A car generator is generally considered one of the most inconspicuous devices in operation, but its importance cannot be overestimated. If only because without it, the battery would seem practically useless: its charge would be enough for several days of operation, after which it would have to be recharged outside the car. And this, for obvious reasons, is an inaccessible function for most citizens. But if you take any modern car, it turns out that without a generator its performance will also be paralyzed, because the brains of the car, the on-board computer, work precisely from the generator. What can we say about the mass of other devices that require connection to the on-board network. So information about what components the generator consists of and what the principles of its operation are will be useful for most car enthusiasts.
Operating principles and design of a car generator.
How to check the operation of the generator
The battery in a car is an important element of the system, which is responsible for providing the car’s on-board network with electricity. The generator is used to charge the battery while it is active. Unstable operation of a device generating electricity causes a voltage drop in the network and failure to restore the capacity of the power source.
Normal generator performance means timely and complete replenishment of the battery charge level, which decreases under load. Checking the battery charge level from the generator is simple and can be done by the car owner himself.
Diagnostics of an automotive energy-generating device includes a visual inspection of the unit, its elements and related parts, as well as voltage and current measurements. At least twice a year, you should check the tension of the drive belt, excessive weakening of which leads to a decrease in the performance of the generator, and sometimes can lead to breakdown of the device. Once a year, you can check equipment elements - fasteners, diode bridge, voltage regulator and others. Timely maintenance of the battery will also guarantee the absence of problems - cleaning the terminals, adding distilled water.
Diagnostics of indicators such as voltage, current, resistance are also necessary twice a year. To carry it out, you will need special devices - a voltmeter, multimeter or load fork.
What is a generator
The answer to the question of what a generator is is quite simple. A simple device, most often located under the hood, serves as an alternating current generator and converter of mechanical energy into electrical energy. With its help, the battery is charged and all electrical systems are powered after starting the internal combustion engine.
It is worth noting that the location was chosen specifically. Installation always takes place in front of the power unit. Modern machine assemblies drive the generator in the form of a belt drive and at the same time act as a starter.
It is very important to monitor the general condition of all technical elements and promptly resolve any problems that arise. At the initial stage, repairing a car’s starter and generator costs several times less than when there is nothing left of them.
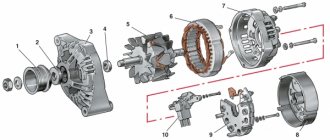
Generator device
The pulley transmits energy from the motor to the shaft using a belt.
Covers on the housing are needed to accommodate the rotor supports, install the unit on the motor and secure the stator. The back cover is needed for the brush assembly and outputs for powering electrical equipment. The stator produces power through a three-phase winding. The rotor is a steel shaft with two bushings. The terminals of this winding are connected to copper rings. The regulator stabilizes the voltage under various factors:
- electrical load surges;
- rotor speed delta;
- temperature changes in nature.
The brush assembly is a plastic element with brushes attached to it that interact with the rotor rings. The electric generator also includes six diodes (three in “-” and three in “+” heat sinks).
The device of a car generator
An obligatory component of any autogenerator is a stator, which is mounted between the front/rear covers. The front cover goes to the drive part, the rear cover is located on the side where the slip rings are installed. Both covers, as a rule, are made of lightweight aluminum alloys and are equipped with ventilation holes through which the fan circulates air inside the generator, cooling it. The brush and rectifier units are mounted on the back cover, which are connected to the voltage regulator. The typical design of the device is a stator located between the covers, held in place by 3-4 long screws.
The stator is a fixed winding, inside of which there is a rotating rotor. Its design is more complex, it consists of a number of windings, slip rings, and a drive shaft. Rings made of copper or brass are connected on one side to the excitation winding, and on the other to the brushes, which are supplied with voltage from the battery when the power unit is started. Some generator models are characterized by a brushless design, which increases their service life (and reliability), but this is achieved by increasing the weight of the device and the noise level during operation of an automobile electric generator system. The consequence of rotor rotation is a change in the magnitude and direction of the magnetic flux in the stator, which ultimately leads to the generation of an alternating voltage current. But since the vast majority of on-board consumers of a modern vehicle are designed to operate with constant voltage, the vehicle’s electric generator also consists of a rectifier, whose task is to convert voltage from alternating to direct.
Voltage regulators are usually built into the electric generator, structurally connected to the brush assembly. Their task is to influence the excitation current in order to change it by manipulating the time the windings are turned on to the mains. Some models of voltage regulators are able to change the voltage rating, taking into account the current air temperature in the engine compartment, which allows for the most optimal battery charging characteristics. Car generators are designed and manufactured either in a compact design (with a pair of internal fans) or in a classic design (with a fan located at the pulley). Let's consider the design features of individual components of an electric generator.
Stator
The operating life of the generator largely depends on the design of this fixed element. The stator is manufactured using the following technology:
- stamped plates made of special transformer metal about one millimeter thick are used as the basis for installing the winding;
- a certain number of such plates (usually 36) are assembled into bags by riveting or welding, which are insulated around the entire perimeter, covered with a polymer film (a more modern version) or epoxy;
- The starter windings are placed in the bags, secured with wedges.
It is the starter that is the place where alternating electricity is generated, which, after processing at other generator components, is supplied to the on-board network or to the battery.
Rotor
It consists of a shaft made of alloy steel or other materials with similar characteristics, and an excitation winding (coil), also coated with a completely dielectric varnish. Pole magnetic halves are mounted on the coils, the characteristic feature of which is:
- beak-shaped appearance resembling a crown;
- the presence of six petals;
- production by casting or stamping.
The rotor shaft is mounted on rolling bearings (in this case the shaft is hardened), at one end there is a groove for a key through which the drive pulley is attached. Instead of a key, a nut can be used, which has a head designed for a hex key, which avoids turning the shaft if it is necessary to dismantle the generator or remove the pulley. As the rotor rotates, it generates electricity from the stator, so it is also one of the main elements of the device.
