The hydraulic compensator (HC) in the VAZ 2112 21124/21126 engine is the most important component of a car engine. Their use on the VAZ-2112 engine makes it possible not to periodically check thermal clearances, as on 8-valve VAZ engines. It eliminates the thermal gap between the valve lifter and the camshaft cam. Eliminating this gap allows you to ensure uninterrupted operation of the engine at the level of design parameters. During operation, if the operating conditions and instructions of the manufacturer are not observed, premature wear of this part occurs. At the same time, a characteristic knocking sound is heard in the engine. This sound tells us that the hydraulic compensator has failed and needs to be replaced. The reasons for failure of the hydraulic compensator may be the following:
• Contamination of the oil supply channels in the engine.
• Wear of the working surfaces of the check valve and plunger pair. • The occurrence of shock loads as a result of non-filling or partial filling of the hydraulic compensator with oil, in other words – its “airing”. Now let’s briefly go over each of the above points. The oil passages of the engine lubrication system must not be allowed to become contaminated. This is a clear violation of operational standards that can lead to serious consequences. The reasons for contamination of the oil passages may be:
• Using motor oil that does not comply with the instructions. • Untimely replacement of engine oil. • Malfunction of the oil filter.
As for increasing the seating gaps in the plunger pairs, in this case, increased oil leakage will occur from the high pressure chamber. In this case, the compensator will lose its resistance force and the effectiveness of the force of pressing the cam on the valve stem of the gas distribution mechanism will decrease. The internal space of the hydraulic compensator must be completely filled with oil. If this condition is not met, then the GC will not eliminate the gap in the parts of the gas distribution mechanism. As a result, dynamic loads will arise, in other words, shocks, which will lead to rapid wear of timing parts and a significant deterioration in engine performance. It should be remembered that malfunctions in the operation of the main engine can also be caused by the ingress of small particles into it with the oil, which appear as a result of wear of engine parts. In this case, the node may jam. If you do hear the aforementioned knock, then you should not immediately dramatize this event. The price for carrying out work to replace hydraulic compressors of a VAZ 2112 or Priora 16 valves in a car service center will fluctuate around 3,000 rubles, however, such work can be done with your own hands, you only need to strictly follow our detailed instructions below.
What to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking?
Few drivers know what to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking. This is a fairly common situation. But most people do not know the reasons for such phenomena and are afraid of them. In fact, this may be quite common and should not be a cause for concern. Depending on the characteristics of the knock, we can draw a conclusion about its nature and danger to the engine. Some types of knocking are quite harmless. You can ride with them, but this problem may lead to others. Therefore, it is still better to eliminate the cause immediately. Moreover, in most cases this does not require any special costs.
Need to know
What is important to know about VAZ engines in the context of history? The very first tens of engines produced by the plant also had 8 valves, volume 1.5 and 1.6 liters. On these ones the valves did not bend when the belts unexpectedly broke. But this happened (or rather, did not happen) due to the design of these engines. In the event of a crisis break, the pistons did not meet the valves. For which the designers have great respect. This allowed many owners of the first ten cars to avoid additional engine repairs in the event of timing outbursts on top of everything else.
With the advent of the 2112 model, a new engine began to be installed on the car - 1.5 liters in volume, but with 16 valves (although the problems with the engine on the 2112 were not resolved). For those times - quite progressive. The engine power and throttle response have increased. The design of the head has also changed. During the change, annoying flaws were not immediately discovered (but after some time). Among which is our problem under consideration.
Device
What to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking? Before answering this question, it is necessary to understand the structure of the hydraulic compensator, which mechanics often abbreviate to “hydric”. It is from the peculiarities of its structure that the reason for some knocks follows.
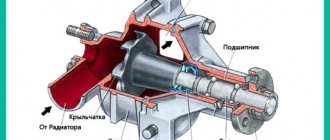
The hydraulic compensator itself consists of a cylindrical piston, whose bottom receives the force from the camshaft pusher. There is a plunger located inside it. With its help, force is transmitted from the camshaft to the valve stem. The plunger moves quite freely in its seat. This is necessary to ensure a thermal gap. When the engine is running, the camshaft cam pushes the piston, which opens the valve through a plunger. The thermal gap is adjusted using oil supplied to the head under pressure. Accordingly, adjustment occurs by changing the pressure. To avoid oil leakage from the hydraulic valves during parking, a ball valve is used.
