Hello, dear motorists! Today's topic is devoted to a small part, which, if it malfunctions, can cause you unpleasant moments and an uneven running car engine.
Let's consider the role played by the camshaft position sensor (camshaft), the causes and signs of its malfunction, and, of course, how to replace the camshaft sensor with your own hands.
While the principle of operation of the camshaft sensor is almost the same, its location depends on the type and model of the engine. Therefore, when checking faults and replacing the sensor yourself, start with the manual in your hands.
What is a camshaft sensor
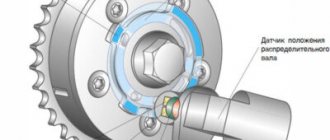
Camshaft position sensor
The camshaft position sensor performs the task of determining the angular position of the timing belt, corresponding to the position of the engine crankshaft. The engine management system, receiving information from the camshaft (camshaft) sensor, performs fuel injection and ignition.
The operation of the camshaft sensor is based on the Hall sensor principle. That is why the camshaft phase sensor is sometimes called a Hall sensor.
The operation of the Hall sensor is based on measuring the direction of movement (voltage change) of charge carriers. The change is recorded at the moment the semiconductor crosses the magnetic field. A permanent magnet placed in the sensor creates this magnetic field.
A metal tooth (reference mark) placed on the camshaft gear (or on the drive disk) closes the magnetic gap. And, when the reference passes by the camshaft sensor, it causes a voltage pulse in the sensor, which is then transmitted to the electronic control unit.
Voltage pulses are supplied at different times. The ECU recognizes the position of the piston of the first cylinder of the engine at TDC (top dead center) of the compression stroke, and ensures the injection and ignition of the fuel mixture.
For engines with a variable valve timing system, the sensors are installed on the camshafts of the intake and exhaust valves.
The camshaft timing sensor on a diesel engine measures the position of the pistons of each cylinder at TDC on the compression stroke.
How to check the camshaft sensor
When the Hall sensor occurs, we receive a signal from the malfunction indicator. It should be noted that the camshaft sensor is functionally connected to the crankshaft sensor. And while driving, if a malfunction of the camshaft sensor occurs, the control system reads information from the crankshaft speed sensor. The engine is even able to restart after stopping.
Checking the camshaft sensor is based on the driver’s knowledge of typical malfunctions and their symptoms. And after identification, the logical action is to replace the camshaft sensor.
What are the typical causes of camshaft sensor failure?
- the toothed disk of the pulse sensor is broken,
- the mounting ears have ruptured, the sensor has moved,
- short circuits in the internal circuit of the sensor,
- increase in engine temperature.
Typical symptoms of a Hall sensor malfunction
- the engine ECU operates in emergency mode,
- fuel consumption increases noticeably,
- The engine control light on the panel lights up,
- a fault code is registered.
Naturally, you will not be able to determine a sensor malfunction by eye. To do this, you will have to contact a car service for testing. Checking the signal reception from the sensor is carried out using an oscilloscope. During the memory test, a complete list of faults will be shown.
Visually, you can only check for external mechanical damage to the sensor, clean the sensor head, check the electrical circuit: for breaks, for correct connection of the connection connectors.
Replacing the camshaft sensor is a completely do-it-yourself task. Before purchasing a new sensor and replacing it, use the car manufacturer's recommendations from the manual, use only those parameters specified by the manufacturer.
Characteristic symptoms of the problem
Practice shows that a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor does not lead to engine failure and immobilization of the vehicle. The engine continues to operate with some deviations that interfere with the normal operation of the car. Symptoms of DPRV failure are quite vague and similar to problems with other measuring elements:
- Unstable engine operation at idle and while driving.
- Instead of dynamic acceleration, after pressing the gas pedal, there is a series of small jerks and a sluggish increase in speed.
- The power of the power unit decreases. The effect becomes noticeable when the load increases - on a hill, sharp acceleration, while towing a trailer.
- The Check Engine light on the dashboard does not always come on. But many drivers note that if the meter is faulty, the display flashes after the crankshaft speed increases to 3000 rpm or more.
- Fuel consumption is naturally increasing.
If the measuring element is faulty, the control unit prepares and supplies an enriched air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. This results in an increase in gasoline consumption and unstable idling. Jerks and drops in power are caused by untimely supply of a spark - the controller “does not see” the end of the compression stroke in the cylinder and cannot clearly determine the ignition timing.