Current collection unit
The brush type autogenerator is equipped with a current collecting unit, the design of which provides for brushes to slide along the commutator rings, through which current flows to the stator excitation winding. Classic brushes are made of copper and graphite. They have been replaced by electrographite components, which are characterized by less wear, but when using them, the effect of a voltage drop on the collector half-rings is observed. The latter are made of brass/stainless steel in order to reduce the degree of electrochemical oxidation. The current collection unit operates in the mode of increased friction of its parts, so rings and brushes are classified as consumables - they wear out an order of magnitude faster than other units. Therefore, the design of the autogenerator provides for easy access to the brushes to allow for their periodic replacement.
Regulator relay
The alternating current generated by the stator, after conversion to direct current, is supplied to the regulator relay. Its inclusion in the generator is due to the following reason: the crankshaft of the power unit can rotate at different speeds, depending on the needs of the car owner at a particular time. However, structurally, the self-oscillator is not capable of generating the same voltage in accordance with the timing diagram. The regulator relay is intended for thermal compensation, that is, monitoring the current temperature in the engine compartment in order to artificially reduce/increase the charging voltage, which has a positive effect on the battery life. But the default temperature compensation rating is 0.1 V/degree. Some models of electric generators, which do not include a relay regulator, are equipped with manual summer/winter switches. They are located in the cabin (rarely) or in the engine compartment.
Note that in passenger cars, voltage regulators are connected to the stator with the negative wire of the on-board electrical network, however, there are also antagonistic options, and they are not interchangeable. So when replacing generators, this point must be monitored.
Rectifier (diode) bridge
It is this component of the self-oscillator that is responsible for smoothing the variable voltage amplitude into a constant curve. Structurally, such a rectifier can be manufactured in two versions:
- the diode bridge is a separate electronic unit, soldered or pressed into plate heat sinks shaped like a horseshoe;
- the rectifier is soldered onto the board, and the heat sinks, characterized by the presence of fairly impressive fins, are soldered directly to the diodes.
In some cases, the main rectifier is supplemented with another, secondary diode bridge, to improve the output voltage characteristics. It is a compact electronic unit with miniature diodes of round or elongated cylindrical shape. The additional bridge is connected using bus technology. The rectifier is considered the most common cause of generator failure, since any metal object accidentally falling into the space between the heat sinks of the bridge can cause a short circuit.
Generator functions
When starting the engine, starting current is supplied to the starter from the battery. But the battery itself does not produce energy, but only accumulates it and then releases it. If you use only the battery to power all consumers, it will quickly discharge. A car generator produces electricity, charges the battery and powers the vehicle's on-board network while the engine is running (when it reaches a certain crankshaft speed).
Car generator
The generator begins to produce electric current starting from the idle speed, however, it reaches optimal operating mode when the engine reaches 1600-1800 rpm or more.
Basic parameters of the generator
The main nominal parameters are determined based on the technical requirements for the design of a specific vehicle model:
- Voltage. In accordance with GOST 52230-2004, it is selected from the range from 7.14 to 28 V.
- Recoil current.
- Frequency of excitation and self-excitation.
The current-speed characteristic determines the dependence of the rated current of the generator on its rotation frequency. The voltage in the on-board network of passenger cars and commercial vehicles, as well as buses, is 12 V, for particularly powerful and special vehicles - 24 V. The maximum output current is determined at a rotor speed of 6,000 min-1. Another important characteristic of this unit is efficiency. For modern models this figure is at the level of 50-60%.
The car engine does not work
Has a good battery
(read about his choice here) there should be at least 12.4 on the terminals. The normal voltage is 12.5 - 13. A lower value indicates the highest degree of discharge. Another reason is a decrease in capacity due to the onset of sulfation of the plates, for example. And this is already a “ringing bell” for the car owner. Moreover, at voltage = 12 and below, starting a car is quite problematic, especially when cold weather sets in.
A common and affordable method for checking the battery
and your car’s generator without spending money at a service station.
What should you know about the on-board voltage of your iron horse?
Greetings car enthusiasts. Today I’ll tell you how to increase the voltage on a car’s generator in a simple way, if for some reason it does not correspond to the norm of 14.4 volts. So, to solve this problem, there is a very simple way to increase the voltage of the generator with a diode, which we will simply add to the main circuit of the generator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KhKVUQ_c-Wg
2D219 diodes are suitable for this purpose; 2D 213 (diodes naturally have a letter index).
It is the letter index of the diode that will be responsible for the amount of the required voltage drop across this diode.
The diodes used must have a breakdown voltage of about 20 volts and a current of at least 5 amperes, the voltage drop across the diode should be in the range from 0.6 volts to 1.2 volts (here you need to look at how much you need to raise the voltage).
Probably for those who do not understand electricity, nothing is clear at all. I'll try to explain it more simply.
Let's assume that your generator produces 13.3 V - 13.5 V at partial load, and this is unacceptably low for recharging the battery and, in turn, the battery in the near future simply will not be able to provide the necessary energy to start the car.
But if you use a diode to increase the generator voltage by about 1 V-1.1 V, then everything will fall into place.
The voltage at the generator output will increase by reducing the voltage supplied to the power output of the voltage regulator, so the regulator does not seem to receive additional voltage in order to operate within the specified limits. The voltage is extinguished at the diode and thereby the regulator increases the excitation voltage (on the brushes), and the generator, in turn, produces a voltage higher by exactly the amount by which we extinguished the diode. Something like that.
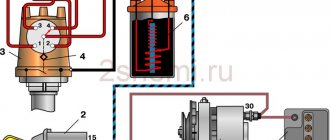
The figure shows a standard circuit for connecting a generator to a car's power system; there is no diode to increase the generator voltage.
The power diodes are indicated in green, the diodes supplying the voltage regulator are indicated in blue, the yellow square is the voltage regulator itself, the light in the instrument panel is indicated in red (battery charging), the purple rectangle is the load (it is a variable value).
This circuit already contains a diode, which is installed in the gap between the power output of the voltage regulator and the diodes of the generator feeding it.
Now let's look at how to increase the generator voltage.
The current from the battery runs through the light bulb (which lights up) and then through our diode to increase the voltage of the generator, the voltage regulator is powered, which opens its internal transistor to its full extent, and the current begins to pass through the brushes, and since the brushes are installed on the generator armature, then The rotor winding is accordingly also energized. And in order for the generator to work, you just need to start turning it using the engine.
