Engine connecting rod and piston group
Device Features
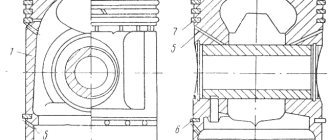
The piston is made of aluminum alloy and coated with a layer of tin to improve run-in. The piston skirt is oval in cross section and conical in height. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin and at a distance of 52.4 mm from the piston bottom.
The hole for the piston pin is shifted from the axis of symmetry by 2 mm to the right side of the engine. Therefore, for proper installation of the piston into the cylinder, there is a “P” mark near the hole for the piston pin, which should be facing towards the front of the engine.
Since 1986, repair size pistons for all engine models have been manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm. Until 1986, pistons of the following repair sizes were produced: for engines 2101 and 2103 - with an increase of 0.2; 0.4 and 0.6 mm; for 2105 and 21011 - with an increase of 0.4 and 0.7 mm.
The piston rings are made of cast iron. The outer surface of the upper compression ring is chrome plated and has a barrel shape. The lower compression ring is of the scraper type (with a groove along the outer surface), phosphated. The oil scraper ring has slots for oil removed from the cylinder and an internal coil spring (expander).
The piston pin is steel, tubular in cross-section, pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod and rotates freely in the piston bosses.
The connecting rod is steel, forged, with a split lower head in which the connecting rod bearing shells are installed. The connecting rod is processed together with the cover, so during assembly the numbers on the connecting rod and the cover must be the same.
Selection of piston to cylinder
The calculated gap between the piston and cylinder (for new parts) is 0.05-0.07 mm. It is determined by measuring the cylinders and pistons and is ensured by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinders. The maximum permissible gap (if parts are worn) is 0.15 mm. Note. The piston diameter is measured in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 52.4 mm from the piston crown. According to the outer diameter, the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) every 0.01 mm, and according to the diameter of the piston pin hole - into three categories every 0.004 mm. The piston class (letter) and piston pin hole category (number) are stamped on the piston bottom.
If a used engine has a gap exceeding 0.15 mm, then it is necessary to re-select the pistons to the cylinders so that the gap is as close as possible to the calculated one.
Spare parts include pistons of classes A, C, E. These classes are sufficient to select a piston for any cylinder during engine repair, since pistons and cylinders are divided into classes with a slight overlap of sizes.
Disassembly and assembly
Disassembly. Remove the piston pin retaining rings from the piston, remove the pin and disconnect the connecting rod from the piston. Remove the piston rings.
The connecting rod bolts are pressed into the connecting rod. Therefore, in order not to disturb the fit of the bolt in the connecting rod, it is not allowed to press the bolts out of the connecting rods when disassembling the engine and connecting rod-piston group.
If some parts of the connecting rod and piston group are not damaged and have little wear, then they can be used again. Therefore, when disassembling, mark them in order to later assemble a group with the same parts and install them in the same engine cylinder.
Assembly. Before assembly, fit the pin to the piston and connecting rod. For new parts, the class of pin holes in the connecting rod and piston must be identical to the class of the pin. For used parts, for proper mating it is necessary that the piston pin, lubricated with engine oil, enters the hole of the piston or connecting rod by simply pressing the thumb and does not fall out of it.
Replace the finger that falls out with another one of the next category. If a third category pin was inserted into the piston, replace the piston pin and connecting rod.
Assembly of the connecting rod and piston group is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly. After installing the piston pin, lubricate it with engine oil through the holes in the piston bosses. Install the piston rings in the following order.
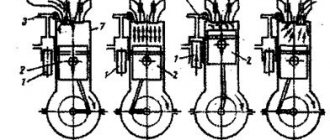
Lubricate the piston grooves and piston rings with engine oil. Orient the piston rings so that the upper compression ring lock is at an angle of 45° to the piston pin axis, the lower compression ring lock is at an angle of approximately 180° to the upper compression ring lock axis, and the oil scraper ring lock is at an angle of approximately 90° to the axis upper compression ring lock
Install the lower compression ring with the groove facing down. If the ring is marked “TOP” or “TOP”, then install the ring with the mark facing up (towards the piston bottom).
Before installing the oil scraper ring, check that the joint of the spring expander is located on the side opposite to the ring lock.
Checking technical condition
Clean the piston from carbon deposits and remove all deposits from the lubrication channels of the piston and connecting rod.
Inspect the parts carefully. Cracks of any kind on the piston, piston rings, pin, connecting rod and its cover are not allowed. If there are deep marks on the working surface of the liners, replace the liners with new ones.
Check the gap between the piston rings and the grooves with a set of feeler gauges by inserting the ring into the corresponding groove. The calculated gap (rounded to 0.01 mm) for new parts is 0.04-0.07 mm for the upper compression ring, 0.03-0.06 mm for the lower one and 0.02-0.05 mm for the oil scraper ring . The maximum permissible wear gap is 0.15 mm.
