How to repair and adjust the turbine actuator yourself
Turbocharging today is one of the most common methods that allows you to significantly increase the power of a gasoline or diesel engine without increasing the displacement of the power unit.
Installing a turbocharger is also a more efficient solution compared to mechanical superchargers. The basis of turbocharging is the supply of air to the cylinders of the internal combustion engine under pressure.
The more air you can supply to the engine, the more fuel you can burn. Civilian versions of turbo engines do not have too much boost, which is enough to achieve the required performance. It is quite obvious that in order to achieve maximum performance, turbines are installed on the engines, which are capable of providing high pressure. In this article we will talk about why an actuator on a turbine is needed, what is the principle of operation of a turbine actuator, as well as how to check a turbine actuator and configure this element.
Why do you need an actuator?
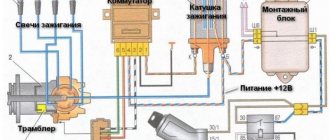
The main purpose of this component is to select the optimal gear for the most efficient operation of the motor. The actuator consists of the following components:
- an electric motor that starts the operation of all mechanical elements;
- a travel sensor, whose task is to determine the required gear (for this, the system records engine performance);
- gear change mechanism.
The main mechanism consists of several additional elements:
- internal lever,
- shafts,
- ring gear.
This is interesting: What is a VIN chassis body?
Turbine actuator: operating features
An actuator, also known as a wastegate or vacuum regulator, is a valve for relieving excess air pressure at high engine speeds. The purpose of this solution is to provide a kind of protection for the turbocharger and engine. The specified regulator for protection against excess loads is located in the exhaust manifold (in fact, on the turbine itself); the installation location is the area in front of the turbine.
The wastegate works according to the following principle: if the engine speed is high, resulting in an increase in exhaust gas pressure and charge air pressure, then the valve opens. Its opening redirects part of the exhaust gases bypassing the turbine wheel.
This happens when the turbine wheel is spun by the exhaust gases to too high a speed, as a result of which the actuator initiates the operation of the bypass valve, that is, the exhaust gases pass by the turbine wheel. It turns out that the wastegate simply does not allow the turbocharger to spin up to its maximum under the influence of too strong exhaust flow at high engine speeds.
Let's add that turbo engines are initially precisely tuned from the factory. When tuning an internal combustion engine or installing a turbocharger on an atmospheric engine, the actuator must be configured separately. Setting up and adjusting the turbine actuator is an important point, since the health of the engine and turbocharger depends on the normal operation of the system. It is advisable to configure the wastegate using special equipment, but you can also do it yourself, which we will discuss below.
Turbine operating principle
Let's consider the operation of a turbocharger with an electronic actuator and smoothly move on to what is USEFUL AND NECESSARY TO KNOW for everyone who operates a vehicle with any turbocharger, diesel or gasoline engine.
Working principle of a turbocharger
In the figure we see how the operation (movement, change in direction of the blades) of a variable geometry mechanism driven by an electronic actuator occurs.
At low engine speeds, the variable geometry blades are in a half-closed or almost closed (this gap is important) state, looping the air flow of the exhaust gases, thereby maximizing the impact on the edges of the turbine wheel (rotor) blades. The car is ready to start, and now everything depends on the amount of exhaust gases, i.e. pressing the gas pedal. In this position of the geometry blades there will be maximum boost, i.e. maximum acceleration in the future. When the blades of the variable geometry mechanism are opened, the direction of the exhaust gas flow changes and is directed more towards the center of the rotor, and the flow speed is reduced by opening the blades, thus minimally affecting the turbine wheel blades.
There is a controversial issue regarding the description on Internet pages of the operation of the variable geometry mechanism, i.e.
at what position of the geometry blades does the car accelerate, but if you combine theory with practice, it happens exactly as described above.
To achieve correct and maximally correct operation of the turbocharger, it is necessary to adjust the electronic actuator using special electronic equipment (drive tester). The drive tester can be used both in stationary mode to adjust a turbocharger removed from the internal combustion engine, and in portable mode from a battery to check directly on the car itself
Turbine with servo drive
Let's touch on a turbocharger with an electronic actuator (with a servo drive) in a little more detail. There are two main types of servo failure: mechanical failure and electronic failure.