As you can see from this diagram, the light bulb will go out due to the fact that the same positive voltage will come to it from both sides.
But the diode to increase the voltage of the generator will put on itself a certain amount of volts (depending on which diode you choose), and the regulator will accordingly receive less of this voltage.
This means that the same internal transistor of the voltage regulator will be open a little more (i.e. exactly those volts that we did not give to the voltage regulator).
This looks like cheating the voltage regulator, the on-board network receives the required voltage of 14.4 volts, and the regulator thinks that it is less in the on-board network and therefore adds it. Well, in general terms, I think we’ve figured out how to increase the voltage on a car’s generator using a diode.
Read more: What oil to use for a turbodiesel engine: tips
The figure shows where and how the diode needs to be tricked. What composition you make depends only on you, whether you want it inside the generator or outside it.
As a recommendation, I can advise placing the diode outside and not covering it with anything, it will cool better (it gets very hot).
And the most important thing is that the picture shows the location of the break; in fact, it is not necessary to cut, there is a terminal there; you just need to take it out and make another one (in general, you’ll figure it out) then insert the diode between the terminals.
I also advise you to look at the interesting article “How an electronic voltage regulator of a car works”, from which you will learn a lot of interesting things about the voltage regulator of a car generator, and in the article “How to check the operation of a generator in a car yourself” you will read about how to properly check the generator without removing it from the car.
That’s all, I consider the topic of how to increase the voltage on a car’s generator to be considered.
Sincerely, blog author: Doctor Shmi
How to increase generator voltage
Many motorists have encountered the concept of low voltage in the network. The culprit of the situation was the generator, which produced an insufficient amount of current. Is there any way to increase the voltage produced by the unit? How to increase the power of the generator without damaging the circuit and the overall system.
Installing a diode with a toggle switch is the easiest way to increase the voltage. There is no need to bother, look for a lot of information in books, etc. Everything is as accessible as possible, no special difficulties.
The purpose of this method of increasing the voltage in the vehicle's on-board network is to deceive the regulator, which is located inside the generator. As you know, on old domestic car models (kopek, VAZ 2105, etc.) the voltage drop sometimes reaches critical values - sometimes it drops to 12.5 volts. The battery, of course, will not be charged at this voltage.
A voltage regulator is the same brushes, a tablet, a chocolate bar - there are many names, but it is the same element that is responsible for regulating the voltage in the generator. On our domestic cars, mostly older ones, the tablets are of poor quality. They do not regulate voltage well, and as mentioned above, sometimes the current value drops below the baseboard.
So, what you need to do is insert an additional diode into the circuit. By this we will achieve the following: by how much the voltage on the diode is reduced, the regulator will increase the total current in the circuit.
Diode installation diagram
There are several ways to integrate a diode. One of the best - remotely. Take a simple toggle switch and install it somewhere convenient.
Simple toggle switch
Obviously, the toggle switch should be routed through the wire to the generator. You can insert the diode into the slot in the generator bridge, in the place where the wiring runs from the excitation winding to the regulator. That is, we simply insert the diode into the wiring between the bridge and the regulator.
We connect a separate toggle switch to the diode through two wires, as shown in the photo below.
Diode connection
When the voltage in the on-board network is sufficient, for example, in the summer, the diode is simply installed and not used. If the current is low, just turn on the toggle switch by activating the diode. In this way, we deceive the regulator.
The following diodes can be used.
Their analogues, for example, imported ones, are also suitable. They are much more compact, made of plastic (body). Domestic - metal.
Using a diode, you can provide a voltage drop of 0.9 or 1.2 volts. Thus, if the drawdown reaches 13-13.6, then approximately 1 volt will be added by the regulator. This is normal for winter loads. The standard drawdown of the regulator should be up to 13.8 volts, not lower. At this value, the battery can still charge, but if the voltage is lower, it won’t.
Read more: Which oil is better to fill in the gearbox: manual transmission and automatic transmission || Which oil is better to pour into the gearbox of a manual transmission and an automatic transmission?
A drop in voltage below standard values for modern calcium batteries is especially critical. The fact is that low drawdown kills such batteries; they deteriorate. Naturally, an increased voltage indicator is not recommended. It should be no more than 14.6 volts (more about this in the table at the end of the article).
Where to put the diode
Installing a diode in a circuit is a universal solution that gives good results. However, there are some important points to keep in mind:
- Observe polarity when connecting an additional diode. If you break this rule, the battery will not be charged.
- The diode must be selected so as to deliver a current of at least 5 A.
- It is advisable to install the diode outside the generator, as it will get very hot.
- Silicon diodes are considered more efficient. They are capable of taking voltage within 0.8-1.2. But germanium diodes are no more than 0.7 volts.
What is a car generator? Principle of operation, how does it work and what is it for?
Today we will find out what is called a car generator, what is the operating principle of the unit, what main components does the device consist of and how does this part of the power supply system work?
WHAT IS A CAR ALTERNATOR? PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION, HOW IS IT DESIGNED AND WHAT IS IT NEEDED FOR?
Good afternoon, today we will learn what is called a car generator
, what is
the principle of operation
of the unit, what
are
components of the device and how is
this part
the vehicle’s
power supply system arranged In addition, we will tell you about the features
, main
technical characteristics
of a car
generator
and
how the devices differ
from each other.
In conclusion, we will talk about how to properly operate
a car
generator
, why you need
a voltage regulator
in
power supply
system of a particular car, and what is called
the cooling system
of the device.
So, what is a car generator? The generator or vehicle power supply device is the main source or supplier of electricity for any modern vehicle. To understand the principle of operation of the generator, you need to know what main components this unit consists of. For reference, we note that when starting the power plant, the main consumer of current is the starter; the current at this moment can reach hundreds of amperes, which often causes a significant drop in battery charge. When the engine is started, the generator immediately becomes the main source of power supply to the vehicle equipment.
SIGNS OF GENERATOR BELT WEAR AND ITS REPLACEMENT
REPLACING THE TIMING BELT. SERVICE INTERVALS
Thus, the generator is a source of constant recharging of the battery while the engine is running. If the generator stops working, the battery will quickly discharge and die. The generator's job is to supply the required current to charge the battery and therefore ensure optimal operation of the vehicle's electrical equipment. Note that when the battery is recharged, the voltage difference between the battery and the generator becomes insignificant, which in turn leads to a decrease in the charging current in the circuit.