On various car models, additional symptoms of a malfunctioning camshaft sensor are noted:
- the engine suddenly stalls while driving, but starts without problems;
- cold starting of the engine becomes difficult;
- on cars equipped with a robotic gearbox, difficulties arise with automatic gear shifting;
- the engine “troits” - skipping ignition cycles is heard, sometimes popping sounds are observed in the exhaust manifold;
- On some cars, the power plant fails due to lack of sparking.
Reference. The service life of the element is quite long. On domestically produced cars, the resource reaches 80–100 thousand km, on imported cars – 150 thousand km. When searching for the causes of a malfunction, you can focus on the specified periods.
Driving with a broken air pressure sensor is acceptable for a short period. Jerking, rich fuel mixture and electronic errors accelerate the wear of spark plugs and engine parts. After detecting the listed symptoms, you should send the car for diagnostics or find the source of the problem yourself.
Operating principle of the sensor
General view of the camshaft sensor
The camshaft sensor or phase sensor is a part of the main power unit of the car, which is responsible for reading information about the location of the camshaft and is also involved in adjusting the ignition angle.
This meter is similar in principle to a Hall sensor .
We recommend: Electronic control unit - what controls the engine?
Reading occurs using a special camshaft gear that has no teeth. The missing elements are located in such a way that when this gap hits the sensor, the first piston is at the dead center, at the top or bottom.
Phase sensor operation diagram
A signal is triggered and transmitted to the engine's electronic control unit when the sensor hits the missing teeth. In turn, depending on the received indicator, the ECU adjusts the ignition angle. Thanks to the installation of such a system, Samara-2 engines have become more efficient and popular.
Location of the sensor under the hood of the VAZ-2114
The camshaft sensor on the VAZ-2114 is located near the air filter, at a very close distance from the cylinder head. This meter location is almost always standard for other cars in the injection group.
Camshaft sensor location
The main reasons for sensor failure
Before proceeding directly to the diagnostic process, it is necessary to find out the causes of the malfunction of the VAZ-2114 phase sensor.
So, let's move directly to the most direct and indirect indicators:
Electrical circuit of the sensor
- Check Engine on the dashboard indicates that a malfunction has occurred. In this case, the engine starts without waiting for a response from the camshaft sensor, and the ignition system works based on the latest indicators.
- Increased consumption of the fuel mixture can also serve as an indirect indicator of a malfunction of the air flow control valve.
- The car begins to lose power and dynamics as a whole.
The combination of these reasons can serve as an indirect indicator of a malfunction of the camshaft sensor.
What is a camshaft position sensor
The camshaft position sensor is also called the cylinder sensor or camshaft sensor. In sequential fuel injection systems, the electronic control unit must determine which cylinder should be injected next. This information affects engine operation and comes from the DPRV. As the engine rotates, the DPRV sends a signal to the on-board computer whenever a particular cylinder is at top dead center (TDC). Thus, the duration of pulse injection is estimated, for which the camshaft sensor is responsible.
In simultaneous fuel injection systems, the on-board computer is not used to determine the cylinder and injection order, since this is not necessary for the operation of the system. When a signal is received from the crankshaft or distributor, the exact cylinder is determined by recognizing the mechanical positions of the crankshaft, camshaft and valves.
Types of sensors used
The most popular are 2 types of DPRV, which look almost the same and differ slightly in design:
- inductive;
- Hall Sensor.
An inductive sensor is needed to register the cylinder and can be located inside the camshaft. Therefore, a device with a magnet is mounted near it. Each time a magnet passes through the DPRV, its magnetic field changes and the resulting pulse is sent to the on-board computer for subsequent processing.
The Hall sensor may be located inside the camshaft. A screen with a socket and a magnet is installed on the shaft. When the screen passes between the magnet and the hall sensor, the DPRV turns on and off. While the socket is in front of the DPRV, the voltage returns to the amplifier through the third signal cable. As long as there is a solid sector of the screen in front of the sensor, the feedback voltage is interrupted as the magnetic field disappears.
What does the performance of the DPRV depend on?