Failure of the mechanical part of the electronic actuator occurs mainly due to poor performance (seizing, jamming, breakdown) of the variable geometry turbocharger mechanism.
In turn, damage or complete breakdown of the variable geometry mechanism (mainly paired with the rotor (shaft) of the turbocharger) occurs due to the destruction of the engine (pieces of the valve, seat or valve guide, pieces of the piston) or, importantly, due to a damaged air duct or air filter and sometimes due to a non-working EGR valve
Common Wastegate Problems
Now let's talk about common malfunctions in which replacement of the turbine actuator is inevitable or repair of this element is required. Let's start with the fact that there are several reasons for the failure of this part. First of all, electronic components break down, the electric motor may malfunction, and the teeth of the valve drive gears also break.
In some cases, the problem is eliminated after diagnosis at specialized turbine repair services. Specialists check the functionality of the controller and perform a number of tests. A common malfunction that repair of a turbine actuator without replacement can help eliminate is a failed cuff (turbine actuator membrane).
In the mid-day case, significant mileage and natural wear of parts lead to breakdown, and as a result, the specified cuff is often damaged. To eliminate it, it is necessary to remove the turbine actuator, after which the old membrane is removed from the housing. Next, the surfaces should be degreased, after which the new cuff is glued to the body with two caps and additionally undergoes a circular rolling process. Then the turbine actuator is adjusted.
Central locking actuator
The design of a car's central lock is simple. It consists of a control unit and actuators - actuators (they are also sometimes called activators). When you turn the ignition key or send an electronic signal from the remote control, control contacts are activated, which, through the central unit, give a signal to all locking devices to open or close.
Design and operation of the lock actuator
Sectional view of a lock actuator
This device is an electric micromotor connected to a rod via a rack and pinion gear. The rod of the mechanical lock, in turn, is mounted to the rod. When a signal is sent to the engine, the rod moves, which closes or opens the mechanical door lock.
Due to the design feature, the rod travels a short distance. Therefore, voltage cannot be applied to the electric motor for a long time . Modern automatic systems do this in approximately 2 seconds. They are quite sufficient to operate each of the drive motors.
There are two wires going to the drive motor . Current flows through one of them, and a “mass” is formed on the second, that is, a connection to the car body. The distribution of which wire to supply voltage to is handled by the central electronic control unit. Depending on this, the direction of rotation of the motor shaft changes , and as a result, the direction of movement of the rod. That is, the lock on the door is opened or locked.
Possible malfunctions of the lock actuator
Possible malfunctions of the central locking actuators may include:
Lada Priora door actuator repair
- Failure of all actuators . The first possible reason is the action of a long command pulse , which led to the burnout of the windings. The second reason is a malfunction of the generator , as a result of which increased voltage was supplied to the actuators. The solution is to replace the actuators and, if necessary, repair the generator.
- Wedge of one or more actuators in one position when the collector units melt. The solution to a faulty lock actuator is to replace the failed actuator.
- A short circuit in the actuator control circuits or insulation damage. The solution is to inspect the wiring and, if necessary, replace damaged sections.
- Short circuit, damaged wiring in the actuator power wires or short circuit of the commutator plates. The solution is to replace damaged sections of wiring , repair insulation, or replace the actuator.
- The fuse has blown . The solution is to replace it.
- Noisy operation of the actuator . A possible reason is wear on the operating gears. The solution is to replace the gear mechanism .
Often the solution to troubleshooting and repairing the lock drive is to replace the lock actuator.
Replacing the central locking actuator
Replacing the lock actuator
Replacing the lock actuator yourself is not particularly difficult , although this will require removing the entire door trim in order to get to the fasteners and wires. If there are additional buttons on the door, for example, for electric windows, then you need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery. Otherwise, you can do without it.
During the work, follow the manual for working with your car. After all, in each model the door trim is attached in its own way . As a rule, the actuator can only be reached by removing the casing. In rare cases, it is necessary to dismantle additional mechanisms. The actuator is usually mounted on a pair of bolts or screws. To remove it you need to unscrew them and disconnect the chip.