Check the gap in the piston ring lock with a set of feeler gauges, inserting the rings into a gauge having a hole diameter equal to the nominal diameter of the ring with a tolerance of ±0.003 mm. For normal size rings with a diameter of 82 mm, caliber 67.8125.9502 can be used. The gap should be between 0.25-0.45 mm for all new rings. Maximum permissible wear gap - 1 mm
Passenger cars are equipped with different types of engines; power units may differ in volume, power, and design.
If oil consumption in an engine increases, the most common reason for this is worn or broken piston rings; replacing them is quite labor-intensive work, and also requires certain plumbing skills.
general description
These power units are designed for installation in small class passenger cars. The Volzhsky Automobile Plant began producing engines in 1976. The same unit was installed on the VAZ-21074, Niva-2121.
The engine has a resource of 125,000 km, however, this is only passport data. Practice shows that VAZ-2106 engines are capable of traveling from 200 thousand km and above. Naturally, this is subject to high-quality and timely service. The motor has a potential of 80 l/s without any resource losses.
Specifications
So, VAZ-2106-1000260 is a gasoline power unit. The power supply system may be different. Old VAZ-2106 engines were carburetor, modern ones are injection. Its volume is 1568 cm3. According to the passport, the power is 77 l/s. Torque is 104 Nm at 3000 rpm.
Fuel consumption in the city is 10.3 per 100 km. On the highway you can drive a little more economically. Consumption is 7.4 liters according to the passport. When operating a car in a mixed cycle, the appetite will be about 10 liters. For efficient operation, engines need not only fuel, but also motor oils - the unit consumes 0.7 liters of lubricant for every 1000 km. Pour 3.5 liters of oil into the unit.
Disadvantages and advantages
The 2106 engine has significant disadvantages:
- excess heat is transferred to the well of the piston bottom and fins by steel control plates inside the bosses;
- dynamic loads are reduced due to the displacement of the finger from the axis of symmetry to the right;
- When assembled into an engine, the pistons are mounted with markings in one direction, which increases labor costs and the human factor.
The internal combustion engine uses a cylinder head from model 2103, a starter 35.3708 and a G221 generator for an engine with a current of 42A. Oil consumption does not exceed 700 g/1000 km. The instruction manual states that it is recommended to add 200 ml less lubricant than the volume of the system as a whole. The markings for which oil to pour are given in the upper table.
Distinctive features
They represent a fairly successful improvement of the previous model. In the process of creating the power unit, engineers used the most modern technologies at that time. The manufacturer set the task of improving the design and technical characteristics of the engine at any cost and by all available means.
The power of the VAZ-2106 engine was increased by increasing the total effective volume. During development and production, engineers paid special attention to improving the quality of processing of combustion chambers. Thanks to improvements and upgrades, 10002011 was born. Apart from the diameter, there are no other differences in this block from the basic design.
In production, during technological processes, engineers and specialists give each cylinder of the block a certain class. Nowadays five or more such classes can be distinguished. They differ from each other by 0.01 mm. These classes are assigned symbols - A, B, C, D, E. To find out which class a particular unit is assigned to, just look under the engine. The letter is indicated at the bottom of the base. with index 21011-10005011-10 remained without any changes. To adjust the overall size of the cylinders, developers and engineers had to use new cylinder head gaskets.
As for pistons, standard pistons accepted all over the world have a lot of similar characteristics. This engine used parts of the piston system from unit 21011. The nominal diameter of such a piston, according to the passport data, is 79 mm.
The new modification of the engine has special cylindrical holes. Volumes have also increased. During operation in each area, the piston warms up more evenly and not immediately, but gradually. Thus, the developers managed to compensate for thermal deformation. The engineers also decided to place special temperature control plates in the piston bosses. Since 1990, power units have been equipped with OZONE 2107-1107010-20 carburetors, as well as a vacuum ignition distributor.
Pistons
Many domestic and imported cars use repair pistons manufactured at the production facilities of the Kostroma manufacturer of piston groups, Motordetal-Kostroma. This company produces pistons with a diameter from 76 to 150 mm. Today the following types of pistons are produced:
- solid cast;
- with thermostatic insert;
- with an insert for the upper compression ring;
- with oil cooling channel.
Pistons produced under the specified brand have their own designations. In this case, information (marking) can be applied in two ways - laser and micro-impact. First, let’s look at specific examples of markings made using laser engraving:
- EAL - compliance with the technical regulations of the customs union;
- Made in Russia - direct indication of the country of origin;
- 1 - group by mass;
- H1—diameter group;
- 20-0305A-1 - product number;
- K1 (in a circle) - sign of the technical control department (QCD);
- 05/15/2016 - a direct indication of the production date of the piston;
- Sp 0.2 - gap between the piston and cylinder (temperature).