How to solve the problem?
The most effective solution is to replace the hydraulic compensators on the VAZ-2112. But if carbon deposits have formed in the system, then these mechanisms are removed and washed. After washing, it is sometimes possible to restore their functionality. However, if the car has high mileage, then the compensator breaks and then only needs to be replaced.
The quality of the mechanism largely depends on what kind of oil is poured into the engine and how often it is changed. For quiet and reliable operation of the automatic thermal gap compensation mechanism, it is necessary to fill in high-quality synthetic oil and change it regularly. Then the elements will last longer. Sometimes a less viscous oil may be required to increase the pressure in the system.
vote
Article rating
Types of knocks
We've sorted out the structure, now let's look at the causes of knocking and their varieties. After all, knocking can happen in different ways and some of the sounds are quite harmless:
- The knocking noise appears upon startup, but disappears almost immediately. This is a common phenomenon characteristic of “hydrics”. It occurs due to ball valves remaining open, oil gradually leaking out of them. During engine operation, the amount of oil is restored. Actually, you don’t need to do anything here. This is a normal technical process;
- The knocking is heard constantly, but disappears when the speed increases. This problem can occur if the ball valve is faulty, or if the part is contaminated with low-quality oil;
- Knocking occurs only on a hot engine, in case of increased wear of the hydraulic valve. When cold there may be no knocking;
- If knocking is heard only at high speeds, but not at low speeds, then the reason is in the oil. Check the oil level and condition. If the level is higher than usual, the crankshaft whips up the oil during operation, and a kind of foam forms in it. It gets through the oil intake into the cylinder head and, accordingly, into the hydraulic compensator, the operation of which is disrupted. If the level of lubricant is too low, it simply does not reach the hydraulics. In both cases a knock will be heard.
What to do? The most common cause of knocking is a lack of oil. Perhaps, after adding a fresh portion of lubricant, your car will stop rattling. You can also identify the knocking hydraulic valve and clean it. If all this does not help, then the faulty part should be replaced.
Prevention measures
As usual, there were several of them. Firstly, it was recommended to carefully monitor the condition of the timing belt, constantly check it, and at the slightest suspicion, immediately replace it with a new one. Some drivers even carried spare belts with them, and at the first opportunity (after some short time of operation of the said spare part) they tried to replace it.
This method, of course, worked, but not without fail. You could get low-quality cooperative belts (as they were called then, which meant not factory ones), with a hidden defect. And then, if you don’t watch, it’s simply impossible to protect yourself from danger. Well, the factor that you simply can’t get enough belts also has a certain significance.
The second way to avoid expensive repair work was engine boring
, which was produced by experienced craftsmen at the service station.
A little time passed, and VAZ designers stopped mocking the people by installing improved engines in the 2112 (also 16 valve, but already 1.6 liters). These models already had special recesses on the pistons that prevented the valves from meeting them if the belts broke. This means spending public funds on very difficult repairs.
A separate discussion is this modification. It was produced from 2004 to 2008 and featured a 1.6 l/16 engine, where the problem was successfully solved due to the greater depth of the piston grooves (more than 6 millimeters). In addition, the design of the cylinder block was also changed. On such engines, the valves also did not bend when the timing belt broke.
Checking hydraulic compensators
To identify the problematic part, you need to remove the valve cover. This way you will have access to “hydrics”. After which the engine is brought by the crankshaft to a position where the cams do not act on the compensators. Next, use a simple block to press the hydraulic compensators one by one. A working piston should move downwards under great force. If it does not move, then the reason is a jammed plunger. If there are problems with a lack of oil, the piston will go down almost without resistance. In the latter case, you can remove it and try to clean it.
