the ignition key to the ignition on position. If we see that the tachometer needle begins to move a little along the scale, and then returns and repeats this three times, the device is fully operational. In this case, the reasons for its failure should be looked for elsewhere.
Another possible result when running the test is that the tachometer needle refuses to move without the dial jerking, indicating a broken gauge. But before you start looking for a new dash, since tachometers are not sold separately, try checking the ground wire from pin 1 of the VDO X1 white strip. If the ground wire is OK, there is only one way out, replace the instrument cluster.
If your test shows that the tachometer is working properly, a driver who does not have knowledge of electrical engineering can only check the condition of the contacts for oxidation in the sockets through which signals from the ignition are received. The coil bank and electronic controller are supplied to VDO terminals 2 and 3 of X1. Tachometer terminal 2 is the low voltage input from the engine control unit, and terminal 3 is the high voltage input from the ignition coil assembly. The location of the ECU pins will depend on the brand of your ECU.
Why do you need a tachometer?
The main task of the tachometer is to help the driver select the correct gear. Timely gear shifting to a lower or higher gear allows you to extend the life of the engine and other components. You can talk about the best speed range for engine operation for a very long time. But it all depends on the type of your vehicle and travel conditions, so it’s not possible to talk about universal advice; we can only give some basic points.
Fuel consumption will be less when driving at low engine speeds
. This statement is only partly true; you can read more about this in the article on how to reduce fuel consumption.
Low speeds mean a reduction in engine tractive effort
. Regardless of your skills and abilities, when overcoming a steep climb or getting ahead or overtaking, you will have to press the gas, and sometimes even press the pedal to the floor. In this case, the fuel mixture will become richer and you will not be able to save gasoline.
Engine life is an important aspect. If we think logically, the lower the speed, the less rotation of parts and their friction, and accordingly wear
.
But there are some pitfalls here. The main stone is the oil pump, or more precisely, its operation, which depends on engine speed. At low speeds, the oil will not reach the liners and their wear will be inevitable
. The gap in the liners will increase and they will begin to wear out even faster.
Also, one of the negative aspects of driving at low speeds is the shock loads in the transmission and engine
. There are no good consequences from impacts, and the mechanisms fail faster. But constantly driving at high speeds is also not worth it.
The lubrication and cooling system operates without a safety margin. When parts from the cooling system fail, the coolant temperature sensor begins to show something is wrong - the arrow moves into the red zone. You will get nothing but problems from this. Those who like to drive fast should definitely watch the tachometer needle and temperature gauge. You can read more about what causes engine overheating. A serviceable engine filled with good oil can withstand heavy loads without any special consequences. Nothing will be worse than a decrease in resource.
Classification by operating principle
- Mechanical or electromechanical tachometer with direct drive. The revolutions are transmitted to the dial indicator through a flexible shaft, which receives the revolutions through a worm gear directly from the crankshaft or one of the transmission shafts. The indicator is based on the phenomenon of eddy current induction. The operation and design of a magnetic tachometer is very similar to the operation and design of a car speedometer. This tachometer design is not used in modern cars.
- Electric tachometer. A characteristic feature is the connection to an electric generator. Mainly used in diesel engines, but for uniformity, this type of device can also be used in gasoline engines.
- Electronic. The signal can be received both from the ignition system and directly from the computer. Installed in gasoline and diesel engines.
Design and principle of operation
Main components of electric and electronic tachometers:
- Unit of measurement or signal converter. It can be based on analog circuit elements or built on special microcircuits;
- Display with analogue or digital speed indication;
- auxiliary elements.
Electronic tachometers work by converting individual signals or pulses received from the ECU, ignition system or alternator into a signal that the display unit can understand.
The electronic tachometer works by converting individual signals or pulses received from the engine control unit, ignition system or generator into a signal that can be read by the display.
What is a tachometer sensor
A tachometer sensor is any device designed to record important signals necessary for the operation of the measuring instrument. Among such sensors are the idle speed sensor and the crankshaft sensor.
The crankshaft sensor records the angular position of the crankshaft at certain points in time. The sensor can be installed at the rear or front of the engine, most often near the flywheel. Such a device allows you to accurately measure the speed and transmit the corresponding signal to the car’s dashboard.
The idle speed sensor is installed in the vehicle's intake system. He also takes part in determining the crankshaft speed based on the amount of fuel supplied. The idle speed sensor is installed on the engine carburetor and, through wires, sends the impulse necessary for the tachometer to operate.
Another option for connecting the device involves connecting it to an electronic engine control unit. Finding it is not difficult, since not a single wire will stick out of it. Thus, the sensor works in close cooperation with the ECU and transmits the corresponding readings to the measuring instruments.
That's probably all you need to know about a car's tachometer. As you can see, with due attention this is a fairly simple and important device that should not be neglected at all.
