The VAZ classic family cars: 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107, 2121, 2123, 2131, 21053, 21213, 21214 have a four-stroke engine.
The carburetor was installed on the engines of Zhiguli cars until 2000 and subsequently, after a simple modernization, an injector was used on cars 2105 and 2107. This is an in-line engine with vertically arranged cylinders in a block. The channels of the cooling system in the cylinder block are made along the entire height of the cylinders, effectively cooling the piston group, piston rings from “stagnation”, and also preventing deformation of the cylinder block from local heating.
The crankshaft is located at the bottom of the cylinder block on five main sliding bearings. Oil seals made of oil-resistant rubber are used as seals to prevent oil leakage.
An important engine component is the cylinder head. It is a complex cast aluminum alloy block with valve seats and guide bushings pressed into it. The cylinder head contains a cooling jacket and oil passages for supplying lubricant under pressure to the camshaft bearings and rockers that drive the valves.
Oil seals are installed on the valves to prevent oil from entering the combustion chamber. A total of 8 valves are used.
The camshaft is mounted on the cylinder head and is driven by a double-row chain from the crankshaft. Semi-automatic chain tensioning device, powered by a spring. It is possible to install a device for automatic chain tensioning, the rod of which adjusts its position based on the oil supply under pressure.
Unlike the UMZ engine installed on Gazelle, Volga, UAZ cars, the transmission of movement to the valves from the camshaft is carried out through levers (rockers), without the use of rods and rocker arms. The OHC rocker system ensures stable operation of the valves at idle and at high crankshaft speeds, reducing the ringing noise of their operation.
Adjusting valves of VAZ 2106, 2107, etc. According to the maintenance instructions, it is performed every 10,000 km and, due to the simple and compact layout of the engine, there are no difficulties in the procedure.
Is valve adjustment necessary?
Internal combustion engines use intake and exhaust valves. The intake valve is responsible for supplying the fuel-air mixture to the cylinder, and the exhaust valve is responsible for removing exhaust gases.
For proper operation of the VAZ 2107 engine, there must be a gap of 0.15 mm between the rocker and the valve stem. If this distance is greater, a characteristic “knock of valves” will appear. If the distance is less or there is none at all, the valve will not close completely, which can lead to “burnout of the plates.”
In addition, an incorrectly set thermal gap leads to a decrease in engine efficiency.
Operating principle of internal combustion engine timing valves
An ordinary ordinary driver, when it is necessary to adjust the valves, does not do it himself, but goes to a car service center. Because this requires certain skills and time. To teach yourself how to adjust valve clearances, you need to know the principle of their operation.
Specifically, I already wrote an article about adjusting VAZ valves.
An internal combustion engine has two shafts: the crankshaft (crankshaft) and the camshaft (camshaft). They are connected to each other through pulleys and a belt, through sprockets and a chain. The most common option is a timing belt driven engine. The crankshaft to camshaft transmission ratio is 2:1 (two to one).
The cams have a special irregular smooth shape that closes and opens the valves so that they correspond to the position of the crankshaft and camshaft, the engine stroke and valve timing.
When the internal combustion engine is running, it heats up accordingly, its parts heat up and expand due to high temperature. Because of this, the distance between the camshaft and the valve tappet changes slightly.
Question: why does the engine run differently when cold and when hot? Answer: because when the engine warms up to operating temperature, the valve tappet is pressed tightly against the valve and camshaft. This ensures efficient operation of the internal combustion engine.
And, if the valve end stops above the pusher, then a gap appears between the seat and the plate, and this leads to a decrease in compression in the cylinder.
It’s easy to check the compression: turn off the engine, unscrew the spark plug, screw in a special pressure gauge instead, turn the ignition key, get out and see what pressure the pressure gauge of a given cylinder shows.
And, if the end of a closed valve is located below the pusher, then during a certain valve timing phase, the valve will not open to the full distance it should. And this leads to a loss of power due to the slow removal of exhaust gases.
Probe for adjusting valves VAZ 2107
The distance between the rocker and the rod on a cold engine should be exactly 0.15 mm. To check and adjust, you can use either a set of universal probes or a more convenient special probe.