Now let's look at the designations applied using the so-called micro-impact, using specific examples:
- 95.5 - overall diameter size;
- B - diameter group;
- III - group according to finger diameter;
- K (in a circle) - quality control (quality control) sign;
- 04/26/2017 - direct indication of the production date of the piston.
It is worth noting here that for the production of different pistons, different aluminum alloys with alloying additives are used. However, this information is not indicated directly on the piston body, but is recorded in its technical documentation.
Change of oil
If you violate the manufacturer's regulations and do not change engine oils on time, this will lead to cylinder wear. Their diameter will increase by 0.15 mm. Do not use inexpensive and low-quality oils. The level should not be below average. The car's mileage is over 60 thousand km. If there is not enough oil, the cylinders will fail.
If the unit consumes more oil than it should, this may indicate that the valves or rings have failed. In this case, the first thing they do is measure the compression and then look for the cause of the increased appetite.
Replacing piston rings on a VAZ 2107 car
A rag will be useful for repairs, because there are still oil residues in the system (even if you drain everything first). It’s also worth adding a few liters of kerosene to your arsenal (to clean parts from coking oil deposits) and a few metal brushes.
First of all, you need to remove the engine from the car, this will take around several hours. Then he removes the remaining parts one by one. It should be noted that except for the ignition distributor, the parts will not need to be unscrewed, which greatly facilitates the work. Having gotten rid of unnecessary spare parts, all that remains in front of you is the engine.
We unscrew the nuts along the entire perimeter of the engine in order to remove the upper valve cover. Here, be sure to remember that the cover washers have a specific shape, so it’s absolutely not worth losing them! Because they can only be replaced with similar ones, which you will have to buy at a car store.
The valve cover and cylinder head can now be removed. It should be remembered that the bolt that secures the head is hidden under the shaft housing, so it is necessary to loosen the chain and gears in advance. Once the camshaft is loosened, the cylinder head can be unscrewed and removed. Since it is constructed of aluminum, you must remove it very carefully to avoid scratching or damaging it.
After all the operations performed, the cylinder block will be open and the bottom of the pistons will be visible. Thus, it will be possible to immediately visually assess the condition of the entire mechanism. Now let's move on to the bottom part, because there is no need to remove anything from the top. Here you have to unscrew 19 bolts that secure the engine to the sump. In addition, do not forget about the original washers, which again must be preserved. You should be especially careful when removing the pan, because there is an oil pump intake nearby, which can be very easily damaged, and this is exactly what you do not want.
Source
Winter operation and engine starting
In winter, the manufacturer recommends starting the engine manually using the starting handle. It is also important to warm up the battery - to do this, turn on the headlights for a couple of seconds. To prevent the engine from stalling, depress the clutch before starting. The thing is that the gear oil in the gearbox is too thick and it takes time to become liquid again. There will be no such problems with winter oils.
The starter starts the engine only when the clutch is depressed. To prevent the engine from stalling, pull out the choke. It should be released as slowly as possible as the engine warms up and the VAZ-2106 engine speed drops to idle.
Periodically press and release the accelerator pedal to supply lubricant to the engine components and mechanisms. The engine must idle for at least five minutes.
Features of a major overhaul
Before repairs, the first step is dismantling. To overhaul this engine, you will need special tools - metalworking and measuring. The assembly process is best left to specialists, but many car enthusiasts assemble these engines themselves.
To dismantle the cylinder head casing and flywheel, you should have some experience or contact a service station. Disassembling fingers requires special skills. Diagnostic skills are also required to perform major repairs. The repair work is completed by installing the VAZ-2106 engine back into the car.
Story
The first VAZ-2106 car rolled off the third line of the main conveyor on February 21, 1976. When the production of the VAZ-2106 (Lada 1600) model, which was redesigned for domestic operating conditions from the FIAT 124 Speciale of the 1972 model, was mastered in Togliatti, no one could have imagined that it will become the most popular and mass-produced product of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant.
VAZ-2106 is a restyled version of the VAZ-2103. The “Six” differs from the VAZ-2103 in a more powerful 80-horsepower VAZ-2106 engine with a displacement of 1.6 liters, a different electrical circuit and a modified design of the body and interior. Ergonomics have been improved, the design has been simplified and “modernized” by reducing the number of chrome elements and increasing the number of plastic ones.
Compared to Moskvich cars, these 5-seater sedans, distinguished by better dynamics and a truly comfortable interior, were the height of comfort and prestige for wide sections of car enthusiasts in the USSR. In the late 1970s, the VAZ-2106 immediately gained fame as a “chic” and fast car, but expensive and less “practical” than other Zhigulis. Decent dynamics for that time (maximum 150 km/h and 16 seconds to 100 km/h), embossed seats with headrests, an instrument panel with a tachometer and excellent sound insulation - there was something to appreciate.