The performance of the DPRV depends on the temperature conditions. Overheating will damage it. The sensor will not work if the wires through which it transmits and receives the signal are faulty, or the reference point is broken. Damage or contamination of the sensor itself plays an important role. Also, under difficult operating conditions (off-road driving, cargo transportation), the sensor may move or, even worse, a short circuit may occur. In order to eliminate sensor failure at the most inopportune moment, diagnose it and replace it after 4-5 years.
Main sensor malfunctions and their causes
The main symptoms of a malfunctioning camshaft sensor:
- the “check engine” signal comes on and driving dynamics deteriorate;
- the number of revolutions increases or decreases independently;
- a warm engine is unstable at idle speed;
- under dynamic loads, detonation occurs in the power plant;
- higher fuel consumption;
- The engine does not start.
If you notice such symptoms, check how the camshaft sensor is working. It may have failed and needs to be replaced. The causes of sensor malfunction can be: failure of the disk with reference points, displacement of the DPRV installation, short circuit inside the device, overheating of the motor.
How to check the camshaft sensor
Before checking the camshaft sensor with a tester, you need to visually inspect the sensor housing and gear rotor for damage or the presence of metal shavings. This may also be the reason for its malfunction.
Important! Be sure to turn off the ignition before starting the test. After this, start disconnecting the wires from the device.
Diagnostic tool
To check the camshaft sensor you will need: a multimeter/tester, pliers and a screwdriver. The multimeter/tester will guide you to perform a detailed test of the device. It will show exactly what is wrong with the sensor itself or the wiring.
Test scheme
Before starting to diagnose the sensor, examine the connector which should have: positive, negative contacts and a contact for signal transmission.
1. Turn the ignition on and check the camshaft sensor with a multimeter. Connect the tester ground to the engine ground. The measurement must correspond to the voltage readings at the battery terminals. If the readings do not match, then the sensor's power supply circuit has failed.
2. After this, measure the voltage at the sensor ground in a similar way. The voltage should be zero.
3. Connect the positive and negative wires of the camshaft sensor. Connect the middle contact through the tester. Thus, we connect one wire of the multimeter to the signal terminal of our sensor, the other needs to be powered to the input to the control system.
4. After this, crank the engine with the starter. If the sensor is working, it will show a voltage from 0.4 to 5 volts. If the values are different, the sensor should be replaced.
If, after checking, you find the cause of the breakdown in the sensor itself, do not delay replacing it. Without it, the engine will work, but in emergency mode, fuel consumption will increase significantly, since fuel is now supplied to all cylinders simultaneously.
Did you know? Some car enthusiasts completely forget about the possibility of failure of the camshaft sensor because they rely on its durability. And it can fail at any moment
Instructions for checking and replacing
If the above methods failed to normalize its condition, then this part must be replaced. There is nothing complicated in replacing, as well as in checking, since their camshaft is mounted without adjusting the gap. Thanks to this function, you can avoid mistakes when installing a new device. If the gap is adjusted, certain standards must be observed.
If you are not sure that replacing the camshaft sensor yourself will be successful, take it to a special service center. There the replacement is made using an oscilloscope. When starting the oscilloscope, stability of data reading is observed at different engine speeds.
If you have an oscilloscope and you are confident that you can do such a procedure, do it. Just pay close attention to the changing data that the oscilloscope will show. If it shows straight stripes and there are no gaps, that's good. Because you just have to remove the old one and install a new one.
In principle, if you use this method, you need to take into account many points and features that the tester provides in order for the replacement of this camshaft part to be successful. Since, if the indicator does not work, then, logically, the engine should not work. But technology is a delicate matter, and sometimes it malfunctions. If the sensor and built-in electrical devices do not know the location, they go into an emergency state. And, being in this state for a long time, the sensor fails.
We recommend: Computer engine diagnostics - what errors can be identified?
How does the camshaft sensor work?
Based on the principle of operation, DPRVs are classified into 3 types:
- magnetic dprv;
- optical dprv;
- dprv Hall.
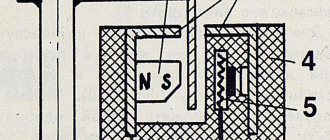
A magnetic or induction camshaft position sensor works because a metal tooth is constantly moving in a magnetic field. This sensor has two outputs.
The operating principle of an optical sensor works by emitting a beam of light from a source, which is tracked and recorded by reception and interruption by a photocell.