Depending on which part has failed, you need to replace it. Most often, the micromotor windings burn out . Since no one rewinds them, it will be enough to replace it by first purchasing a similar one.
How to adjust the turbine actuator
The need to adjust the wastegate is indicated by the appearance of a recognizable rattling sound at the installation site of the turbocharger at the moment when the engine is turned off. Vibrations and rattling also appear during gas pumping, at the moment of releasing gas. Such rattling appears as a result of the fact that the actuator rod begins to dangle; the rattling sound itself is created by the “gate” of the regulator. Insufficient air pressure will also indicate problems with the actuator if no problems were found with the inlet seal and other elements of the turbocharging system.
I would also like to add that many drivers resort to manipulating the wastegate not only because of problems, but also in order to increase performance and boost pressure, that is, they implement a kind of tuning of the system.
- To increase blood pressure, there are several options available. The simplest is to replace the regulator spring. The more elastic the spring is, the more pressure the turbine will produce until the valve is activated.
- Another option is to tighten or loosen the end of the regulator, which directly affects the opening and closing of the damper. If the end is relaxed then the valve rod lengthens, tightening will result in shortening. The shorter the pull, the tighter the damper will close. Accordingly, greater pressure and time will be required to open. This allows the turbine to reach high speeds, and this happens quite quickly.
- The third option for increasing boost is a boost controller. This mechanism is a solenoid that can replace real pressure data. Such a device is placed in front of the actuator; the main task is to reduce the pressure on which the operation of the wastegate depends. The boost controller actually partially bypasses the air, which prevents the actuator from assessing the actual pressure.
Turbine actuator: how it works and what it is needed for
Many drivers prefer to tune the engine with a turbocharger. This is a unit whose correct name is a turbine actuator. If configured correctly, the device can seriously increase the power characteristics of the motor. Nowadays, high-pressure actuators are widely used. The design of the device has a valve that prevents pressure from increasing when the engine operates at high speeds.
Special actuators
As already mentioned, actuators are used everywhere, which puts forward certain requirements for the stability of the device. To perform more complex tasks, there are special actuators. Today they are widespread in the far north, in space or under water. Structurally, they are not much different from their analogues. The main feature is the tightness of the housing. The waterproof and dust-resistant design adds a class of protection to the actuator, allowing for trouble-free operation of the mechanism in difficult conditions.
Protection classes
- IP54 – provides protection against penetration of splashing water from all directions.
- IP65 – prevents the penetration of water jets into the housing (any angle of attack).
- IP67 – the device is capable of functioning when completely immersed under water.
How does a diesel engine turbine actuator work?
In the slang of car enthusiasts, this unit has different names - for example, wastegate, vacuum regulator. Like other mechanical components, the actuator can break, and then in order to continue operating the turbocharged engine, it must be replaced. But replacement is not so bad. Then the wastegate will have to be adjusted, and this is a serious task that only an experienced driver can perform correctly.
The regulator is placed in the exhaust manifold of the car. The principle of its operation is simple. As the speed increases, the engine begins to operate at higher speeds. The exhaust gas pressure increases. It becomes necessary to guide it past the turbine wheel. Then the wastegate begins to operate - its valve opens and allows gases to pass through itself.
Turbine actuator does not work: signs
There are several symptoms of a turbocharger failure, but the main one is blue exhaust. It is especially pronounced during acceleration, but when the operation of the power unit stabilizes, the exhaust acquires its normal color. The smoke turns blue due to the combustion of oil that entered the engine due to its leakage from the turbocharger.
Black smoke may also come out of the exhaust pipe, which indicates the combustion of enriched fuel due to an air leak in the intercooler. The exhaust may also be black due to a breakdown of the turbocharger control system.
White smoke also indicates a turbocharger malfunction. The exhaust turns white due to a blockage in the turbine oil line drain. Other obvious signs of actuator malfunction are oil leaks on the turbine and a significant increase in its consumption. This is evidence of a blockage in the air supply channels or oil pipeline.
If the car starts to accelerate slower than usual, the problem may also be with the turbocharger. Its malfunction may cause insufficient air mass to enter the power unit. Lack of air leads to a serious drop in engine power.