At one time, the car enjoyed considerable popularity among car enthusiasts due to its smooth ride, good handling, high maintainability and relative durability. In terms of build quality, the “six” occupied one of the leading positions among other VAZ cars.
In 1979, the plant launched the production of less powerful modifications VAZ-21061 with a 71-horsepower VAZ-2103 engine and VAZ-21063 with a 64-horsepower VAZ-21011 engine. They were not popular among the people, but the scale of their production increased (especially 21063), and in conditions of Soviet shortages, the consumer had to put up with the combination of an expensive and heavy body with a weak engine, which noticeably worsened the dynamics. Since 1980, Ozone carburetors of type 2107 began to be installed. .Changes in electrical engineering due to changing technology occurred constantly. In 1977, cars began to be equipped with new terminals and wiring connections, and since 1986, a new relay has been installed.
In 1982, the first modernization of the car was carried out. The VAZ-2106 began to be equipped with modernized 75-horsepower (according to the new GOST) VAZ-2106 engines. Reflectors were no longer installed on the rear wing along the molding line. In 1988, the exhaust system was modernized: it was equipped with a disposable gasket and nut. In 1990, VAZ introduced a kind of Luxury package - the VAZ-21065 with a standard VAZ-2106 engine with a contactless ignition system, a Solex carburetor (21053-1107010-03), halogen headlights, improved upholstery and other seat headrests. Export modifications of the VAZ-21064 externally differed from the VAZ-21065 in bumpers with built-in turn signals and a slightly different electrical circuit. Since 1985, first for export modifications, then sometimes for “domestic” ones, they began to install a 5-speed gearbox of the VAZ-2112 type, and later of the VAZ-21074 type, which significantly reduces fuel consumption on the highway and engine noise.
But times are changing. By the end of the 1980s, this model, with modifications, remained the most widespread and popular in the VAZ program. Of course, it was no longer considered prestigious, but the good memory of the first family of Zhiguli cars supported a steady demand for the “six”. It was not even affected by the dominance of the low-power modification of the VAZ-21063 and the sharp deterioration in the quality of assembly and components in the 1990s. Over time, the car became so affordable that it became an unpretentious “workhorse.” He also has a permanent army of fans.
However, now the VAZ-2106 is gradually losing ground, primarily due to the obsolescence of the design and interior, as well as the rather low driving qualities organically inherent in the classic layout. Nevertheless, the “six” has every chance of celebrating its thirtieth anniversary on the assembly line.
Production of the VAZ-2106 began at the Volzhsky Automobile Plant in 1976. Since 1998, the car was produced on an assembly line in Syzran. In 2002, production was moved to Izhevsk. In January 2006, the VAZ-2106 was discontinued 30 years after production began.
Modifications
- VAZ-21060
- working volume 1600 cc - — a pickup truck with a tent built into the body, made by order of the technical directorate.
- VAZ-21061
- VAZ-2103 engine, displacement 1500 cm3.
But initially the VAZ-21061 was a car version for Canada
“Canadian” version with powerful bumpers made of aluminum profile. it was assigned the index 21061, but then Canada “disappeared”, and it was worn by the most “frail” modification with a 1.3 liter engine.
- VAZ-21062
- Export version of the VAZ-2106 with a right-hand steering wheel. - VAZ-21063
- working volume 1300 cc (from VAZ 21011 (modification of VAZ 2101)) Ozone carburetor 2105-1107010-20 - VAZ-21064
- The VAZ-21064 model is an export modification of the VAZ-21061
. - VAZ-21065
- Displacement 1500 cc, bumpers from VAZ-2105, electric heated rear window, more powerful generator, five-speed gearbox, contactless ignition system, carburetor "SOLEX-21053", electric windows of the front doors, safety steering wheel, other upholstery interior, other seats with headrests. - VAZ-21065-01
- Displacement 1500 cc, bumpers from VAZ-2105, electric heated rear window, more powerful generator, five-speed gearbox, contactless ignition system, 3.9 rear axle gearbox, Solex 21053 carburetor, electric front doors - VAZ-21066
- Export version of the VAZ-21063 with a right-hand steering wheel. - VAZ-21067
- Izhevsk VAZ-2106 models of the latest releases had the index VAZ-21067, they were equipped with a VAZ-21067 engine with a volume of 1600 cm3, which is a modification of the VAZ-2106 engine with a fuel injection system and a catalytic converter that complies with Euro 2 toxicity standards. Izhevsk cars of the VAZ-21067 model do not have a distributor, a mechanical fuel pump with a manual pumping lever and a carburetor. The components of the power system for the injection “six” were borrowed from front-wheel drive VAZ cars. The control unit is “January 5.1”, only with its own calibrations. The air and fuel filters, the ignition module are also unified. The receiver is from a Nivov injection engine. The speed sensor is installed on the gearbox at the connection point of the speedometer cable, and the latter is connected through an adapter - the same as on the Niva VAZ-21214. The neutralizer in the exhaust system and the adsorber provide Euro 2 not only for exhaust, but also for fuel evaporation. The octane number of the gasoline used has not changed - AI-92, because the engine compression ratio has remained the same. - VAZ-21067-20
- experimental, with a 2106 injection engine, displacement 1600 cubic meters. cm, 2005, left hand drive - VAZ-21068
- was released as a carrier of units during the development period of the new VAZ-2108 and VAZ-21083 engines. - VAZ-21069
- The VAZ-21069 model is completely identical in appearance to the VAZ-2106, but with a two-section VAZ-411 RPD with a power of 120 hp. Since 1983, a VAZ-413 engine with a power of 140 hp could be installed, and since 1997, a universal RPD for rear-wheel drive and front-wheel drive VAZ VAZ-415. The cars were manufactured to order from the special services. - - “Pseudo-seven” for the Brezhnev family, made from the usual “six”. Received the nickname "half past six."