To understand how a generator functions, it is necessary to understand its design and the elements that ensure its optimal and uninterrupted operation. The first thing you need to start with is the drive and mounting of the generator. As a rule, the generator is driven by a part such as a crankshaft pulley. It is believed that the larger the diameter of the pulley on the crankshaft, the smaller the diameter of the pulley of the generator itself, therefore this leads to higher operating speeds of the power supply device, that is, the generator. This nuance suggests that the generator in this case is capable of delivering more current to its consumers, that is, to the electrical equipment of the car.
On most modern vehicles, the drive in the generator system is performed by a consumable element called a serpentine belt, popularly known as a rivet belt. Thanks to the extreme flexibility of this consumable element, almost any size pulley can be easily installed on the generator. This, in turn, makes it possible to obtain high gear ratios at the output, which makes it possible to use high-speed devices to supply the car with current.
An important point in the optimal operation of the generator belt is its tension, which is fixed between the tension rollers when the unit is stationary, that is, when the machine engine is not running.
DEVICE AND STRUCTURE OF A CAR GENERATOR
So, what components does one of the most important elements of a car’s electrical supply system – the generator – include? A typical generator includes a stator with a winding, which is sandwiched between two special covers. The first cover is called the front cover, it comes from the side of the drive itself and the back cover, which is located on the side of the slip rings. In most cases, generators are mounted in the area of the front part of the vehicle's power plant using special bolts located on brackets. In addition to the above-described elements, there are also mounting feet and a tensioning eyelet for the device. These parts are located on the covers. The image below clearly shows a typical circuit and the main components of a car generator.
CASE COVERS, VENTILATION NOZZLES AND GENERATOR BRUSH ASSEMBLY
As a rule, generator housing covers are made of light aluminum alloys and have special ventilation nozzles through which air penetrates and creates ventilation of the device. Typical generators are equipped with ventilation nozzles only in the end part, and compact type devices, in addition to end ventilation windows, are also equipped with holes on the cylindrical part above the frontal sides of the stator winding.
The next element of the generator that is worth considering is the brush assembly. It is located on the cover, on the slip ring side. The brush assembly is combined with a voltage regulator and a special rectifier element.
GENERATOR STATOR
The aluminum generator covers are tightened together with 3 or 4 screws so that the stator is located between the 2 covers. As for the seating surfaces, they seem to grip the stator along the outer surface. As for the stator, it consists of a core, a winding, a slot wedge, a special slot and a lead for connection to the rectifier.
The generator stator itself is made of steel sheets with a thickness of 0.8 to 1 millimeter, but sometimes it is made in the form of winding on a plate, which resembles coiled wire into a ball. When a stator package is produced by winding, the yoke of the element above the grooves often has certain protrusions. Such protrusions indicate the position of the layers relative to each other. In addition, these protrusions improve stator cooling due to the developed outer surface.
Due to the fact that every year automakers are increasingly trying to save metal in the manufacture of components for vehicles, almost 90 percent of modern stators are made in the form of wound packages, which are assembled from individual horseshoe-shaped segments. Horseshoe-shaped segments, which are manufactured in the form of separate sheets of metal, are fastened together into a single monolithic structure by welding or rivets. Most machine generators have 36 slots in which the stator winding is located. The grooves themselves are insulated with special film insulation, sometimes by spraying with an epoxy compound.
GENERATOR ROTOR
The next important element of the generator is the rotor, which has a pole system that includes pole halves, an excitation winding, slip rings and a shaft. The pole halves have 6 beak-like protrusions on each half. Pole-type halves are made by stamping and often have projections. If there are no protrusions, when pressed onto the shaft, a special bushing with an excitation winding is installed between the pole halves, which is wound on the main frame. Winding is done only after installing the sleeve inside the frame.
Rotor parts such as shafts are often made of machine-cut steel and soft alloys. As for the bearing roller, which operates at the end of the shaft from the side of the slip rings, it is made of alloy steel, plus the tip, known as the journal, is also hardened. In addition, at the end of the shaft, which is equipped with a thread, a special groove is cut for the key so that the pulley can be secured.
However, on imported cars, the key is usually missing. In this case, the end part of the shaft has a certain recess or protrusion for a key, often a hexagon. These design features help keep the shaft from turning when the pulley nut is tightened. In addition, this ensures ease of work when disassembling the generator, in the event that it is necessary to remove the pulley and fan.
GENERATOR BRUSH UNIT
Any modern generator has a brush assembly, the design of which contains special brushes, that is, sliding contacts. As a rule, 2 main types of components are used in car generators: copper-graphite
and
electrographite
. Electrographite brushes have an increased ability to drop voltage in a circuit with a ring, compared to copper-graphite brushes. This nuance negatively affects the output parameters of the generator, but they are able to provide less wear on the slip rings, since the brushes are pressed against the slip rings with spring force.
GENERATOR RECTIFIER UNITS
Also, an important role in the operation of the generator is played by rectifier units, which again come in two types
: in the form
of heat sink plates
into which power rectifier diodes are pressed using the pressing method and in the form of, on the contrary, soldered and then sealed silicon diodes. For reference, we note that in designs with increased ribbing, diodes in most cases are of the tablet type. Elements such as diodes are specially soldered to heat sinks. The diodes of the additional rectifier often have a cylindrical plastic housing. Diodes are included in the electrical circuit using busbars.
GENERATOR BEARING ASSEMBLY
They are radial ball bearings with a one-time filling of special grease, which is designed for the entire service life of the part. In addition, the bearings are equipped with seals with 1 or 2 rings, which are built into the unit. As for roller bearings, they are used on the slip ring side. The fit of ball bearings is carried out on the shaft from the side of the slip rings and is very tight, and on the drive side, on the contrary, it is sliding. The insert into the cover seat, the bearing fit on the ring side is sliding, and on the drive side it is tight, as if pressed.