Malfunctions and repairs of the new 21127 Priora engine
Engine VAZ 21127 1.6 l. 106 hp a new VAZ engine, a continuation of the Prior engine 21126 and based on the same modified block 21083. The engine is an in-line 4-cylinder injection engine with overhead camshafts, the gas distribution mechanism is belt driven. A special feature of the 127 engine is that it was equipped with an intake system with a resonance chamber with an adjustable volume: controlled flaps reduce or increase its volume depending on the number of revolutions per minute. The chamber volume varies from larger to smaller, and the minimum volume value is used in the mode from 3500 rpm. In addition, now instead of the mass air flow sensor, DBP+DTV is installed, along with the mass air flow sensor the problem of floating speeds has gone away, and this is where the differences between the 126 and 127 engines end. At the same time, the 21127 Priors engine still bends the valves, the other problems remain the same, noise, knocking, tripping... the reasons that give rise to them are described in the article about the 126 engine. According to the sensations and reviews, the engine began to drive more interesting from the bottom than the usual 126 engine, at the top the situation is the same, the changes are insignificant, but noticeable.
Replacement
Experienced car enthusiasts advise replacing hydraulic compensators as a set. They wear about the same. Therefore, if one fails, the other will soon fail. To replace the hydraulic valves, you will have to remove the camshafts, as well as some other engine parts. In principle, the work is not difficult and does not take much time. This should only be done on a completely cooled engine.
For greater reliability, you need to change the engine oil at the same time. When you first start the engine, do not be alarmed; you may still hear the same knocking noise. It will end after half a minute, as soon as the required amount of oil is filled into the hydraulic compensator. If replaced correctly, the motor will run quietly for a long time.
Conclusion. The engine on the “two-wheeler” has a lot of advantages; it is quite resourceful, and at the same time not gluttonous. But it has one drawback, valve knocking. Therefore, novice drivers often ask what to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking. Before answering this question, it is necessary to find out the exact reason for this phenomenon. After which, it can be eliminated.
Didn't find the information you are looking for? on our forum.
The result of the work
Having completed the installation work, we check the operation of the engine. Immediately after starting, the engine may work, making extraneous sounds in the form of clattering or tapping. They indicate that the hydraulic compensators need to be pumped, i.e. fill with oil, expelling the air.
To carry out this procedure, start the engine and run it for 5 minutes at 2500 rpm. After this, go to idle speed and wait 30 seconds. Next, turn off the engine and wait a minute.
Next time you start, listen again. If the sound does not disappear, repeat the procedure. Usually after 3-5 such pumpings the extraneous sounds disappear.
Features of recessed pistons
The 10th family of cars was discontinued due to the presence of many technical flaws. The updated family has gone through major changes that affected environmental issues and increased engine power. It should be noted that all 16-valve engines are currently installed not only on Priora, but also on other VAZ models, including Kalina and Granta. However, the engine bends the valves on every such car.
The exception to the fact that if the timing belt breaks, these parts will not meet the pistons are the first eight-valve engines. Modern production of domestic cars does not provide for the use of these units. New eight-valve counterparts with increased power also bend the valves.
conclusions
Replacing hydraulic compensators on a VAZ-2112 is not so easy, but you can do it yourself. Of course, this will require time and effort. The choice of product should also be taken quite seriously, because the resource of use depends on the quality.
A hydraulic compensator (HC) is a part of the engine block head, the purpose of which is to automatically adjust the thermal clearances of the engine valves in order to prevent the formation of gaps between the valves and the camshaft cams.
Detailed instructions for disassembling and repairing the VAZ 2110 engine:
2. Remove the clutch from the engine.
3. Remove the tension roller, camshaft drive belt and spacer washer, which is installed under the tension roller.
4. Remove the toothed pulley from the camshaft.
5. We unscrew four bolts, three of which attach the water pump. Unscrew the fastening nut on the rear cover of the camshaft drive belt and remove the cover.
6. To remove the water pump, insert a screwdriver between the block and the flange of the pump housing and thus move it from its seat. After completing these operations, remove the water pump.