| Model | Engine displacement, cc | Location of controls | Notes |
| 2106 | Out of production in 1993. | ||
| 21061 | |||
| 21062 | |||
| 21063 | |||
| 21064 | |||
| 21065 | |||
| 21066 | |||
| 21067 | |||
| 21067-20 | 1600 (single injection) | experimental with injection engine 2106, 2005 | |
| 21069 | with engine from Samara-21083, 1988 |
Cylinder block
The 2112 cylinder block is made of high-strength cast iron, and at first glance, is similar to the 21083 block. The main differences are the diameter of the head mounting bolts and holes for them in the block reduced to 10 mm, lugs for the fuel injection system sensors and a completely different technology for honing the cylinders during production .
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Material | Ductile iron |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82,0 |
| Intercylinder distance (distance between the axes of adjacent cylinders of the block), mm | 89,0 |
| Block height (distance between the upper plane of the block and the axis of the crankshaft), mm | 194,80 |
| Diameter of boring of crankshaft supports (for main bearings), mm | 54,52 |
| Weight, kg | 28,810 |
For the VAZ 2112 block, five size groups are defined. Size classes are designated by letters: A, B, C, D, E.
Technical characteristics of the VAZ-2106
Year of release
| Lada 1600 GL (Nederland) | Lada 1600 LS (export version) | VAZ 2106 | VAZ 21061 | VAZ 21063 | Lada 1600 (2106) | Lada 1600 ES 4-Door Saloon UK market (21064) | |
| Modification | — | — | 1600 | 1.5 | — | 1.6 | — |
| — | — | 1976 | 1976 | — | 1977-85 | — | |
| Geometry | |||||||
| Body type | Sedan | Sedan | Sedan | Sedan | Sedan | Sedan | Sedan |
| Number of doors | — | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | — |
| Number of seats | — | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | — |
| — | Left | Left | Left | Left | Left | Right | |
| — | 4116 mm | 4166 mm | 4166 mm | — | — | — | |
| — | 1611 mm | 1611 mm | 1611 mm | — | — | — | |
| — | — | 1440 mm | 1440 mm | — | — | — | |
| Wheelbase | — | 2424 mm | 2424 mm | 2424 mm | — | — | — |
| Front track | — | 1365 mm | 1365 mm | — | — | — | — |
| Rear track | — | 1321 mm | 1321 mm | — | — | — | — |
| — | — | 170 mm | 170 mm | — | — | — | |
| Curb weight | — | 1030 kg | 1045 kg | 1085 kg | — | — | — |
| Full mass | — | 1430 kg | 1445 kg | 1485 kg | — | — | — |
| Engine | |||||||
| Engine | — | — | VAZ 2106 | VAZ 2103 | VAZ 21011 | VAZ 2106 | — |
| Location | — | front, longitudinal | front, longitudinal | front, longitudinal | front, longitudinal | front, longitudinal | — |
| — | — | petrol | petrol | petrol | petrol | — | |
| Supply system | — | — | carburetor | carburetor | carburetor | carburetor | — |
| Cylinder diameter | — | — | 79 mm | 76 mm | 79 mm | 79 mm | — |
| Piston stroke | — | — | 80 mm | 80 mm | 66 mm | 80 mm | — |
| Compression ratio | — | — | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.5 | — |
| — | 1.568 l | 1.57 l | 1.452 l | 1.294 l | 1.57 l | — | |
| Turbocharging | — | — | No | No | No | No | — |
| Power | — | 78 hp | 80 hp at 5400 rpm | 77 hp at 5600 rpm | 69 hp at 5600 rpm | 80 hp at 5400 rpm | — |
| Torque | — | — | 122 Nm at 3000 rpm | 106 Nm at 3500 rpm | 94 Nm at 3400 rpm | 122 Nm at 3000 rpm | — |
| Fuel brand | — | — | AI-93 | AI-93 | AI-93 | AI-93 | — |
| Transmission | |||||||
The main parts of the VAZ 2106 car engine: 1 – crankshaft pulley; 2 – generator drive belt; 3 – front crankshaft cuff; 4 – camshaft drive chain; 5 – spring plate; 6 – guide sleeve; 7 – valve; 8 – internal spring; 9 – outer spring; 10 – lever spring; 11 – adjusting bolt; 12 – valve drive lever; 13 – camshaft; 14 – oil filler cap; 15 – cylinder head cover; 16 – spark plug; 17 – cylinder head; 18 – flywheel; 19 – rear crankshaft cuff; 20 – oil pressure sensors; 21 – piston; 22 – oil level indicator; 23 – oil drain plug; 24 – connecting rod; 25 – oil pan; 26 – drive shaft of auxiliary units; 27 – crankshaft.