A Hall effect sensor monitors changes in the magnetic field around it. Hall-effect DPRVs have three outputs. The Hall effect is also called Hall voltage.
The most rarely used camshaft position sensors are optical ones. Don’t be surprised if the car has more than one or even two DPRV sensors, this is also possible.
What have you heard about the safety of the SRS system? It consists of impact sensors, actuators and an SRS control unit.
The principle of operation of a Hall sensor is that it detects changes in voltage that crosses its magnetic field. The sensor structure contains a piston magnet and a semiconductor element, which records voltage changes. If the magnetic field does not change, then the sensor will not detect any changes. The magnetic field will only change if there is any metallic element in that environment. The notches or teeth on the camshaft are precisely metal elements that change the magnetic field.
As was already mentioned above, the DPRV is also called a phase sensor. This name comes from the fact that the sensor records the cylindrical phases of intake and exhaust.
Replacing the RV position sensor
If during the inspection it turns out that the camshaft position sensor itself has failed, then it must be replaced. As a rule, these units are non-repairable, since their body is sealed and cannot be disassembled. The sensor is inexpensive, and the replacement procedure is simple, and even a novice car enthusiast can handle it.
The sensor replacement algorithm is as follows:
- With the engine not running, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect the “chip” from the camshaft position sensor (as when checking).
- Depending on the vehicle model, it is necessary to remove parts that prevent access to the sensor. For example, on modern cars like the Lada Vesta, it is necessary to remove the bracket for auxiliary units.
- Using a wrench, unscrew one or two mounting bolts, depending on the type of fastening. The size of the wrench can be different, usually for VAZs it is a 10 mm wrench.
- After dismantling the mount, you must similarly remove the sensor from its seat.
- Installing a new sensor is performed in reverse order.
- Connect the negative terminal to the battery.
When purchasing a new camshaft position sensor, you need to pay attention to the condition of its O-ring. It is usually sold separately. When changing the sensor, it is advisable to also change the O-ring, since over time it wears out and loses its elasticity. You can use an old ring only in case of emergency, when it is not possible to buy a new one.
Conclusion
The camshaft position sensor is a simple but important device in the engine, and the normal functioning of the engine depends on its operation. Therefore, when identifying signs of its failure, it is advisable to carry out the appropriate diagnostic procedures as quickly as possible. They are simple, and even a novice car owner with no experience can handle them. The same goes for replacing it. The price of a phase sensor for VAZ cars as of winter 2019 is about 400 rubles.
Hello, dear motorists! Let's continue the theoretical work on engine tuning. More specifically, camshaft tuning. You have already made your choice of a sports camshaft. We have already realized that without a split gear, all efforts to optimize valve timing are in vain.
Troubleshooting DPRV
If the Check Engine indicator on the panel has already come on (it may not be lit constantly, but may appear periodically), you just need to read the fault code using a diagnostic device. If you do not have such a device and it is impossible to buy it, you need to contact a specialist.
After receiving the exact fault code and decoding it, we recommend performing several simple tests. The presence of one of the above DPRV fault codes does not always indicate that the sensor must be replaced. Sometimes the source of the problem is damage to the wiring, connector, etc. It is quite possible to fix such problems on your own.
But to check the functionality of the camshaft position sensor itself, you need to perform several steps. Of course, it is difficult to check the signal without special equipment. But checking the camshaft sensor with a multimeter will provide basic information.
First, visually check the condition of the sensor connector and the wires that go to it. Make sure there is no dirt, oil or rust that could cause problems. Check the wires for damage. Sometimes problems are caused by broken wires, poor connections, or defects in the insulating layer caused by exposure to elevated temperatures. The DPRV wires should not come into contact with the high-voltage wires of the ignition system.
After that, we pick up a digital multimeter; it “knows how” to check the value of alternating and direct current (AC and DC, respectively). But you need to obtain information in advance about what these indicators should be for the sensor used on your car.
Some sensors have connectors designed so that you can connect additional wires to them to read data with a multimeter.
If this is not possible, try disconnecting the DPRV connector and connecting thin copper wires to each terminal of the connector. After this, install the connector in place so that two wires protrude from its body.