7. Remove the head from the cylinder block.
8. Unscrew the bolts (there are 16 of them) securing the oil sump, then remove it together with the gasket.
9. Unscrew the bolts (there are 3 of them) securing the oil receiver and remove it. Please note that there are spring washers under the bolt heads.
11. Then rotate the crankshaft so that the piston that is being removed hits BDC (bottom dead center). It is necessary to unscrew the two fastening nuts to remove the connecting rod cover.
12. Now remove the connecting rod cover. In cases where it is difficult to dismantle the cover, you can first remove it with light blows of a hammer. It may be that the cylinder number on the cap will not be visible, in which case the cap should be marked with the cylinder number.
13. Using the handle of a hammer, push the connecting rod inside the cylinder, then carefully remove the piston and connecting rod from the cylinder. During the process, you need to make sure that the lower head of the connecting rod does not touch the cylinder mirror, since this can damage it. We remove the remaining pistons in the same way.
14. If you need to remove the piston from the connecting rod, then mark it with the cylinder number so as not to confuse them when installing them. There should also be a cylinder number on the connecting rod: if it is not visible, then we mark the connecting rod as well.
16. Unscrew the bolts (there are 6 of them), remove the crankshaft rear oil seal holder and the gasket. Remember that there are spring washers under the bolt heads.
17. Remove the toothed pulley from the crankshaft. If the key does not fit tightly in the groove of the shaft elbows, be sure to remove it so that it does not get lost.
18. Unscrew the six bolts, under the heads of which there are spring washers, and remove the oil pump and gasket.
19. We unscrew the mounting bolts on the five covers (each with 2 bolts) of the main bearings.
21. Remove the crankshaft of the VAZ 2110 car.
22. We remove the crankshaft thrust half-rings on the middle support.
23. If you do not plan to replace the liners, then as you remove them, remove them from the block beds and from the main bearing caps.
24. On the non-working side we mark the liners relative to the beds and covers.
25. If there is a need to remove the engine mounts and generator brackets, unscrew the bolts (3 pieces) securing them and remove the water pump supply pipe by unscrewing its fastening.
26. Remove the piston rings using a special puller. If there is no such device, then remove the rings from the piston by carefully releasing the ring locks.
27. Remove the oil scraper ring expansion spring from the auto engine piston.
28. Remove the retaining rings that hold the piston pin on both sides of the piston. There are recesses in the piston bosses for easy removal of the rings.
29. Using a suitable mandrel, push the pin out of the piston, then remove the piston from the connecting rod.
30. Remove the liners from the connecting rod and its cover. If they remain on the crankshaft, remove them from the shaft. If replacement of the liners is not required, then as they are removed, we mark them with respect to the numbers of the covers and connecting rods.
This completes the process of disassembling the VAZ 2110 engine. Good luck with the completion of the renovation.
Detailed video lesson: engine assembly
Video about overhaul of VAZ internal combustion engine:
Video - VAZ 2112 engine assembly:
Sequence of operations
To replace the hydraulic compensators of the VAZ 2112 and other models, you need to drive the car into an inspection hole, drive onto an overpass, or lift it with a jack. It is important to ensure reliable fixation of the vehicle and sufficient illumination of the work area. Now you can start working:
- For safe work, you need to turn off the on-board power supply; to do this, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Removing the plastic engine shield - unscrew the four bolts.
- Now you need to loosen the mount of the generator on the mounting plate; to do this, loosen the nut.
- You need to remove the generator drive tension belt. To do this, loosen its tension by rotating the nut counterclockwise.
- Removing the engine intake manifold and receiver. The hole must be closed to prevent dirt and foreign objects from getting into them.
- Then you need to dismantle the right wheel and the plastic shield covering the engine compartment. Now use the pulley bolt to turn the crankshaft clockwise.
- The lower pulley rotates to the camshaft timing pulley mark to the antennae on the rear timing cover.
- The camshaft pulley fastenings are loosened and the timing belt is removed.
- To completely dismantle the camshaft pulleys, you need to check the marks on the timing belt housing. They must line up exactly with the marks on the pulleys.