It is worth especially noting once again that the gap of 0.15 mm is set on a cold engine. If work is carried out “hot”, then it is necessary to take into account the coefficient of thermal expansion and set gaps of 0.20 mm.
We will also need two open-end wrenches - 13 - for the head of the adjusting bolt - 17 - for the locknut
Valve adjustment marks 2107
Before starting the adjustment, it is necessary to set the TDC (top dead center) of the gas distribution mechanism (GRM). To do this, you need to turn the crankshaft and align the point (hollow) on the sprocket with the protrusion on the body. In this position, you can begin adjusting valves 6 and 8.
You can rotate the crankshaft in the following way. Put the gearbox at 5 speed. Using a jack, lift one of the front wheels and turn it until the marks are in the position corresponding to TDC. In the same way, you can rotate the crankshaft to adjust subsequent pairs of valves.
The procedure for adjusting the valves of the VAZ 2107
So, our crankshaft is set to the TDC position according to the marks (see above). Now insert the feeler gauge between the camshaft lobe and the valve arm (rocker). It is very important that the probe fits into the gap “with interference.” If the dipstick dangles or does not fit in, it is necessary to make an adjustment.
1) Loosen the lock nut (17). 2) Turn the adjusting bolt (key 13). 3) Tighten the counter nut. 4) Check the gap again with a feeler gauge (it should fit “with interference”) 5) If the gap is too large or too narrow, loosen the lock nut again, turn the adjusting bolt and tighten it.
We repeat the above steps until we achieve the correct gap of 0.15 mm.
Adjusting valves on a VAZ 2107 by micrometer
Instead of a feeler gauge, a micrometer mounted on a special rail is used to adjust the valve clearance. With its help you can control the amount of free play of the rockers. A gap of 0.15 millimeters corresponds to a rocker free play of 0.52 millimeters.
The rack has special nuts that allow it to be screwed onto the camshaft mounting studs. This allows it to be installed sequentially over each pair of valves. It is necessary to tighten the rack fastening nuts well so that it does not swing during measurements. After this, you need to fix the micrometer (indicator) on the rail so that it rests against the edge of the rocker that presses the adjustable valve.
To check the clearance, you need to lift the rocker cam with a special grip or finger and check the amount of free play using the arrow of the device. If it is not equal to 0.52 mm, then it should be set in the same way as when adjusting using a feeler gauge.
This adjustment method is more accurate and reliable. The feeler gauge, passing between the rocker and the camshaft, ignores the possible gap that appears as a result of wear on the parts.
Valve clearance adjuster
A more effective and efficient way to adjust the valve mechanisms of the power unit is to adjust them using a device, which is a special rail with an indicator attached to it. This adjustment is much more accurate manually, since when using the device, it detects and takes into account all defects on the surface of the adjustable parts.
For mechanical adjustment, in addition to dismantling the cylinder head cover, you will additionally have to remove the accelerator drive, the protective shield on the ignition distributor, the exhaust hose from the crankcase, and for carburetor cars, the carburetor “pan”.
Using a special wrench, you need to rotate the crankshaft until the marks on the camshaft sprocket align (this is described above). To make this process easier, you can use a bright marker to mark the camshaft sprocket every 90 degrees. After that, we install the device rail on the valve being tested and fix it in a stationary state. We put an indicator on it and place its foot on the edge of the adjustable valve. To correctly perform this procedure, you will need a special grip, with which you need to clamp the cam and pull it up (a simple wrench will do). As a result, the indicator readings should deviate by 52 divisions. If they are slightly too low or too high, the valve needs to be adjusted. And then everything is extremely simple:
- using a 17mm wrench, loosen the locknut on the adjusting screw;
- the gap is adjusted with a key of 13, and all readings are clearly reflected on the indicator scale;
- the adjustment is checked and the locknut is tightened;
- At the end of the stage, it is again necessary to check the correct settings of the valve mechanism.
As you can see, this adjustment is much more accurate and simpler. But we should not forget that a highly qualified specialist will perform it at a high level and using a standard set of probes. In conclusion, it is worth emphasizing that most sets of feeler gauges contain an adjustment diagram that contains data on the angles of rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft, indicating the numbers of cylinders and valves.