Main components and assemblies in the engine compartment of the VAZ 2106
Knots and assemblies of the VAZ 2106: 1 – radiator; 2 – battery; 3 – suction pipe; 4 – air filter housing; 5 – oil filler plug; 6 – vacuum brake booster; 7 – brake system reservoir; 8 – hydraulic clutch release reservoir; 9 – expansion tank of the cooling system; 10 – washer reservoir; 11 – ignition coil; 12 – radiator cap (plug); 13 – electric fan; 14 – upper radiator hose; 15 – breaker-distributor; 16 – cylinder head cover.
Technical characteristics of the VAZ 2106 engine and design description
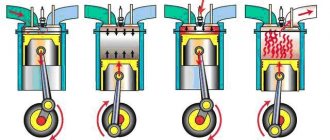
The car is equipped with a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve engine with an overhead camshaft. The power supply system is carburetor. The operating order of the cylinders is: 1–3–4–2, counting from the crankshaft pulley.
The VAZ 2103 engine differs from the VAZ 2106 engine in its smaller cylinder diameter (76 mm versus 79) and, accordingly, the cylinder block, the size of the pistons and piston rings, as well as the cylinder head gasket. The cylinder heads of both engines are the same and their parts are interchangeable. The engine cylinders are arranged vertically in one row and combined into a block. A block head common to all cylinders is installed on top of it. The bottom of the cylinder block is covered with a stamped steel pan, which also serves as a container for oil.
The pistons have two compression rings and one oil scraper ring. The crankshaft rotates in five bearings in the cylinder block. From the pulley at its front end, a V-belt drive drives the generator and coolant pump located on the right side of the engine.
In the front part of the engine there is a drive for the camshaft and a drive shaft for auxiliary units: ignition distributor, fuel and oil pumps. The drive is carried out by a double-row bush-roller chain.
On the right side of the engine, in addition to the generator, there is an exhaust manifold, starter and intake pipe with a carburetor and air filter. On the left side there is an oil filter.
To install the engine assembly with gearbox and clutch, a three-point suspension scheme is used. The two front supports are located on either side of the cylinder block and are attached to the cross member of the vehicle's front suspension. The rear support is located on the gearbox and rests on a cross member fixed under the floor of the body.
The elastic cushions of the front supports consist of rubber with vulcanized steel washers and mounting bolts. To increase the rigidity of the supports, there are springs in the central hole of the cushions, supported by insulating rings, and to soften impacts, rubber-metal buffers are located inside the springs. The cushions are attached to the brackets using intermediate plates. The right cushion is protected from heating from the side of the exhaust pipe of the mufflers by a protective casing.
The rear support is also rubber-metal, it consists of three steel plates with rubber separating them. The middle plate is attached to the gearbox, and the outer plates are attached to the cross member of the rear engine mount. Steel spacer bushings are placed between the crossbar flanges to protect the flanges from deformation when tightening the fastening bolts.
The cylinder block is made by casting from special high-strength cast iron. The holes for the cylinders are bored directly in the block and additional inserts (liners) are not used in the cylinders. To obtain a special profile and surface cleanliness, the cylinders are honed. By diameter, cylinders are divided into 5 classes every 0.01 mm, designated by the Latin letters A, B, C, D and E. The class of each cylinder is marked on the bottom plane of the cylinder block.
The holes for the main bearings of the crankshaft are bored together with the bearing caps. Therefore, they are not interchangeable either with each other or with the covers of other cylinder blocks. In order not to confuse the lids, markings are made on them. The bearing caps are attached to the cylinder block with self-locking bolts, the replacement of which with any other bolts is unacceptable.