- Using the heads, 15 fasteners of the cylinder head cover are unscrewed.
- Now twenty fasteners of the camshaft bearing housing are unscrewed.
- The camshaft bearing housing is removed.
- The camshaft is completely removed, along with the seals.
- A magnetic screwdriver is applied to the end of the hydraulic pusher, so it is removed from the head socket.
- New spare parts are installed in place of the old compensators in the cylinder head sockets.
- The cams and bearing journals are lubricated with oil, the shafts are installed in the head supports. Note! To easily distinguish the intake camshaft from the exhaust device, there is a belt on its first journal.
- Now you need to tighten the nuts until they touch the cylinder head of the bearings. The operation is performed in a certain sequence, it is shown in the figure.
- The valve cover, timing belt and pulleys are returned to their original locations. Further operations are performed in reverse order.
Other cases in which dismantling of the cylinder head is required
Of course, it is not necessary to remove the cylinder head for every breakdown. This is only necessary if major repairs are needed. Such “major” cases include:
Of course, repairing it yourself or through a service in any case involves certain financial costs. To ensure smooth operation of the engine, regular diagnostics of the cylinder head are necessary. It is recommended to use high-quality fuel. In addition, try to prevent the car from overheating - because of this, the cylinder head may lead.
If some points remain unclear to you, then you can visually familiarize yourself with the process of replacing valves by watching the video:
Source
Which VAZ 2110 engine is better to choose/buy (reviews)
| VAZs of the tenth family are still very popular, despite the fact that this model has already been discontinued. Many people buy “tens” on the secondary market, others restore their cars in garages, and all these car enthusiasts are united by the common question “which VAZ engine is better?” |
The following engines were installed on cars of the tenth family:
More details about the characteristics of VAZ 2110 engines. Each engine has its own advantages and disadvantages, in short:
What engine would you recommend to buy for a VAZ 2110? Participate in surveys and leave reviews about VAZ engines of the tenth family. xn--2111-43da1a8c.xn--p1ai
What it is?
The part is a small hydraulic device. It automatically eliminates the effects of linear expansion in the valve train mechanism during engine operation as parts expand.
The gaps are adjusted using the oil pressure in the engine. The gap is adjusted between the valve and the camshaft. With the help of such compensation of thermal gaps, the engine does not lose dynamic characteristics, fuel consumption is optimal after warming up. Also, due to the presence of hydraulic compensators in the VAZ-2112, the engine is quieter than similar engines with a mechanical valve adjustment system.
Product delivery options
Note! Below are the shipping methods available specifically for this product. Payment options may vary depending on the shipping method. Detailed information can be found on the “Delivery and Payment” page.
Parcel by Russian Post
Available payment methods:
Shipping throughout Russia. Delivery time is from 5 to 12 days.
Parcel by Russian Post 1st class
Available payment methods:
- Cash on delivery (payment upon receipt)
- Using cards Sberbank, VTB, Post Bank, Tinkoff
- Yandex money
- QIWI
- ROBOKASSA
Shipping throughout Russia. Delivery time is from 2 to 5 days. More expensive than regular delivery by Russian Post, approximately 50%. Parcel weight up to 2.5 kg
Express Parcel EMS
Available payment methods:
- Cash on delivery (payment upon receipt)
- Using cards Sberbank, VTB, Post Bank, Tinkoff
- Yandex money
- QIWI
- ROBOKASSA
Shipping throughout Russia. Delivery time is from 3 to 7 days. More expensive than regular delivery by Russian Post, approximately 100%.
Transport companies
Available payment methods:
- Using cards Sberbank, VTB, Post Bank, Tinkoff
- Yandex money
- QIWI
- ROBOKASSA
Delivery is possible to any locality where there is a representative office of the transport company. Delivery time is from 2 to 10 days. Sending large parcels is approximately 50% more profitable than by Russian Post.
Pickup from our warehouse
Available payment methods:
- Cash upon receipt
- Credit, installments
- Using cards Sberbank, VTB, Post Bank, Tinkoff
- Yandex money
- QIWI
- ROBOKASSA