Features of adjustment 2107 injector
- Firstly, there is no slider on the injection model, so the rotation angle can only be set along the camshaft (the same as for the carburetor model)
- Secondly, there is no need to remove the air filter housing to gain access to the cylinder head cover (unlike the carburetor model)
- Thirdly, to turn the crankshaft on an injection model, you won’t be able to use a 38mm wrench. You can jack up the rear wheel, put the gearbox in high gear and change the crankshaft angle by turning the rear wheel.
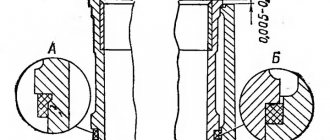
All valve train parts
1 - valve; 2 - retaining ring; 3 - guide sleeve; 4 — oil deflector cap; 5 — support washer of the outer spring; 6 — support washer of the internal spring; 7 — internal spring; 8 — outer spring; 9 — spring plate; 10 - crackers; 11 — valve drive lever; 12 — lever spring; 13 — adjusting bolt; 14 — lock nut of the adjusting bolt; 15 — bushing of the adjusting bolt; 16 — locking plate of the lever spring.
When is it necessary to adjust valves?
The normal gaps between the cams and levers provided for by the design of the VAZ-2106 engine are 0.15 mm, and reducing or increasing them will entail a number of consequences. Although their non-compliance with the established requirements does not pose an emergency hazard to the entire engine, it causes rapid wear of parts, engine overheating, a decrease in its power, and increased fuel consumption.
Typically, valve thermal clearances are adjusted every 20-30,000 km, as well as after any repair work related to the gas distribution mechanism. In addition, such a need may arise due to malfunction of other engine systems or mechanisms.
The main sign that it is time to adjust the valves is a characteristic knocking sound coming from under the valve cover. It can also be clearly heard from inside the car when the hood is closed. It is important here not to confuse this sound with the clatter of piston pins, which can occur during detonation. Valves, unlike fingers, “knock” both at idle and under load. The latter, in the event of detonation, reveal themselves only under load.
Which engines need valve adjustment and when?
It should be noted that not all internal combustion engines require periodic valve adjustment. The fact is that now in many modern internal combustion engines that are equipped with passenger cars, so-called hydraulic compensators are installed in the systems of their gas distribution mechanisms. These devices independently adjust the gaps in real time, and therefore their value is always optimal.
If the vehicle engine does not have hydraulic compensators, then the valves must be adjusted manually. It’s quite easy to know that it’s time to do this by looking at some of the symptoms. One of them is the characteristic “clicking” of the valves, which was already mentioned above, and the other is that the engine begins to “trouble,” and compression in its cylinders either drops significantly or completely disappears. As soon as at least one of these symptoms appears, it is necessary to check the size of the gaps in the valve mechanism.
This should also be done without waiting for “alarm bells”, as part of routine vehicle maintenance activities. The frequency of checking valve clearances is indicated in the technical documentation for each vehicle, and, as a rule, is once every 25,000 - 30,000 kilometers. It is usually carried out at service stations, but, with certain skills, you can check the valve clearances yourself.
Preparation stage
Adjusting the valves of the VAZ-2106 is not particularly difficult and does not require the use of special tools. Here you will need:
- a set of wrenches (heads) for 10, 13 and 17;
- key (head) 36 for cranking the crankshaft;
- Screwdriver Set;
- a measuring probe with a thickness of 0.15 mm (included in the tool kit for the car from the factory, can be purchased at any auto store or a special strip with an indicator);
- new valve cover gasket;
- automotive sealant;
- assistant (for greater convenience when setting valve timing).
The car must be placed in a viewing hole, secured with the parking brake, and the engine must be allowed to cool completely. After this, open the hood and remove the air filter: it will interfere with the removal of the valve cover.
If there is HBO (gas)
If the car is equipped with gas equipment, valve adjustment acquires its own characteristic features. The gaps for the intake valves can be set according to the instructions, as for gasoline. But graduation requires special attention. This is due to the characteristics of the fuel-air mixture on gas, the combustion temperature of which is higher and the combustion time is lower. It is better to adjust the exhaust valves in the presence of gas equipment twice as often, and set the gaps themselves to the maximum allowable according to the instructions. Some experts advise betting 10–20% more than recommended.