Another sign of a breakdown in the turbine is loud noise when the engine is running. Its appearance is caused by air leakage between the compressor outlet and the motor. Along with the noise, an unpleasant grinding noise appears when the turbocharger is turned on. Grinding or noise may be the result of cracks, dents, or other mechanical damage that the unit blades touch.
If oil consumption has increased significantly and the exhaust has become more toxic, check the air filter or the air duct connected to the turbine. Maybe the problem is that these elements are clogged.
The last sign of a wastegate not working is the most common. This is the oil exiting the compressor. The reason is not original - it is the same littering of the turbogenerator axle casing. Also, oil leakage could be caused by a malfunction of the lubrication system or its coking.
Electronic revolution
About 20 years ago, the electronic revolution began in turbo manufacturing. Pneumatic ones have been replaced by so-called electronic actuators or electronic control units TK. Initially, they were used in the design of diesel turbines with SAR, characterized by a complex algorithm for controlling the nozzle apparatus (photo 3). The electronic actuator includes a servo drive with a gearbox and position sensor and a “brain” - a programmer (photos 4 and 5). Thus, the pneumatic drive has given way to an intelligent servo drive. Turbines began to be regulated by wire, by wire, receiving control commands directly from the engine ECU. The most advanced actuators are equipped with a feedback function with the motor control unit - they not only receive, but also send signals to the engine command center.
Photo 3. Intelligent servos started in the design of Garrett VNT turbines
Photo 4. The electronic control unit of the TC consists of a servo drive with a gearbox and a position sensor...
Photo 5. ...and the programmer board combined with the unit cover
The mass introduction of electronic drives began in the mid-2000s, on the eve of the introduction of Euro V toxicity standards. Since then, electronic “mold” has affected most of the TK models. But its expansion turned out to be not as comprehensive as it seemed at first. Still, an electronic actuator is far from a budget solution. Its use in the design of a heating complex leads to a significant complication and increase in cost of an already expensive unit. Therefore, along with purely electronic ones, hybrid actuators appeared - pneumatic actuators with electronic sensors that monitor the position of the rod (photo 6). Having started in the design of diesel turbines with PCA, recently electronic control units have begun to appear on gasoline turbines with bypass regulation (photo 7).
Photo 6. Budget version of turbo electronics - pneumatic actuator with rod position sensor
Photo 7. Electronic units are also used in modern turbines with bypass regulation
Thus, today a great variety of electronics can be found in turbines. More than 200 models of Hella electronic units alone are known. On turbines from global manufacturers you can also find components with the logos of Bosch, Mahle, Siemens and others. In the matter of “electronization” of turbines, the Honeywell concern, the founder of this direction, is leading. In terms of the number of electronic “garretts” it significantly exceeds its competitors.
How to check the turbine actuator?
Diagnosis of an electronic turbocharger begins with a test with a tester. The actuator can be tested on the car, or it can be pre-dismantled. The following are subject to verification:
- vacuum valve;
- actuating mechanism;
- turbine valve.
Diagnostics should be carried out periodically, even if the wastegate does not cause it. When a minor breakdown of the turbine occurs, this leads to excessive heating of the bearings and, as a consequence, to complete breakdown of the unit.
Testing can be done like this: start the engine and accelerate in place. In this case, you need to look at the wastegate rod - at some point it will start to move. Remember at what engine speed the turbocharger started to operate - this will be a guideline for checking its serviceability. More accurate readings can be obtained at the stand.
Setting up the turbine actuator
The turbine actuator must be adjusted. If this is not done, the entire system will shake while the engine is running. If the adjustment is made incorrectly, the boost will be insufficient. However, incomplete boost may occur if the system's intake has lost its tightness.
Let's start setting up. You can do it in different ways:
- Increase the pressure by replacing the old spring with a more elastic one. If, on the contrary, you need to reduce the pressure, you can install a spring made of mild steel. To lengthen the thrust of the bypass valve, you need to loosen the end of the actuator; to decrease it, on the contrary, tighten it. If the thrust is reduced, the damper will be pressed tighter. Then, to open it, you will have to apply significant force, which means the impeller will spin faster.