Another option is to pierce each of the wires with a needle or pin (do everything carefully so as not to short the wires!). After such a diagnosis, damaged areas of insulation should be well wrapped with electrical tape to prevent moisture from getting inside.
Checking the two-wire camshaft position sensor:
- If your car uses an electromagnetic DPRV, switch the multimeter to AC mode.
- Another person must turn the ignition on by turning the key in the lock without starting the engine.
- Voltage should appear in the circuit. Connect one of the multimeter probes to ground (any metal component of the engine), and connect the second one in turn to the camshaft sensor wires. The absence of current on all wires indicates a problem in the wiring that goes to the sensor.
- Ask the person in the car to start the engine.
- Touch one multimeter probe to one wire of the DPRV connector, and the other to the other. Values will appear on the device screen, which should be compared with the operating readings given in the car’s operating instructions. As a rule, the readings on the screen vary within 0.3-1 volts.
- The absence of a signal indicates a malfunction of the camshaft sensor.
Checking a three-wire DPRV:
- Identify the power, ground and signal wires (use the repair instructions), and then check the integrity of the wiring that goes to the sensor. The multimeter must be switched to DC mode.
- Another person must turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- We connect the black probe of the multimeter to “ground” (any metal part of the engine), and the red probe to the power supply wire of the DPRV. The results obtained should be compared with the data in the operating instructions.
- An assistant must start the engine.
- Touch the red probe of the multimeter to the signal wire of the DPRV, and connect the black probe to the ground wire. If the sensor malfunctions, the voltage will be lower than stated in the repair manual. Sometimes the multimeter does not show anything at all, which also indicates a sensor failure.
- Remove the DPRV and check the element for mechanical damage or contamination.
Below is a video that clearly demonstrates how you can conduct such tests. In some cases, the electrical circuit is working properly, and the sensor also gives correct readings during tests. The question arises: why do errors and problems appear in engine operation? Sometimes the causes are related to other engine components. Errors may appear due to a loose timing belt or a faulty tensioner. Because of this, the DPRV will transmit the wrong signal.
Replacing the Lacetti camshaft sensor
Removing the decorative trim of the engine
Next, disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
But I advise you not to do this. Because we will remove the sensor through the top and the wires will help us with this. The wires will also hold the sensor so that it does not fall down when we unscrew the bolts that secure it.
Next, remove the air filter housing. To do this, unscrew the collar securing the corrugation with a screwdriver and disconnect the corrugation from the air filter housing.
Then we tighten two bolts (one with a 10 mm head, and the other with a 12 mm head) securing the housing and remove the housing.
The next step is to remove the upper timing case. It is secured with three bolts.
The first one is here
The second one is here
The third one is here
A 10 mm socket wrench works well for this.
Next, move the cooling system hose towards the engine, unfasten the casing and remove it.
We see the camshaft sensor and two bolts securing it.
Next we have two options. The fact is that the bolts are in a very inconvenient place and the support bracket prevents them from being unscrewed normally.
Therefore, you need to decide how to proceed:
- We hang the engine and unscrew the support bracket. After this, we quite easily unscrew the sensor mounting bolts.
- Using sleight of hand and a suitable tool, unscrew the sensor mounting bolts. It will be difficult, but possible.
Personally, I always choose the second option.
To do this, the first and mandatory action will be to seal all the voids under the sensor with a rag, so that accidentally dropped bolts or keys do not cause us trouble. Since to get them out you will have to remove the lower timing case with all that it entails.
Attention! The rag must be absolutely clean so as not to contaminate the timing belt!!!
Next, use our 10 mm socket wrench to unscrew the top bolt.
If suddenly your key is a little thicker and does not fit a little to fit it onto the bolt head, then engage fifth gear and slightly rock the car back and forth. This is necessary so that the camshaft pulleys rotate and the groove, and not the pulley tooth, hits the key. This will help you win a little more space and perhaps it will be enough for you.
If you do not have miniature fingers, then unscrew the bolt only a couple of turns. And then we hook it with soft wire
This will allow you to easily unscrew the bolt completely and pull it out by the wire. This is a 100% guarantee that it will not fall anywhere.
Using the same wire, it is easy to install it to screw in the new sensor, since fingers cannot fit in there.
Unscrew both bolts in this way and remove the camshaft sensor
Unplug it from the connector and throw it away.