Using the above methods, you can quite accurately adjust the thermal clearances of the valves, simultaneously optimizing the valve timing and generally improving the operation of the entire gas distribution mechanism. This will increase the service life of engine components and its service life.
Adjustment using a feeler gauge
1.Using a 10mm wrench (socket), unscrew the eight bolts securing the valve covers. Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hoses from it. Carefully remove it and set it aside.
2. Before proceeding with the adjustment, you need to check the tension of the timing chain. If she's okay, we move on.
3. Set the piston of the fourth cylinder to the position of its top dead center. To do this, you will need to turn off the gear, go down into the pit, remove the engine mudguard, then use a “36” wrench or a similar head placed on the crankshaft pulley mounting nut to turn it until the marks on the camshaft sprocket and its bearing housing coincide . The same procedure can be carried out by jacking up and turning one of the rear wheels with 4th gear engaged, or by slowly pushing the car (if there is no inspection hole).
4. When the marks coincide, valves 6 and 8 (counted from the front of the engine from left to right) should be completely closed, and their clearances between the cams and levers should be maximum.
5.Insert the dipstick into gap 6 of the valve. It should enter there with noticeable resistance. If the gap is greater than the thickness of the feeler gauge, or the feeler gauge cannot be pushed into the gap, adjustment is required.
The importance of adjusting engine valve clearances
After the start, the engine and all its parts begin to heat up, and therefore expand. At the same time, we should not forget about the natural wear and tear of rubbing and contacting parts. This necessitates strictly defined gaps between certain components. And the thermal valve clearances (between the camshaft cam and the valve stem) are among the most important.
If the gap is too small, the engine will not be able to fully realize its potential, which will immediately affect the dynamic and speed characteristics of the car. At the same time, the exhaust valves will overheat and their edges will melt.
If the gap is larger than required, the car owner will be alerted to the characteristic “clatter” of the engine, which can sometimes go away as the car warms up. With increased clearance, the camshaft lobe begins to "knock" against the rocker of the valve stem instead of pushing through it.
Valve mechanism in section using the example of an engine with two camshafts
The need to adjust the valves is ripe if the following signs are visible:
- there is an extraneous, slightly ringing sound in the area of the cylinder head cover;
- the gas distribution mechanism was repaired;
- the last adjustment of the valve thermal clearances was carried out more than 20 thousand km ago;
- engine output has dropped noticeably;
- As a consequence, high fuel consumption is possible.
Most modern engines use hydraulic compensators to adjust thermal clearances. It is convenient and does not require third-party intervention, although there is an opinion that components still wear out a little faster. The engines of many cars, in particular VAZ classics, require manual adjustment of thermal clearances. Some people consider this a simple matter, others, on the contrary, consider it a responsible and serious job. It all depends on experience, variations of techniques, dexterity and patience. It is recommended to carry out work after approximately 20 thousand km since the last adjustment.
Adjusting valves using a gauge indicator (rack)
Most car owners adjust the valves using the method described above. But there is another method that provides the most accurate determination of the thermal gap. Here its measurement is carried out using a special rod and an indicator (dial micrometer). The adjustment itself occurs in the same way, i.e. by tightening and unscrewing the valve adjusting screws in the same sequence as turning the crankshaft.
The only thing you need is the reading table that comes with the device. With its help, you can find out what the gap should be (in the indicator readings) at a certain air temperature.
Measurements of the size of the gaps are carried out as follows.
1. We attach the rack to the camshaft bed and screw it on.
2. We fix the indicator in the holder and fix it on the rack above the rocker (rocker arm) of the valve that we plan to regulate. It must be fixed so that its rod rests on the very tip of the rocker platform.
3. Having determined the air temperature, look at the table and find out how many divisions the indicator needle should deviate under such conditions. At 20 0 C, this is 52 divisions, which are equal to the same 0.15 mm.
4. Having set the arrow of the device to “0”, raise and lower the rocker arm and see how much the arrow deviates. If this value is greater than 52, for example, 70, turn the indicator dial counterclockwise by 18 divisions.