GENERATOR COOLING SYSTEM
The generator cooling process occurs with the help of 1 or 2 fans, which are mounted on the generator shaft. In classic forms of the generator, air is sucked by a centrifugal fan into the cover from the side of the slip rings, and in devices that have a brush assembly, the voltage regulator with a rectifier protected by a frame is located outside the internal cavity, the air enters through the protection nozzles. Thanks to the presence of nozzles, the air is clearly directed to the hottest places, usually to the voltage regulator and rectifier.
The image above shows 3 types of generators: classic design
(
A
),
for increased temperature in the engine compartment
(B) and
standard design
(
B
), and the arrows indicate the direction of the cooling air flows.
GENERATOR VOLTAGE REGULATOR
Why do we need a regulator that controls the voltage in the generator? Everything is very simple. The fact is that the regulator ensures that the generator voltage is maintained within certain ranges to ensure optimal operation of the device and electrical equipment that is connected to the vehicle’s electrical circuit. Often, generators are equipped with semiconductor electronic voltage regulators that are built into the device. As for the principle of their operation, it is the same for everyone, however, their execution patterns and design features may vary.
For reference, we note that voltage regulators often have certain thermal compensation properties, that is, the ability to change the voltage that is supplied to the battery.
This process is carried out depending on the temperature that develops in the engine compartment in order to optimally charge the battery. For example, the lower the given temperature in the engine compartment, the greater the voltage will be supplied to the battery and vice versa. The temperature compensation indicator can reach a value of 0.01 Volt
per
1 degree
Celsius.
FEATURES AND POSSIBLE PROBLEMS IN THE OPERATION OF THE GENERATOR
The most dangerous problem in the operation of a generator is its short circuit, or rather the heat sink plates, which are connected to ground and brought to a positive charge. In the case when such a situation occurs randomly between the plates in the device, a short circuit immediately occurs throughout the entire battery circuit. The most unpleasant consequence of this problem may be a fire, and then a fire. To prevent this, many automakers today partially or completely cover some parts of the alternator rectifier with an insulating layer. In addition, manufacturers combine heat sinks with the main circuit boards into a monolithic design of the rectifier unit using insulating material that is reinforced with special connecting busbars.
Video: “What is a car generator? The principle of operation, how it works and what is it for?”
In conclusion, we note that when switching on, as well as frequent use of energy-intensive current consumers, for example, a rear or windshield heater, headlights and the presence of low engine speeds during this period of time, the total current consumption in this case becomes greater than what the generator can provide . As a rule, in this case, almost the entire load falls on the battery and it will quickly begin to discharge.
THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR ATTENTION
.
LEAVE YOUR COMMENTS
AND
SHARE WITH FRIENDS
.
What is a generator for?
A UPS is required in the following situations:
- for a comfortable stay in summer cottages when there is no possibility of connecting to electrical networks;
- during construction work on a land plot - buying or renting a generator will be cheaper than buying the necessary battery tools;
Using an electric generator
- when repairing a car in a garage;
- during hiking and traveling, outdoor recreation, etc.
However, many owners of country and country houses purchase an electric generator even if there is a central power supply. This is a kind of “insurance” against unplanned power outages or emergency situations. After all, an unscheduled power outage can lead to dire consequences - freezing of the heating system, damage to the autonomous sewage system, etc.
Note: In the event of an accident in urban conditions, the period without power usually does not last long. The opposite situation can happen outside the city limits. Therefore, many owners of private houses prefer to have a “backup” power supply option in the form of an electric generator. You can also often find an electric generator in production.
What is a generator called?
A generator (from Latin “producer”) is an electromechanical device that converts kinetic energy into electric current. Generating electricity is the main task of an electric generator - an uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
What is an electric generator?
Note: A home generator set is a device that converts energy from combustion of fuel (diesel, gasoline or gas) into electricity.
What does a generator consist of?
In fact, any type of electric generator consists of 2 interconnected main parts:
- internal combustion engine can be:
- push-pull;
- four-stroke;
- alternator (the generator itself).
Electric generator device
Important to know: The operation of generator sets is accompanied by noise and emissions of exhaust gases. Therefore, their installation requires a separate room equipped with a special ventilation system.
What kind of charging should go to the battery from the generator?
It is traditionally believed that 13.5-14.5V should be supplied by the generator to the battery and this is absolutely enough to replenish the battery costs.
It is worth considering that using a battery with a higher power in a car than the manufacturer recommends also requires the installation of a more productive generating device.
It is necessary to take into account the load that the generator must withstand - it is calculated based on the maximum indicators of all electrical appliances and car systems.
Do not forget that the charging current from the energy-generating device will allow you to start the car in the cold season. In order to avoid problems with starting the car, we recommend purchasing generating equipment, the charge current of which will be approximately 10% of the capacity of the power source. That is, a battery of 100 A/h requires a generator that can produce 10A. Please note that for many cars, 100 amp equipment will operate at its maximum capacity, because the power consumption of the automotive system is in the region of 80 amps. Therefore, the choice of a source generating energy must take into account both the battery capacity and network consumption.
What are the features of gasoline generators
Such a generator is a source of electricity of relatively low power, so it is worth buying only if there is no need for uninterrupted operation of the network. Its limit is 12 hours of continuous operation. During an hour of operation, such a unit consumes approximately 1-2.5 liters of fuel.
The undoubted advantage of a gasoline electric generator is that it is not afraid of temperature changes and can operate in any weather. It is most often used in household farming; it is also suitable for a country house. Such installations are usually light in weight, so they can be taken on a hike.
There are also digital gasoline generators, they are often called inverter generators; they have special electronics installed that allow them to receive electricity from the engine and convert it into a voltage of 220 volts.
How long does it take to charge a battery from a generator?
When the engine is running, the generator, generating energy, replenishes its supply in the battery. The charging duration depends on several criteria:
- ambient temperature;
- remaining battery charge;
- the duration of its service life;
- the magnitude of the charging current of the generating source.
How long does it take to drive a car to charge the battery? To fully charge the battery, the car must be in continuous motion for at least three hours. The storage sources of those cars that regularly travel long distances will not need to be recharged from external network devices.
Car owners often have a question: does the battery recharge if the engine is running and the vehicle is not moving? When all vehicle systems are functioning correctly, battery energy is available to start the engine or to operate electrical appliances when the engine is off. Consequently, when the engine is running, regardless of whether the car is in motion or not, the drive begins to recharge, restoring the energy reserve. The only difference is that recharging at idle, as when driving at low speed with constant stops in the city cycle, occurs more slowly than in a car moving for a long time.