- You can increase the boost by installing a boost controller. This mechanism is capable of changing pressure. In order for it to reduce pressure on the wastegate, it must be installed in front of it. The boost controller takes on some of the load as it releases some of the air.
Actuator replacement: when is it required?
Sometimes the turbine fails immediately, but usually it happens gradually. To detect a breakdown at an early stage, you need to take a closer look at the operation of the machine. If all efforts to repair this device fail, you will have to buy a new actuator.
Previously, replacement was carried out together with the turbine, but now the actuator can be replaced separately. Some technicians generally recommend not trying to repair this device, but replacing it immediately - unless, of course, the problem is a soured connection. The unit will definitely have to be replaced if the rod joint on the regulator is worn out. This work is not that difficult. After replacing the device, it will take time to adapt.
Aggressive driving style and the use of low-quality fuel and engine oil lead to premature failure of the actuator. In order for the unit to last longer, this should not happen - it is better to use only certified technical fluids.
The turbine drives oil into the intercooler: what to do?
The oil in the intercooler can cause serious malfunctions, including failure of the internal combustion engine. In this article we will tell you why oil appears in this unit and how you can fix this problem.
How to repair a turbocharger?
A turbocharger is a part that can significantly reduce engine fuel consumption. Repairing a turbocharger is quite difficult; professional tools are required.
Turbocharged engines and features of their operation
Turbocharged power units: their design features, performance characteristics and the most common causes of breakdowns.
Application of two-way valves in automotive systems
Since numerous vehicle systems constantly require shutting off, redirecting and mixing various flows of liquids or gases, the use of various bypass devices, such as valves, is required. The principles of their operation are based on different drives: pneumatic,
Turbocharging system on diesel engines
Many modern cars use turbochargers to increase engine power. They come in different types and shapes, but the principle of their operation is the same. The idea of turbocharged engines arose a long time ago. Some of the first turbochargers were installed on racing cars at the beginning of the last century.
Possibility of installing a turbocharger on atmospheric power units
The idea of turbocharging power units arose out of the need to economically increase engine power. Adding power by simply increasing the volume has become impractical, since this leads to significant fuel consumption. Turbocharger technology is based on air supply to the chamber
What to do if the turbine breaks down
If a malfunction is detected, the first thing to do is carry out diagnostics. And the sooner the better. If you replace a faulty part in time, you can avoid more serious problems.
For example, often a car owner does not pay attention to a slight knocking, thinking that it does not matter, as a result, after some time he has to buy a new turbine, although initially a minor repair could have been done
It should be noted that it is not enough to know how a diesel turbine works - you need to have a perfect understanding of all its components. Only with the appropriate skills, experience and equipment will it be possible to carry out high-quality repairs. That is why we recommend that you do not try to repair the unit yourself (you can only make it worse), but contact. We have been specializing in turbine repair since 1998, and therefore we know everything about them.
5 reasons to contact us:
- High-precision diagnostic equipment is available (Bosch and Delphi stands);
- The staff includes specialists with extensive practical experience in such work.
- Quick repairs within a day without loss of quality.
- We use only original components and repair kits.
- We provide an official guarantee on components and repairs performed.
At the first sign of a defect, contact us. We will determine the cause of the problem and offer an effective, cost-effective way to solve it.
Turbine actuator aka Wastegate, or turbine control valve
As the English name suggests, this turbine control valve
serves to discharge excess exhaust gases rotating the rotor impeller through the outlet, or bypass, channel. If this is not done, the shaft will acquire excessive speed at high crankshaft speeds, which is fraught with an emergency increase in boost pressure, and with the throttle closed, a surge in the supercharger. Reducing the performance of the compressor will not help, then its capabilities at low and medium speeds will not be enough, the engine will fall into the so-called “turbo lag”. Device failures are associated precisely with cases of excess or lack of injection flow. Let's take a closer look at their manifestations.
Wastegate - a limiter in the service of increasing power
Some turbochargers do without bypass mode. These are low-pressure turbines; due to their compactness and low performance, they do not operate in modes that require limiting the flow from the hot side. Sometimes it is enough to dump the excess at the output, for which a simpler device is used.