A tachometer is a measuring device used to determine the rotation speed of moving parts in mechanisms and assemblies. Typically, the results of its measurements are calculated by the number of revolutions per minute. The device is used in cars, motorcycles, tractors, combines, sea and river vessels, airplanes, helicopters and other equipment with an internal combustion engine. Its presence allows you to control the load limits in the operation of the motor, to increase its service life.
Why do you need a tachometer in a car?
The device can be found on the dashboard of almost every car with rare exceptions. It is used by the driver to monitor engine operation. The fact is that operating the engine at high speeds carries the risk of damaging it. By monitoring the tachometer, you can adjust the gas pedal pressure so that the crankshaft rotates in a safe mode.
The presence of a tachometer in a car provides:
- Extending the life of the motor.
- Optimization of fuel consumption.
- Selecting the correct driving mode depending on the load.
- Elimination of impact on the transmission when changing gears.
Car tachometers have a digital scale, the last numbers and divisions on which are marked in red. This is how the device highlights the critical speed for a given engine. When this operating level is reached, the crankshaft rotates at the maximum speed for the engine. This is accompanied by accelerated heating and increased vibration, which can damage the piston group, valves, timing belt, etc. By looking at the tachometer , the driver can prevent such a load and change to a higher gear in time, while releasing the gas pedal.
After a certain speed limit, different for each engine, it begins to burn fuel more intensively. By monitoring the rotation of the crankshaft using the tachometer, you can prevent an operating mode in which the car begins to consume more fuel.
Using a tachometer, the optimal engine speed is selected to start moving or climb downhill. The best moment to switch between gears depends on this data.
The tachometer reading is especially important when driving a vehicle with a trailer. In the technical documentation for the car you can see information of this kind “120 horsepower at 3500 rpm”. By achieving just such a rotation of the crankshaft, the highest traction force can be achieved from the engine. That is, by moving downhill at 3500 rpm, and not more, it is safe for the engine to pull out the load.
In cars without a tachometer, you have to monitor the load on the engine by ear, which is difficult if the interior is sufficiently soundproofed. The driver needs to determine the gain by the roar of the engine and only at this moment shift to a higher gear.
Design and types of tachometers
The main part of the device is the sensor installed directly near the crankshaft. It reads the crankshaft speed and, using electrical impulses or mechanical links, transmits information to the panel.
There are 3 types of tachometers:
- Mechanical.
- Analog.
- Digital.
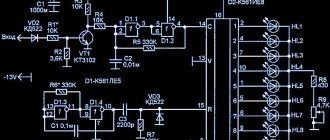
Connection diagram
When looking for the reason why the tachometer does not work, you must first understand the connection diagram and signal type. There are 3 common connection schemes:
- to a contactless ignition system (the tachometer output is connected to the primary circuit of the ignition coil). The operating principle is based on measuring the frequency of voltage surges in the primary circuit of the ignition system. It is impossible to calculate the ignition angle without taking into account the number of crankshaft revolutions, so the sparking frequency directly depends on the crankshaft speed. In 4-cylinder internal combustion engines, one full revolution of the crankshaft corresponds to 2 voltage pulses in the primary circuit. Accordingly, the higher the crankshaft rotation speed, the greater the frequency of voltage surges;
- connection to the contact ignition system. The operating principle and connection diagram are similar to the BSZ, but the measuring device will differ depending on the voltages in the input circuit;
- connection to the engine ECU. The operating principle is still based on recording voltage pulses in the primary circuit of the ignition system, but the signal to the tachometer comes from the engine control unit;
- connection to the generator (the tachometer signal pin is connected to the W pin of the generator). The generator pulley is driven by a belt drive from the crankshaft, so the rotation speed of the generator rotor will always be proportional to the rotation speed of the crankshaft. The change in crankshaft rotation can be calculated by continuously measuring the amount of emf generated across the winding. The principle of operation of a tachometer is similar to a conventional voltmeter.
Types of tachometers
Among the many different types of tachometers, only two are particularly popular:
But these two types of measuring instruments have a number of fundamental differences. They also differ in structure, characteristics, and, of course, in method of application. Therefore, it is further worth considering the question of what a tachometer is, based on its type.
Digital tachometer
The main components of a digital tachometer are a number of different parts. This:
- CPU;
- eight-bit ADC;
- liquid temperature sensor;
- LCD screen;
- optocoupler;
- various microcircuits (which perform reset functions).
Typically, electronic tachometers are made in the form of a screen, the main indicators of which are the engine speed per minute. Compared to an analog tachometer, its design has some disadvantages, although the advantages still prevail. First of all, using such a device is much more convenient.
Analog tachometer
The analog tachometer is the most commonly used measuring device, which is installed in most cars of domestic manufacturers, and on foreign cars too. Structurally, the device looks quite primitive - a regular display and arrow. But, guided by its readings, you can understand how to reduce fuel consumption.
The structure of analog tachometers is much simpler than digital instruments. Their main components are:
- magnetic coil;
- a sensor that reads information from the shaft elbows;
- arrow;
- graduated scale.