Consequently, the answer to the question “How to increase the charging of a generator” is simple: regularly operate the “iron horse”, traveling long distances.
What is a synchronous and asynchronous generator
Inverter generators differ from synchronous generators in that they produce a smoother current sinusoid, that is, the alternating current is of high quality, without surges and drops, which is most important for delicate equipment such as computers, LCD TVs, etc. Asynchronous type generators are insensitive to short circuits and have a high degree of protection from external influences. But with this design, the rotating magnetic field of the rotor cannot be adjusted, so the frequency and voltage at the generator output depend on the stability of the engine. So an asynchronous generator is suitable only for electrical appliances that do not have high starting currents and are resistant to voltage surges.
Synchronous generators are the most common type of gasoline generators; they are used to provide power to household appliances and emergency lighting for a period of no more than 8 hours.
How much current does a car's alternator produce?
Generators have a factory marking plate indicating the maximum current that the device can produce. To measure the actual current, use a multimeter and special clamps placed on the generator wiring. Clamps allow you to accurately determine the current strength in a conductor without destroying the insulating layer.
After installing the meter, the engine starts and is brought to high speeds, ensuring maximum output of the generator. Then you need to turn on the consumers and monitor the change in current in the wiring. These same consumers turn on simultaneously, and a change in the current parameters in the circuit is noted. The result cannot be less than the amount obtained when connecting the devices separately.
The current required for the operation of the self-excitation windings is measured on the wire going to these windings. The measurement is carried out at high crankshaft speeds. A current of 3-7 A is considered normal.
Lada Priora hatchback › Logbook › Combating voltage sags
So, to one degree or another, many Prior owners (and not only them) face the problems of voltage drops when hot and with voracious consumers turned on. This misfortune did not bypass me either. When cold, the voltage is 14.3 on the generator, 14.2 on the battery, 13.9-14 on the onboard, which is very good. All this at idle. But when driving through traffic jams, and with the air conditioning and heated mirrors on (during rain), the voltage on the side panel drops right down to 12.8-12.6. On the highway everything returns to normal, that is, the problem is exclusively when driving in traffic jams. The first thought that arose in my brain was to duplicate all possible wires, both positive and mass. But after thinking a little, I decided to first carry out some measurements, namely, to measure the voltage drop in various sections of the electrical wiring in various operating modes of the car. All measurements were carried out at idle, which is not entirely fair to the generator and wiring, but still. Only side lights are on. I measured the voltage drop between the generator pin and the battery positive terminal. The voltage drop is around zero, which is good. I turned on the high beams, heated mirrors, and the heater at 4 speed. The voltage drop in the indicated area is already 0.4V. It's a lot. Then, with the same load, I measured the voltage drop between the positive terminal of the battery and the red wire coming from it in the mounting block. The drop is zero. Then I measured the voltage drop along the “mass” wires. The voltage drop between the negative terminal of the battery and the metal bracket above the mounting block is zero. The voltage drop between the battery negative and engine ground in load mode does not exceed 0.1V. This is a little good. Where then does the voltage drop come from as the engine warms up and with consumers turned on? I measured the voltage at the generator - 12.8V. This is the main culprit for drawdowns. Either the voltage regulator is drizzling from overheating, or the generator. The generator is new at 100A. The “new model” voltage regulator is the vaunted Orbit. Thus, the only section of the electrical wiring with a relatively large voltage drop of 0.4V is the section from the generator pin to the positive terminal of the battery. Here it was decided to lay an additional wire. In fact, from the generator stud in one corrugation there are 2 wires with a cross section of either 4 or 6 mm^2 (I don’t remember now). The wires are pink and they each go to their own 60A fuse (both blue) in the main fuse box - a black box under the hood near the battery.
It was to this box that I laid a stranded wire with a cross section of 10mm^2. There are two standard wires, and I laid one, but much thicker than the standard ones. I decided to connect the laid wire to one of the standard pink wires. Here the question arises: how to connect? You can, of course, run the wire to the + terminal of the battery through an additional fuse, but I already have so much stuff on the battery terminals that it’s crazy. So I had to drag it to the black box.
I could not directly remove the connector with the pink wire from the plastic case. These connectors are very powerful. So I decided to just cut one of these wires.
Article rating:
Normal voltage of the prior generatorLink to main publication
Related publications
- Lada with a large trunk
Connection diagram
The circuit is divided into power and control circuits. The powerful output of the generator is connected directly to the positive terminal of the battery through a power connector made of a large cross-section wire secured with a nut on a stud.
The thin control wire is most often simply connected to the ignition circuit through a control light. There are also other schemes when the light bulb has its own control from a specially designed contact on the body.
Types of generators
Today there are several types of electric generators, which differ from each other depending on:
- type of fuel to be filled:
- gasoline - they are refueled mainly with AI-92 gasoline;
- diesel – consume diesel fuel;
- gas - requires natural gas to operate;
- the size of the voltage (which the generator produces);
- scope of application:
- household;
- production;
- weight and dimensions of the device;
- device type:
- autonomous;
- stationary;
How are generators different?
- number of phases:
- single-phase - usually used for household needs (lighting, powering household electrical appliances, etc.). On such generators the sockets are made in blue or black;
- three-phase - necessary to power power equipment. These generators have a red socket;
What to connect to the generator
- operating mode:
- basic – for constant (24/7) work;
- reserve – used as spare;
- Efficiency – profitability.
Gasoline generator on wheelset
Note: Thus, when choosing an electric generator for home use, it is important to pay attention to a number of criteria (Which generator to choose, TOP generators).
The principle of operation of a car generator
The operating principle of a car generator can be divided into several stages:
- First of all, the brush-collector unit is used. Energy passes from the battery to it, which reaches the contacts.
- The crankshaft spins the rotor. The design provides for the presence of a stator; it is this part that is responsible for generating electricity. When the rotor begins to operate at full power, the generator becomes the source of energy for the stator.
- The car's network is fed through a special bridge; it converts alternating current into direct current, which avoids overload in the network.