The situation is different with powerful turbochargers, capable of creating very high pressure at high flow rates. Here you will need to limit the exhaust gas flow to a more efficient impeller.
Turbine control valve: design and principle of operation
Turbine valve
consists of a body divided by an elastic membrane into two parts. The first receives the control action of the air supplied to the inlet, and from the second comes a spring-loaded rod mechanically connected to the diaphragm. As soon as the force per unit area of the membrane exceeds a certain value, the spring will compress and the rod will move, opening the exhaust bypass channel. Gases will be directed around the turbine wheel, and its rotation speed will decrease.
Attention
Symptoms of turbine actuator malfunctions
Abnormal condition of the turbine actuator
implies two deviations from normal engine operation - excessive turbine pressure and insufficient pressure, depending on the specific nature of the breakdown.
- the wastegate
“wicket” fails to close, the turbine will rotate at higher speeds, that is, overinflate. Even if no mechanical damage occurs in the unit, which is very likely, the engine will begin to receive an excess amount of air. The consequences will be an over-lean mixture, up to misfire, detonation in the cylinders, and rapid failure of spark plugs. - If the gate is constantly open, the compressor will not be able to develop the required performance and air flow. The engine will lose power, the car will not be able to accelerate vigorously, and fuel consumption will certainly increase due to the over-enriched mixture. This will especially affect transition regimes.
- Intermediate states of uncertain actuator operation
. A characteristic sound of valve rattling will appear, in particular when idling and stopping the engine, power and torque will become uneven, jerking and pick-ups are possible.
Causes of breakdowns, diagnostics, repair possibilities
The main problem with the turbine actuator
– aging of the diaphragm and loss of its tightness. The valve stops responding to changes in output pressure and does not control the opening of the bypass. Checking this is quite simple, just blow into the receiving fitting. There should be no signs of air chamber leakage.
Turbine actuator: operating principle and configuration
For many drivers, a car is simply a means of transportation, while for others, the car is a hobby in which they are willing to invest time and money to improve the basic characteristics. One of the most popular ways to tune a car engine is to install a turbine (turbocharger). A turbine can significantly increase engine power if it is selected and configured correctly.
Currently, the most popular are high-pressure turbines, which differ from the basic versions of turbochargers by the presence of a valve. It is necessary to cope with excess pressure when the engine operates at high speeds.
Please note: In automotive slang, this valve can have different names, among which the most common are the following: wastegate, actuator, vacuum regulator. It should be understood that all these terms mean one part that protects the turbine from overloads when operating at high speeds.
During operation, the turbine actuator may fail, and the car owner will need to replace it in order to continue operating the car with a turbocharged engine. Replacing a wastegate involves not only its installation, but also adjustment, which is extremely important to do correctly. In this article, we will look at how to adjust the turbine valve yourself, without contacting service center specialists.
Variety of actuators
The mysterious concept of “actuator” hides many already known devices. If you do not take into account the jack, then you can start with the central lock - a linear device. Also among the well-known is the turbine actuator. This is a vacuum regulator that protects it from stress at high speeds. There is also a clutch actuator on robotic automatic transmissions.
If we take the field of construction electromechanics, the most common would be the drive for opening and closing wickets and gates. That’s what it’s called – a door actuator. With the help of such a device, automatic garage doors and gates at entrances to the territory are driven.
Satellite dishes, so popular among the population, are also driven by actuators. This may be necessary when there are several positions for receiving information. In order not to install several antennas, they make do with one. Its actuator rotates to the required angle. Let's look at the car options in more detail.
How does a turbine actuator work?
As noted above, the task of the turbine actuator is to reduce pressure when the engine operates at high speeds. It is mounted before the turbine in the exhaust manifold of the car.
The operating principle of the wastegate is extremely simple. When the engine speed increases, and at the same time the pressure of the exhaust gases increases, the task is to let them pass by the turbine wheel itself. Accordingly, at this moment the actuator installed upstream of the turbine opens and exhaust gases exit through it. Due to this, more air enters the valves, which is necessary for maximum acceleration of the turbocharger.