Note: Pay attention to the condition of the wires. They dry out and begin to crack, which leads to short circuits! This problem must be eliminated!
We take a new original camshaft position sensor. Exactly original! Don't skimp on DPRV, DBP and crankcase ventilation valve. Their cheap counterparts don't work.
The original sensor costs 1000 UAH (40 usd or 2540 rubles). The analogue is three times cheaper, but at best it will blow your mind. And in the worst case, the car will be burned.
Check that the plate is straight and not bent
This affects the gap between the sensor and the pulley.
We connect the sensor to the connector and install it in place.
Important! Before tightening the bolts, move the sensor as far to the right as possible! So that it is as close as possible to the right pulley. The video clearly shows how much play the sensor has in its seat.
After this, we start the engine and check its operation. If everything is fine, then we assemble everything in the reverse order.
Meter design and location
The operating principle of the DPRV is based on the Hall effect - the sensor reacts to the approach of a metal mass by changing the voltage on the signal wire. The design of the device is similar to another element - the crankshaft position detector. Inside the plastic case there is a coil where the 12 V on-board voltage is constantly supplied.
The meter is installed on the engine cylinder head in close proximity to the camshaft. The latter is equipped with a special plate or gear, whose rotation affects the DPRV. The work algorithm looks like this:
- After turning on the ignition and starting the engine, a 12 V supply voltage is supplied to the sensor. Through the third signal wire, the element supplies the controller with a voltage of 90–95% of the original one.
- When the protrusion on the rotating part of the camshaft passes next to the DPRV housing, the voltage at the signal contact drops to 0.2–0.4 volts, depending on the design of the device and the vehicle model.
- When the voltage drops, the electronic unit clearly “sees” the valve timing, promptly supplies the fuel mixture to the engine cylinders and directs the spark discharge to the desired spark plug.
Note. On cars with 16-valve engines, 2 sensors are installed - one for each camshaft.
When the meter is faulty, the electronics are unable to control the operation of the gas distribution mechanism. In such cases, the control unit goes into error and is guided by the signals of other meters. Spark generation and fuel supply are adjusted according to the programmed program, which affects the operation of the power unit.
We recommend: The most reliable and durable engines
What is a camshaft sensor, the principle of operation of the camshaft sensor
To understand the operation and principle of operation of the device, you need to know where the camshaft sensor is located. The sensor is located on the side of the pump and power steering pulleys. The sensor axis always corresponds to the direction of the camshaft axis.
The camshaft sensor is a device that ensures the normal operation of the car engine. It determines the angular position of the timing mechanism in relation to the position of the crankshaft. After this, information from the sensor goes to the engine management system to control fuel injection.
To answer the question: “What is a camshaft sensor for?” You need to understand the principle of its operation. The sensor itself contains a magnet that creates a special magnetic field. A reference point (pin or metal tooth), which is located on the master disk. It closes the magnetic gap and changes occur in the magnetic field.
The engine control unit, having received a signal from the sensor, receives data on the position of the piston of the first cylinder. After this, the control system sets fuel injection and ignition of the fuel mixture, according to the operating order of the engine cylinders.
Important! If you notice that the camshaft position sensor has failed, you need to replace it as quickly as possible to reduce fuel consumption and normal vehicle operation.
Checking the performance of the camshaft position sensor without diagnostics
First of all, you need to find out where the phase sensor is located on your car model. You will not be able to find this information in the instruction manual; repair and maintenance literature is required. For example, let's look at the photo of the location of the DPRV in the engine compartment of a VAZ 2112:
The oval connector with three pins is in the center of the illustration.
Checking the phase sensor begins with an external inspection. Before removing the sensor, you need to make sure that the housing, connector are intact, and that there are no signs of burning or technical fluids. Since the device is located under the hood and is not protected from external influences, the cause of the malfunction may be a simple break in one of the wires.
Even if the wiring looks good, it is recommended to check it with a multimeter in the area from the sensor connector to the electronic engine control unit block. After connecting the tester terminals to the connector contacts, ask an assistant to move the cable to look for hidden breaks. After which you need to check the cleanliness of the contacts: they may be oxidized.