5.Next, as in the previous case, use the adjusting screw to adjust the gap until the arrow coincides with zero when the rocker arm is raised.
6. If after tightening the locknut there is an error of 2-3 divisions, this is not a problem, but it is better that it is oriented towards the increase.
How to adjust valves
All procedures must be carried out only on a cold engine. This is done to ensure that the setup results remain standard: this is exactly what they do at the manufacturing plants. It is worth noting that the procedure for adjusting the valves on each car is different: you can find it out from the instructions for the car or the relevant literature. The process is carried out by screwing in or unscrewing special adjusting screws, or by selecting flat washers. Each of these options is considered separately.
Using special tools
Engine valves are adjusted using a set of feeler gauges or a special rack and indicator. Both methods are quite widespread: the first is simple, accessible and requires minimal financial and time costs. To apply the second method, you will have to buy a device and a special device.
Adjustment using feeler gauge and locknuts
This method of setting the timing belt is typical for Russian rear-wheel drive cars (“classics”). Algorithm of actions:
- Remove the air filter housing and disconnect all tubes, cables and levers from the valve cover. To make it easier to turn the engine crankshaft, remove the spark plugs.
- Remove the valve cover and the front timing belt cover (if there is one, it may also be a chain).
- Set the piston of the cylinder from which the procedure will begin (for example, in the Zhiguli “classic” it is the 4th) to the top dead center position: the valves will be in the closed position.
- Observing the indentation mark on the engine shaft pulley, rotate it until it coincides with the mark on the lower front cover of the BC. The recessed point on the timing shaft sprocket should also coincide with the mark on its “bed” (housing).
- Use an open-end wrench to hold the adjusting hardware and at the same time loosen the locknut. Next, you need to use a set of feeler gauges to adjust the valves. Select the thin plate you need and insert it between the rocker arm and the valve stem. When adjusted normally, the feeler gauge will pass through with little friction. The gap value must be adjusted according to the table, which is different for each car (for VAZ2101-07 - 0.15 mm). Now tighten the locknut and check the clearance again. Repeat the operation if necessary. Follow the order of valve adjustment: for example, for a VAZ classic: 8-6, 4-7, 1-3, 5-2.
Adjustment using washers
This type of timing adjustment is more typical for front-wheel drive cars. To produce it, you need:
- Remove the valve cover.
- Find the marks on the engine block, timing belt pulley and, turning the crankshaft clockwise, make sure they match. As a result, the first piston will be in the TDC position.
- Determine the gap between the shim and the camshaft cam (they are the first when viewed from the pulley side).
- If there is a larger or smaller gap, select another washer (each has a corresponding marking; if not, use a caliper, or better yet, a micrometer).
- After installing the washer, check the gap again: the permissible deviation is no more than 0.05 mm in both directions.
- Do not forget that the gap size for the intake and exhaust valves is different - this parameter must be found out from the operating instructions for a particular car.
Adjustment using indicator and rack
This method is considered more accurate and was especially popular during the USSR. This adjustment method is good for engines that have been in operation for a long time, since the device and measuring rod take into account the wear on the surfaces of the parts. Progress of the procedure:
- Remove the valve cover, having first disconnected the levers and cables from it.
- Rotate the engine shaft until the marks match, just as when adjusting the valves using a feeler gauge.
- Take the rack and fix it on the cylinder head (fastening is carried out to the studs of the camshaft housing). There is a small nuance: you do not need to completely screw in all 3 nuts securing the rack, otherwise it will dangle. First of all, tighten the outer hardware, then begin to unscrew the middle bolt until the rail becomes motionless.
- Take the dial indicator and secure it to the rail, and place the device’s foot on the edge of the valve cam.
- Using the included grip, grab the cam and pull it up: the indicator needle should pass 52 divisions (at an air temperature of +20 degrees). If this is not the case, then you need to adjust the valve using one of the two methods described above.
Adjustment of valves
If knocking, unstable operation, or increased vibration occur, you should pay attention to the valves.