- During operation, the voltage indicator changes depending on the speed of the rotor through a special regulator.
Thus, the device of the auto generator simultaneously ensures the operation of the electrical network and increases the amount of battery charge. The machine panel has a warning light. If it lights up, then the generator has failed (the belt has broken or another breakdown has occurred). In this case, the car is supported solely by battery energy. Then the operation of the car is ensured by the charge remaining in the battery.
About causes and consequences
Modern closed-type lead-acid batteries are maintenance-free. The plastic case of the product is hermetically sealed and does not have plugs through which electrolyte was added in old-style batteries. A special relief valve is provided for the release of gases formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
If, due to various malfunctions, the battery has boiled out on the car, it will not be possible to replenish the acid supply, since there are no filler holes. The battery capacity decreases significantly, it stops charging and fails. An unpleasant point: the evaporation of acid does not always occur due to the fault of the power source itself. If you do not find the cause of the phenomenon and install a new battery to replace the non-working one, you risk throwing it in a landfill and wasting your money.
There are 3 reasons why electrolytic fluid boils away from a car battery:
- malfunction of the electronic unit that regulates the level of charging voltage from the generator;
- sulfation and closure of sections (cans) inside the product due to natural wear or increased loads;
- improper charging of the car battery from an external source (charger).
The amount of voltage supplied from the generator is limited to 15 volts by an electronic circuit - the regulator. When it fails, the battery experiences a so-called overcharge with a voltage of over 15 V. The acid boils, and a rapid release of hydrogen begins, escaping through the valve. As the electrolyte level decreases, the battery gradually becomes unusable.
Similar consequences occur when the cans are short-circuited and the battery is constantly charged with increased current from an external source. Signs of boiling are a barely audible hissing of the valve and the release of an unpleasant odor. For obvious reasons, these symptoms cannot be identified while driving, so the problem is often discovered at the last stage, when the lead plates of the battery have been destroyed. One day you come to the garage to pick up your car and realize that the power supply is unable to crank the starter.
Exploitation
The generator itself, installed on the VAZ-2114, is an unpretentious and reliable device. It can easily withstand the most extreme loads and will serve in the most severe conditions, but under one condition - the car owner must operate it correctly.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- Do not leave the generator running if the battery is removed;
- working with electric welding requires disconnecting both it and the battery;
- When connecting wires, you must observe polarity;
- The functionality of this unit is checked only in accordance with the instructions.
In the first case, if there is no battery, electricity will flow unevenly into the car's network, which usually leads to failure of certain devices installed on it.
Failure to comply with polarity often provokes a failure of the entire electrical system of the machine.
Why is there a voltage regulator in the generator?
When the speed of the crankshaft and, accordingly, the rotor changes, voltage surges may occur in the on-board network, which negatively affect the work of consumers. Surges are eliminated by limiting the excitation current transmitted through the brushes from the voltage regulator to the rotor. Control is carried out by changing the connection time of the armature winding depending on the load on the on-board network.
If the regulator malfunctions or the brush assembly and slip rings are damaged, the battery may be undercharged or overcharged. Long-term operation of a machine with such a defect will lead to battery failure.
A generator malfunction can be determined by the indicator on the instrument panel. When the battery charge light comes on after starting, it indicates that the voltage in the network is insufficient, while blinking indicates that it is too high.
Step-by-step procedure for checking the generator
- Turn on the ignition and make sure that all the dashboard lights are on.
- We start the car, and if the generator is operating normally, the battery warning light should go out.
- We wait until the car warms up to its standard operating temperature of 90 °C.
- When it warms up, it is necessary to load the network as much as possible. To do this, we turn on everything that is in the car, including heated mirrors, lights, music, etc.
- We take a pre-prepared multimeter and set it to the “voltage” check mode.
- Next, we call an assistant and ask him to keep the engine speed at idle (within 3500 - approx.).
- Using a multimeter, we connect its probes to the battery, and at the moment when all consumers are turned on, the readings should not fall below - 13-13.2 V.
Chief power engineer: Generator in a car: design, malfunctions, repairs
Since then, the tasks of the generator have not changed, but the loads have increased - if at first the battery charge was spent only on the operation of the starter and headlights, today the car has acquired a large set of voracious consumers in the form of all kinds of optional servos, heaters, electro-hydraulic devices in the steering, suspension and braking system. A modern equipped machine requires a lot of electricity, and the generator, as its main and only producer, must ensure “supply” fully and uninterruptedly.
Live
If you don’t go into engineering subtleties, the basic design of the generator looks like a schoolchild’s simple one. Modern cars use a three-phase alternating current generator, consisting of a stator enclosed in a housing - a stationary external winding - and a moving winding rotating inside it - a rotor. First, the generator itself must receive current from the battery, which is supplied to the rotor field winding, creating the magnetic field necessary for operation. To supply current to the rotor, a commutator with brushes acting as a sliding contact is used. Since the battery and the vehicle's electrical system as a whole only need direct current, the generator is equipped with a rectifier, usually built into the housing. To protect against overloads, a transistor relay-regulator is used that maintains a voltage in the range of 12.5 - 13.5 V, which is mounted, in most cases, externally on the generator housing.
By design, the most common today is the classic mounted version of the generator, when it is installed as a separate device outside the engine and the rotor is driven from the crankshaft by a belt drive. This option has proven to be the most successful so far, since it provides the greatest ease of removing and installing the generator for replacement and repair. Although from time to time various alternative designs are proposed, for example, those where the generator is integrated into the engine. Here, the motor flywheel, equipped with an excitation winding, plays the role of a rotor, around which an external stator winding is installed in the crankcase. In this case, two devices are combined in one - the generator also works as a starter.
By the way, this idea of a “starter generator”, which is gaining popularity today, is quite old and represents the resurrection of old designs in a new way. For the first time, the starter and generator on a car appeared in the form of just such a single device, developed by engineer Charles Kettering, who lived at the beginning of the twentieth century, which was installed on Cadillac in 1912 and a year later on Lancia. However, subsequently both devices were separated - due to the difference in tasks requiring different designs, and ease of maintenance and repair. Therefore, the “integrated” option so far looks like an experiment - the gain in compactness is not too significant, and repairs in case of failure are much more complex and time-consuming. However, about the repairs - a little later. First, how to find out that you need it.