Similar to the device, analog tachometers work just as simply. The signal from the sensor that reads the number of revolutions of the crankshaft passes through the wires and hits the board, which sets the deviation for the arrow, the arrow in turn shows you the real data through a graduated scale.
True, the measurement accuracy of a digital tachometer is slightly higher. Although, this is only noticeable when adjusting the engine, since while driving the revolutions are counted in the thousands and the error does not matter much. Perceiving the readings of such a tachometer while driving is much easier than reading numbers from the monitor of a digital tachometer.
Typical faults
If your car's mechanical tachometer stops working, there is a mechanical problem. Breakage of the flexible shaft cable, wear of the worm gear parts, the appearance of backlash, deformation - all these reasons can lead to the engine speed indicator stopping working.
What to pay attention to if the electronic tachometer does not work:
- Integrity of electrical wiring. In this case, check not only the signal cable, but also the ground, that is, the power supply to the instrument panel;
- quality of contacts. The presence of oxides and loose contact inside the microcircuits can cause the tachometer to fail;
- The continuity of the elements of the measuring unit, which are located behind the protective glass inside the instrument panel. Among mechanical failures of transistors, burned-out microcircuits, traces or burnt resistors, the most common cause of tachometer failure is a violation of solder integrity. For example, in the Mitsubishi Padjero II, the appearance of microcracks in the soldered elements of the tachometer is a constant problem.
On cars with a generator connection circuit, a non-functioning tachometer may be a sign of generator failure. In this case, the failure is accompanied by the inclusion of a low battery indicator and the periodic switching on of a “garland” of warning lights on the instrument panel.
In some types of design, changes in the resistance of the high voltage cables may cause the accuracy of the engine speed reading to be adjusted.
Finding the charging wire and oil pressure wire
Let's find the charging wire. You can also look for it using a voltmeter and a probe. We set the probe to negative and look for the wire. When the engine is running, when it hits the desired wire, the probe light will light up. In this case, it may be that the charging lamp on the instrument panel lights up at half its brightness.
It may happen that the probe will not show anything, but the light on the device will still light up (maybe even at full strength) - this means that this is the charging wire, feel free to cling to it.
If you have removed the dashboard, then searching for the charging lamp can be done differently. We sit down with a probe on the positive, turn on the ignition and look for which wire the negative hangs on. Then start the engine, if the probe light goes out, then you have found the right wire (an example of this particular search method is shown in the video below).
How to find the cause of the problem yourself
In addition to a visual inspection, you will need a universal measuring device for your own diagnostics. If you know how to use a multimeter, you can easily check the power, ground, and also check the signal wire for a break.
The power test is performed in DC measurement mode, and the measurement range is up to 20 V. “Minus” is constant, “plus” appears only after the ignition is turned on. Pulses on the signal line should appear when the crankshaft rotates. To find damage, you need to switch the multimeter to resistance measurement mode - ohmmeter. Sometimes, to detect a bad contact, it is enough to shake the connector or harness in which the wire is laid. Signal speed indicator.
Where do the wires go from the tachometer?
- Registration
- Entrance
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
On the forum for 12 years Messages: 168 From: Kurgan Car: VAZ 21102 8kl 2000.
Where should I connect this wire from the signaling?
The instructions say:
The PURPLE/WHITE wire of the system should be connected: - to a special terminal TACH or - to the top dead center sensor (reference sensor), or - to the output of the Hall sensor (in the ignition distributor sensor), or - to the fuel injector control wire - to negative (-) terminal of the vehicle's ignition coil If the vehicle uses a multi-coil ignition system, the system can be connected to the negative (-) terminal of one of the coils. Please note that the individual coil wires of a multi-coil ignition system will have lower AC voltage. Connecting to the terminal of the car's ignition coil is still the least desirable, since the pulses in this circuit have a complex shape and a high level of interference.
Finding the tachometer wire using a multimeter: 1. Switch the multimeter to AC voltage mode. 2. Connect the multimeter probe(s) to ground (car body). 3. Start the car engine. 4. Check the intended tachometer wire using the red (+) multimeter probe. 5. If the wire being tested is a tachometer wire, the multimeter will display an AC voltage between 1V and 6V.
Googled: White block (X1) 1 Housing (ground) 2 Tachometer (low-voltage input from the ECU) //14v 3 Tachometer (high-voltage input from the coil) //14v -
And where to look for that same wire with 1-6 volts?
Source
Tachometer needle twitches
Owners of Gas 3110 Volgas are most familiar with the problem of vibration arrows. The problem occurs in cars manufactured before September 1999 and equipped with a set of indicators 38.3801 (JSC AVTOPRIBOR). Due to construction defects, the car generator for natural operation when charging, the current is regulated by alternating voltage, supplied winding excitation, towing the arrow.
The tachometer needle may vibrate due to loose alternator belt tension, but in most cases it is possible to repair the tachometer in Bełdze by replacing the instrument panel and modifying the wiring diagram.