If the valve timing of the gas distribution mechanism is disrupted, they do not operate accurately, that is, the full volume of gas does not enter the working area of the cylinders, complete combustion of the fuel-air mixture in the working chamber does not occur, and the cylinders are not purged. This is all accompanied by the appearance of a shock load on the camshaft cams on the drive lever and the shaft rod. Fuel and engine oil consumption also increases. What happens if you drive with unadjusted valves? Answer: rapid wear of engine parts, increasing cost and repair time.
The greatest danger to a car engine is a gap that is less than permissible. Too little clearance between the drive lever and the camshaft cam prevents the valve head from sitting tightly in its seat on the cylinder heads. Through a valve that is not seated, gases from the burnt fuel-air mixture are knocked out of the combustion chamber. Because of this, the exhaust valve cap around the perimeter begins to burn.
Rubber oil deflectors, also known as oil deflectors, also burn out due to a burnt valve cap, which leads to increased engine oil consumption. If the wear of engine parts is large, then it may be better and easier to do an engine swap with your own hands or at a service station.
If you set the valve clearances incorrectly
After 5-10 minutes of operation, the motor reaches operating temperature (this is about 90-100 degrees). According to the law of physics, all parts begin to expand. Engine wear will vary depending on whether the valve clearances are too large or too small.
Gap too big
If the gap is larger than the nominal one, the sound of the engine will be different. As the engine gradually warms up, this unusual sound (clunking) will disappear.
If the valve clearance is large, then the camshaft fist does not press on the valve drain rocker, but knocks on it.
If the engine runs in this mode for a long time, then:
- valve service life is reduced;
- the end of the valve stem may break off;
- riveting;
- there will be an increased noise level of the internal combustion engine.
Since the gas distribution phases are disrupted, engine power may drop by half.
Gap too small
In this case, the valve does not open completely, the exhaust gases do not have time to escape completely, hence the loss of engine power. Valve plates will burn out due to increased overheating.
Consequences of low valve clearance:
- Low compression in cylinders.
- The exhaust gases do not have time to escape through the small gap and the edges of the valves burn out.
- The valve plates do not fit tightly into their seats.
- High load on the timing belt or chain drive.
It is necessary to adjust the valve clearances as soon as possible if the following symptoms appear:
- A ringing sound appeared in the upper part of the cylinder head (cylinder head).
- If the timing belt has been repaired.
- If you have driven more than 25,000 km since the last adjustment.
- If the engine does not pull. Neither uphill nor in a straight line.
- If gasoline consumption has increased.
The procedure for adjusting valves VAZ 2101-2107
First we prepare the car:
- wait until the engine cools down if it was running;
- park the car on level ground;
Valve adjustment procedure:
- Remove the air filter cover and the filter itself.
- Disconnect the filter mounting tubes and remove the mount.
- Remove the air damper control cable (choke).
- Remove the throttle linkage.
- Unscrew the nuts securing the valve cover and remove it.
- Before adjusting the valves, immediately check how the chain is tensioned. If the tension is not normal, you will have to do the work again.
- Remove the distributor cover.
- We install the piston in the 4th cylinder at top dead center (TDC). TDCs are set using marks on the internal combustion engine crankshaft pulley and the camshaft drive cover, and marks are also applied to the camshaft gears and camshaft cover. The mark is set with a special key for the internal combustion engine crankshaft pulley bolt. If you don’t have a key, you can set the 4th piston to TDC by rotating one of the rear wheels. Raise one side with a jack and place the gear shift lever in 4th gear to make it easier to turn and turn the wheel slowly. When setting marks without a key, you will need an assistant to look at the marks.
- When the marks on the camshaft and the camshaft cover are aligned, check that the marks on the crankshaft are also aligned. You can also check whether the marks on the distributor slider match. The contact terminal should be directed to the high voltage wire terminal of the fourth cylinder. We have already discussed how to determine whether ignition is early or late in another article.
- After the marks match, we proceed to adjusting the valve clearances.
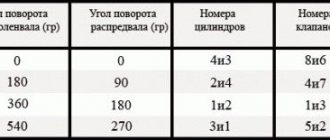
The correct procedure for adjusting the valve mechanism of the VAZ “Classic” 2101-2107. Crank angle Adjustable valves 8 and 6 180 4 and 7 360 1 and 3 540 5 and 2
From the table we see that if the 4th piston is set to top dead center, then we measure and adjust the 6th and 8th valves.