Until the light bulb
The source of information about the state of the power system in modern cars is the battery charge indicator lamp, which is located in the form of a stylized “icon” on the instrument panel. In normal mode, this lamp should light up among others when the ignition is turned on and go out after the engine starts. Here, the flashing of the light indicates that there is contact and the required voltage in the circuit, and the fact that it goes out after starting indicates that the generator is working and is delivering current. If the lamp behaves differently, it means there is a malfunction.
If the lamp does not light up, the cause may be, first of all, a discharged and dead battery. In addition, the problem may lie in a break in the electrical circuit - wiring, ground contact (body), failure of a fuse or (rarely) the lamp itself. This also occurs when there is a malfunction in the generator itself - mainly due to loose contact of the commutator brushes due to their wear or due to defects in the relay regulator.
The same problems with brushes, relays and electrical circuits can occur when the lamp does not go out or blinks faintly when starting the engine. In this case, the cause is often a weakening of the tension or a break in the drive belt, as well as a malfunction of the rectifier unit. This can also mean the biggest problem - a short circuit or break (burnout) in the windings, which usually occurs due to the fault of a faulty relay regulator.
On cars with high and even average mileage, mechanical problems with the generator often begin to arise. And first of all, wear occurs on the bearings in which the rotor rotates. This is determined by the characteristic noise - it can be heard when standing next to the car. In this case, the control lamp may also begin to flash, since when the bearings wear out, the contact of the brushes, as a rule, worsens.
Theoretically, the resource of the generator should be very long - the device is simple, and there is almost nothing to break in it. However, in practice, a significant part of the resource, without any quotation marks, is eaten up by corrosion - the main enemy of all electrical appliances in a car. The Russian climate, as we know, is completely conducive to this: precipitation, changes in temperature and humidity, road salt - all this leads to a car service much earlier than the designers intended and the car owner himself would like.
As for how urgently you need to rush to a car repair station, there is no single formula. Sometimes a flashing lamp means minor “glitches” in the wiring, with which many people drive for a long time - and nothing happens. But, for example, if the lamp blinks due to the regulator relay, then it is possible that there is a burnout or short circuit in the windings ahead, and then, as a rule, the entire generator needs to be replaced. (Although in most cases this malfunction of the relay is detected earlier - from the resulting overcharge it begins to boil away and very noticeably loses the battery capacity.) It is impossible to determine why the “lamp is not burning correctly.” In old cars there were voltmeters, which helped clarify the issue, but now they are not there, since they take up space on the panel, and for the civilized West, a warning light is enough: “something is wrong, it needs to be serviced.” Perhaps the only thing is that You can try to do it yourself before visiting the service station - this is to spray a special aerosol on the electrical wiring, such as WD-40 or its equivalent, which can help with minor “glitches” in the form of moisture on the wiring and contacts. If this does not help, then you will have to go to a repair station, otherwise sooner or later the obvious will happen - the battery will die dead. This occurs especially quickly in city driving with frequent stops and starts. You can, of course, remove the battery from the car every now and then and carry it home to charge it from the mains charger, as some do, but for the modern car owner this is not an option. The equipment must work autonomously.
To the fitters
Of course, now few people will repair the generator themselves. After all, first of all, you need to know where exactly the fault is, and for this you need to check all electrical circuits, which is impossible to do without professional equipment. The only thing you can do on your own (if you don’t have an aversion to soured nuts and engine compartment dirt) is to tighten or replace the alternator belt. Even changing the entire generator alone is problematic in terms of making a decision about such a procedure - maybe the old one, despite its appearance, is completely working, but the problem is in the relay or wiring. The exception here is a generator with mechanical wear, which is clearly noisy. For the rest, it’s better to contact the station. Moreover, the choice of services here is huge: all dealer and non-dealer service stations carry out any generator maintenance. At the same time, there are also specialized stations where they not only exchange for new ones, but also do repairs and restoration, which, for example, for old cars of rare models may be the only acceptable option. And vice versa, for cars of mass models, the service of accepting an old generator as a credit may be attractive, in exchange for which they can immediately supply a ready-made refurbished used or new one.
| Average prices for generators (non-original*), dollars. | |
| Alfa Romeo 145 1.8i Twin Spark 16V from 12.96-12.00 | 180 |
| Audi A4 1.8 from 11.94. | 150 |
| BMW 318i 1.9 (E36) from 07.95-12.98. | 150 |
| Citroen C 5 1.8i from 03.01. | 150 |
| Daewoo Nexia 1.8 from 10.95. | 105 |
| FIAT Brava 1.8 GT 16V from 04.95. | 160/200 |
| Ford Focus 1.8 TD from 01.99. | 150/180 |
| Honda Accord 1.8i from 07.93-10.98. | 90/120 |
| Hyundai Lantra II 1.6, 1.8, 2.0 from 09.95-06.00. | 175 |
| Mazda 626 1.8i from 05.94-03.97. | 140 |
| Mercedes Benz C 180 from 03.93. | 210 |
| Mitsubishi Galant 1.8 from 11.92. | 110 |
| Nissan Primera 1.8 from 06.99. | 180 |
| Opel Vectra 1.8i 16V from 95 onwards. | 100 |
| Peugeot 406 1.6, 1.8, 2.0 from 11.95. | 160 |
| Renault Megane 1.6i. 16V from 02.99 onwards | 90 |
| Skoda Octavia 1.8 from 09.96. | 120/165 |
| Toyota Corolla 1.6 from 04.97-09.99. | 150 |
| VW Golf IV 1.8 from 10.97. | 120 |
| Volvo S 40 1.8 from 09.95. | 165 |
| European cars – Bosch, Valeo, Marelli, Lucas | |
| Japanese cars – Nippon Denso, Mitsubishi, Hitachi | |
| Average prices for generator repairs, rub. | |
| Replacing brushes | 180 |
| Replacement of the collector | 700 |
| Replacing the relay regulator | 350 |
| Replacing bearings | 400-800 |
| Rectifier repair | 600 |
| Replacing the stator winding | 1400 |
| Rotor replacement | 1000 |
| Pulley replacement | 350 |