Another reason for the malfunction, which does not manifest itself clearly, is the presence of an extraneous pulse signal that affects the transmission of information along the data cable. These could be impulses from the injector control wires or high-voltage spark plug wires. To eliminate the negative impact, it is necessary to bring the wiring of all wires in the engine compartment to the standard layout. No foreign wires should be attached to the DPRV cable, especially from non-standard devices: xenon control unit, parking sensors, additional sound signal. Noise from these devices is difficult to diagnose, but can have a negative impact on the operation of the phase sensor.
What are the reasons for the malfunction of the DPRV?
If the camshaft position sensor fails, the injector will fire for each crankshaft revolution, that is, twice as often.
Symptoms or signs of a broken sensor:
- Fuel consumption increases significantly.
- The engine operates asynchronously while driving, that is, it jerks while moving, drives jerkily, and loses speed. The engine may stall as if it has run out of gas. Also, sometimes the car cannot reach a high speed, more than 60 km/h. Cars are equipped with speed sensors. Find out what causes problems with their operation and how to check speed sensors.
- On certain brands and models of cars, if the DPRV is faulty, the gearbox may stall. The way out of a locked gearbox is to restart the engine. If this happens constantly, then you have definitely exited the CMP operating mode.
- When diagnosing yourself with a scanner, malfunctions may occur.
- The spark may also disappear and the engine may not start.
- The check light comes on at idle, but goes out at high speeds.
Such reasons for a non-working sensor are shown on the instrument panel with the corresponding icons. When the DPRV (SMR) is not working, the control unit will record the incorrect operating mode and issue a specific error code. To decipher error codes, you can download the application to your phone or tablet and find out what exactly this error code means.
Here are the most frequently encountered errors:
- P0365 means there is no signal in the camshaft position sensor circuit.
- P0344 warns that the signal supplied by the sensor is weak and intermittent.
- P0343 The signal supplied by the CMP sensor is too high.
- P0342 says the DPRV single level is too low.
- P0341 The valve timing does not correspond to the state of proper engine operation.
- P0340 There is no signal from the sensor at all.
- P0300 stands for a violation of ignition cycles in the ignition system (ignition is often skipped).
Factors influencing the occurrence of reasons indicating a non-working condition of the camshaft position sensor:
- Signal wires are not connected to the sensor.
- There is moisture in the sensor connection.
- The signal wire touches ground (some metal object in the car).
- The signal wire is open and torn off.
- The signal wire closes to the on-board network.
- The sensor insulation is broken, the shielding shell or harness is broken.
- The sensor power cord is torn or damaged.
- The power cables are not connected correctly.
- The high-voltage wires of the ignition circuit are faulty.
- The engine control unit is not working correctly.
- The gap between the sensor and the mark is not in accordance with the norm (the gap is too large or too small).
- The camshaft gear “beats”, that is, it has an exceeded standard of end runout.
- There are metal shavings on the DPRV body.
What happens if the camshaft position sensor malfunctions?
In this case, the engine control unit will continue to analyze information from the crankshaft sensor in a truncated form. That is, the synchronization of the shafts will be disrupted, and the engine will go into an abnormal mode of pairwise parallel fuel supply. This algorithm provides for the injectors to fire twice as often. Accordingly, more fuel will be needed to partially maintain power. In addition, unburned gasoline will end up in the catalysts and exhaust pipe. This malfunction will lead to accelerated wear of the exhaust system with subsequent breakdown of expensive components.
Symptoms of sensor failure
Of course, the list of problems intersects with breakdowns of other components related to the operation of the intake and exhaust systems. Therefore, accurate diagnostics can only be obtained by connecting a car scanner. However, these signs will certainly appear if the DPRV is still faulty:
- unreasonably high fuel consumption;
- the exhaust is dirty, with a pronounced smell of unburnt gasoline;
- jerks in the operation of the internal combustion engine, similar to “triple”;
- at idle speed the engine periodically stalls;
- in cars with an automatic transmission, the transmission control unit can put it in emergency mode (after turning off the engine, the error is reset, then appears again);
- “Check-engine” alarm on the dashboard.
In addition, checking the camshaft sensor is carried out by any available diagnostic program when connected to the OBD port.
Tip: If you notice signs of malfunction or malfunction of the camshaft sensor, have it diagnosed immediately. You can contact a car service or perform a check in a garage.
Operating a vehicle with a faulty or disconnected camshaft position sensor can result in costly repairs.