- We find the 8th valve. The countdown comes from the side of the bumper, the eighth will be the first from the interior.
- We insert a dipstick between the rocker and the camshaft cam. Normal clearance is the passage of the feeler gauge with little noticeable resistance. If a special plate probe with a thickness of 0.15 passes easily or with great effort, then it needs to be adjusted.
- On the side of the rocker there is a nut screwed onto a bolt with a 13 mm head. This bolt sets the gap, and the nut protects against unscrewing. To increase or decrease the gap, loosen the wrench nut by 17 while holding the bolt. When the bolt is loosened, we rotate it and change the gap. When the desired gap is set, we proceed to tightening. After tightening, you need to check again, perhaps the bolt has turned a little and changed the gap.
- Next, we do the same with the 6th valve.
- When a pair of valves 8 and 6 were adjusted. We proceed, according to the table, to setting the gaps of the 4th and 7th valves. But, before you start adjusting valves 4 and 7, you need to rotate the crankshaft 180 degrees. After turning the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine 180 degrees, the piston of the 3rd cylinder will be set to TDC. The angle of rotation when setting the third piston to the top dead position is inconvenient to set. For convenience, we use a marker or felt-tip pen. If the internal combustion engine crankshaft rotates 180 degrees, the distributor slider will rotate 90 degrees. This means that you can use a distributor and a slider to set the 3rd piston to TDC, making marks on the body with a marker: we mark where the contact is now, and mark where it should be strictly after 90 degrees.
- After adjusting the valves of the 3rd cylinder of classic VAZ cars, use a distributor to set the piston of the 1st cylinder by turning the crankshaft another 180 degrees, adjust valves 1 and 3 in the same way. Then, we also set the piston of the 2nd cylinder to TDC and adjust the last valves 5 and 2.
Manual adjustment of internal combustion engine valves
In the process, special adjustment screws of the rocker arms are adjusted. On some vehicle models, adjustment can be made using the head of a special adjusting bolt. You must use a specific key. It is very important to do everything correctly. Let's look at the setup process using the VAZ 2107 as an example.
Before making adjustments, it is necessary to remove the spark plugs from the cylinders (this requires a special key), then remove the air filter, cylinder head cover and timing belt protection (the number of elements whose removal is required depends on the specific car model). The entire gas distribution mechanism opens before us. In order to perform valve adjustment as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to evaluate the tension of the timing chain. If it is loose, the chain should be tightened.
The procedure begins by setting the first engine piston to the initial compression stroke position (TDC). To do this, you need to find a long mark on its body and a mark on the crankshaft pulley, and combine them (the mark on the timing gear should coincide with the mark on the timing case). To adjust, you will need a set of feeler gauges and wrenches “13” and “17”. Directly, the process itself:
- In the installed position of the power unit, the thermal clearances of valves 6 and 8 are adjusted.
- We check the gap using a feeler gauge, which we place between the valve rocker and the cam. Ideally, it should enter with little effort, in which case the valve does not need adjustment. If the probe slips or does not enter, the valve needs adjustment.
- Take the key set to “17” and loosen the locknut.
- Using the key set to “13” we adjust the valve mechanism.
- As soon as the gap is adjusted, it is necessary, using a wrench set to “13”, to hold the bolt for adjustment, and with a wrench set to “17”, tighten the lock nut.
- After tightening the locknut, check the gap with a feeler gauge and adjust it if necessary.
- After the second valve is adjusted, it is necessary to turn the crankshaft clockwise 180 0. With this position, the clearances on valves 4 and 7 are adjusted.
- The next time the crankshaft is rotated 360 0 from the starting position, valves 1 and 3 are adjusted, and when turned 570 0, valves 2 and 5 are adjusted.
- All work is carried out by analogy with the adjustment of 6 and 8 valves.
Starting the power unit after the procedure will provide an opportunity to evaluate how correctly it was carried out. In this case, the quality of valve adjustment must be assessed under different engine operating modes.