The auxiliary drive shaft rotates in two bushings pressed into the cylinder block. The front bushing is steel-aluminium, and the rear bushing is metal-ceramic, bronze-graphite. Spare parts are supplied with bushings of nominal and repair sizes with an internal diameter reduced by 0.3 mm.
The pistons are cast from aluminum alloy. To improve its wearability to the cylinder walls, the outer surface of the piston is coated with a thin layer of tin. To compensate for uneven thermal expansion, the piston skirt has a complex shape. It is conical in height and oval in cross section. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin and at a distance of 52.4 mm from the piston bottom.
Based on the outer diameter, pistons (as well as cylinders) are divided into five classes: A, B, C, D and E, every 0.01 mm, and according to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, they are divided into three categories, every 0.004 mm. The category is indicated by paint on the end (the first is blue, the second is green, the third is red). The piston class (Latin letter) and category (number) are marked on the piston bottom.
Spare parts include pistons of classes A, C, E, which are quite sufficient to select a piston for any cylinder, since pistons and cylinders are divided into classes with some overlapping sizes.
The hole for the piston pin is shifted from the axis of symmetry by 5 mm to the right side of the engine. Therefore, there is a mark on the piston in the form of the letter P for the correct orientation of the piston in the cylinder. The mark should face the front of the engine.
Since 1986, repair size pistons for all VAZ engine models have been manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm. Until 1986, repair size pistons for engines 2103 and 2106 were produced with an increase of 0.4; 0.7 and 1.00 mm. The pistons of engines 2103 and 2106 differ only in size (diameter).
The piston rings are made of cast iron. Top compression ring with barrel-shaped chrome-plated outer surface. The lower compression ring is scraper type, phosphated.
The piston pins are pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod and rotate freely in the piston bosses. According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three categories every 0.004 mm. The category of the finger is marked on its end with the appropriate color: 1st - blue, 2nd - green and 3rd - red.
The connecting rod is steel, forged. The lower head of the connecting rod is detachable; connecting rod bearings are installed in it. The connecting rod is processed together with the cap and therefore they are not interchangeable with the caps of other connecting rods. To avoid mixing up the connecting rod caps during assembly, the connecting rod and its cap (on the side) are marked with the number of the cylinder in which they are installed. When assembling, the numbers on the connecting rod and cap must be on the same side.
The crankshaft is cast from high-strength cast iron and has five support (main) journals, hardened by high-frequency current to a depth of 2–3 mm. At the rear end of the crankshaft there is a socket into which the gearbox drive shaft bearing is inserted. The lubrication channels in the crankshaft journals are closed with cap plugs, which are pressed in and caulked at three points for reliability.
To extend the service life of the crankshaft, it is possible to regrind the crankshaft journals when their surfaces are worn or damaged. By grinding, the journal diameters are reduced by 0.25; 0.5; 0.75 and 1.00 mm.
The axial movement of the crankshaft is limited by two thrust half-rings installed in the cylinder block on either side of the rear main bearing. A steel-aluminum half-ring is placed on the front side of the bearing, and a metal-ceramic half-ring (yellow) is placed on the rear side.
The main and connecting rod bearing shells are thin-walled, bimetallic, steel-aluminium. The shells for the 1st, 2nd, 4th and 5th main bearings have a groove on the inner surface (since 1987, the lower shells of these bearings are installed without a groove). The central main bearing shells differ from other shells in that they lack a groove on the inner surface and are larger in width. All connecting rod bearing shells are without grooves, identical and interchangeable. Repair liners are made of increased thickness for the crankshaft journals, reduced by 0.25; 0.5; 0.75 and 1 mm.
The flywheel is cast from cast iron and has a pressed steel ring gear for starting the engine with a starter. The flywheels are interchangeable, as they are balanced separately from the crankshaft. The flywheel is centered with the crankshaft by the front bearing of the transmission drive shaft.
The flywheel is attached to the crankshaft flange with six self-locking bolts, under which one common washer is placed. It is unacceptable to replace these bolts with any others.
VAZ-2106 is a true classic of the Soviet automotive industry. The car was produced for a long time after the collapse of the Union, which is explained by its incredible reliability. In addition, it stands out from other domestically produced cars due to its amazing maintainability of literally every component, availability of spare parts, and unlimited possibilities for modernization.
An important advantage of the VAZ-2106 is the engine used in this car. This four-stroke unit, equipped until 2002 with a carburetor and then with an injection fuel ignition system, can run on even the lowest quality gasoline, rarely fails in extreme cold, and can be operated successfully in almost any conditions. Any of its problems are eliminated even without the participation of a specialist - any more or less experienced car enthusiast can easily cope with routine repairs.