How Vasya checks the turbine (software)
The inspection methods described above only provide an indirect assessment of the condition of a used turbine. To diagnose it in detail, it is better to use electronic means - a laptop and diagnostic software installed on it. The most common program for this among masters and car owners is “Vasya Diagnostician”. The following is a brief description of the algorithm for checking the pressure in the tested turbine. It is assumed that the car enthusiast knows how to connect to the service connector of the ECU and run the program. All further readings are performed with the machine idling, that is, with the engine and turbine running.
Checking the turbine on the Vasya machine
- In the program, select the section “Selecting a control unit”, then “Engine electronics”.
- Select the “Custom Groups” button. A window for customizable groups opens on the left and a list box opens on the right for selecting groups directly. Here is a description of all the components that affect the performance of the car engine (sensors, executable modules, and so on).
- In the list you need to select the line Absolute intake pressure or “Absolute consumed pressure”. The corresponding pressure will be presented in the left window. The units of measurement in this case are kPa instead of bars.
- When idling, the turbine pressure will be slightly more than 100 kPa (or 1 bar, for example 107 kPa).
- Along with turbine pressure, it will also be useful to include additional functions - the angle of the accelerator pedal, the torque value, the coolant temperature, and so on. This will be useful for understanding the dynamics of the turbine.
- When driving a car, the corresponding turbine pressure will increase and will be about 2...3 bar (200...300 kPa) depending on the type of turbine and driving mode.
It is recommended that before purchasing a used car, you check all its systems, including the turbine, not only visually and tactilely, but also using the described software tools like Vasya Diagnostic.
Common turbine actuator malfunctions
There are three main reasons why a wastegate breaks:
- The electronic components of the system component, which are responsible for its timely opening/closing, fail;
- The teeth of the drive gear break, which leads to difficulties when opening and closing the valve;
- Failure of the electric motor, which is responsible for the operation of the sash, as a result of which the system does not function properly.
In a specialized service center, you can eliminate all the problems described above, but it is important to note that first you need to correctly diagnose the breakdown, which will require special testers. Accordingly, independent repair of the turbine actuator is often impossible due to the lack of necessary equipment.
Most often, when a turbine valve fails, it is more advisable not to repair it, but to replace it. This is especially true when cuffs or valve stem seals fail and cannot be replaced. In this case, you will need to remove the turbine actuator and install a new one in its place. This is done as follows:
The first step is to remove the old cuff from the case;
- Next, it is extremely important to degrease the surfaces so that they are tightly bonded to each other;
- After this, using sealed glue, you need to stick a new cuff onto the body with two caps;
- To create the necessary vacuum, a gap is created between the caps, at the same time additional lubrication is provided;
- Next, the membrane is attached using glue, and it is important to roll it around the entire circumference.
At this point, the installation of the activator can be considered complete. All that remains is to configure it so that it works correctly with the system.
Removal algorithm
As for removing the element, with all three replacement methods without removing the panel, dismantling is performed in the same way. The algorithm for removing the heater radiator is as follows:
- Drain the antifreeze from the cooling system.
- We dismantle the engine air filter along with the air duct.
- Disconnect the battery terminals and remove the battery from the car.
- Remove the battery mounting plate.
- Under the steering rack we find two pipes through which coolant is supplied to the heater radiator, loosen their clamps and pull the tubes off the fittings.
- Near the fittings we find a nut that secures a mounting plate with a rubber seal through which the heat exchanger fittings pass to the engine shield. unscrew this nut.
- Let's go to the salon. On the driver's side, remove the decorative side trim of the center console.
- Unscrew the gas pedal and move it to the side.
- We remove the brake light sensor located near the brake pedal.
- Since it will not be possible to remove the brake pedal without dismantling the steering column and mechanism, we do this. We remove the bracket for fixing the pin that connects the brake pedal to the vacuum booster, remove the pin and bend the stop plate of the brake light sensor. After this, we lift the pedal up and it does not interfere with removing the radiator.
- Unscrew the three screws securing the radiator to the body.
- Since the radiator outlet is blocked by fittings, they need to be sawed off or broken off.
- After sawing off the fittings, the radiator will “come out” of the seat.
But dismantling the heat exchanger is only half the battle; you still need to install a new element, but the fittings prevent this from being done.