The principle of installing piston rings on a VAZ 2107 car
When all the steps are completed and the connecting rod along with the piston are removed, it is necessary to clean them of carbon deposits and dirt. After a preliminary inspection, you need to remove the piston rings. It should be noted here that the rings will have to be replaced, so you should not be afraid of breaking the parts that came off. Now installing new rings, you need to start with the oil scraper ring.
First of all, install the expansion ring, which is made in the form of a flexible spring with a rod or an octagon-shaped plate. When a new ring is installed on the piston, you should gradually push it through and periodically measure the gap, because it must be a certain distance.
If at the extreme point the gap is more than 0.4 mm, then the ring must be changed, and if it is less than 0.25 mm, then the whole problem is in the lock and it should be sharpened. If the gap size is normal, then install the ring. Moreover, it should be taken into account that the locks should not coincide, but rather have a difference of 90 degrees between themselves. This procedure should be performed with all rings on all pistons.
When the replacement is complete, before installing everything back, pay attention to the gaskets and also clean the engine. These operations will improve the performance of the engine.
If compression is insufficient, the VAZ 2106 engine loses power and begins to consume excessively not only gasoline, but also oil. In the best case, you can get by with a simple replacement of the piston rings, in the worst case, a complete overhaul of the engine, starting from turning the cylinders, replacing the piston group and ending with repairing the car’s crankshaft.
If you decide to change the rings yourself, there should not be any special problems when performing this repair. Of course, you will need a considerable list of tools to do this as quickly and conveniently as possible. And also, it is necessary to perform a number of preparatory work to get to the pistons:
Personally, I carried out this procedure with the engine removed, since the car was almost completely disassembled. But everything can be done even with the engine installed, but then it is most convenient to carry out repairs on a pit or a lift.
So, after the pan cover is removed, you can take a 14mm socket with a wrench and unscrew the two nuts securing the connecting rod cover. This is shown more clearly below:
When both nuts are unscrewed, you can remove the cover by hand; it can usually be easily removed without any problems:
Then, with a certain force, you need to press the connecting rod bolt with your hand or even with the handle of a hammer:
Until the piston comes out from the back of the cylinder. It will roughly look like this:
This should be done quite carefully so as not to damage either the piston itself or the cylinder walls:
Next, you can begin to remove and replace the piston rings if the cylinders are not yet worn out. To do this, carefully pry the edge of the ring with your fingernail or finger and remove it from the piston groove:
And carefully turn the ring until it is completely free from the groove:
After all the rings, both compression and oil control, have been removed, you can measure the clearance by inserting them into the cylinder and inserting a feeler gauge into the hole between the two edges:
If the values exceed the nominal values, we replace the rings with new ones. After which you can install all the parts in the reverse order of removal. It is worth paying special attention that when installing the rings, their locks should be directed in different directions for greater tightness of the cylinder.
VAZ-2106 engine weight
On a VAZ-2106 car, the weight of the engine without gearbox is 121 kilograms. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended to try to remove or move this unit alone - this is a direct path to serious injury. It is best to hire an assistant who can help you during the process of dismantling or installing the motor.
With all the necessary equipment, including both the cylinder head and the ignition system, the engine weight will be even greater - 140 kilograms.
Finally, when assembled with the gearbox and the devices attached to it, this value will increase by another 26 kilograms.
As you can see, weight can be considered a significant disadvantage of the car compared to imported analogues. To reduce it, increase power, and also improve dynamic characteristics, many drivers today install parts made of light metal alloys.
In 1984, a diesel version of the “six” was released at a Bulgarian automobile company. Replacing a gasoline engine with a diesel engine didn't have much of an impact on the car's performance. Firstly, the Bulgarians failed to increase the power of the power unit. Secondly, its weight increased by about 10 kilograms, which can also be called a disadvantage of the alteration.
Other characteristics of the VAZ-2106 engine
The weight of the motor is, although important, but far from its main characteristic. That is why we decided to talk about other features of the power unit installed on various modifications of the “six”. For example, engine power on carburetor models was 77 horsepower. After switching to an injector, it dropped to 75 hp. With. However, this parameter can always be increased by carrying out a number of upgrades.
The cylinder diameter of the VAZ-2106 power unit is 79 millimeters, the torque can reach 3000 rpm, and the working volume is 1568 cubic centimeters. Finally, the compression ratio of the engine is 8.5 atmospheres, and the piston stroke is 80 millimeters.
Piston rings. Which ones are better?
The connecting rod and piston group on the VAZ 2106 consists of a piston, connecting rod, piston rings and piston pin. Piston rings differ in purpose: compression and oil scraper. The former prevent gases from penetrating the combustion chamber into the crankcase. Oil scrapers, removing residual oil from the cylinders, prevent its penetration from the crankcase into the combustion chamber. When free, the rings have a larger diameter than the inner diameter of the cylinder. Therefore, the ring has a cutout called a lock.