Types of cooling systems
There are three types of automotive cooling systems:
- air;
- liquid;
- combined.
Air systems are open type systems. They remove heat from heated engine parts with a directed air flow. The liquid system is of the closed type. It removes heat using antifreeze that continuously circulates in the engine cooling jacket. Combined systems combine both liquid and air cooling methods. The vast majority of modern passenger cars, both diesel and gasoline, are equipped with liquid cooling systems. They are used for two reasons:
- high efficiency;
- minimum noise level.
Basic elements of liquid cooling systems for cars
The liquid cooling system of any modern car consists of the following elements:
- engine cooling jacket;
- thermostat;
- central radiator with fan;
- oil radiator;
- stove radiator;
- expansion tank;
- cooling pump.
The cooling pump can rightfully be considered the main element of the automotive cooling system. After all, without this device, all other parts of the system simply will not be able to function, and any malfunction of the unit entails overheating of the motor and its failure. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at the water pump.
Consequences of untimely replacement of the water pump
After the main issues related to the design, operation and malfunctions of the water pump have been considered, it is worth considering the consequences of untimely replacement of the product.
Many motorists, after the appearance of a whistle or pump leakage, continue to drive in such a faulty technical condition, without thinking about the consequences of this. Thus, there are indirect signs that the situation has reached a critical point.
For example, a constantly running cooling fan may not only indicate an inoperative thermostat, but also a lack of “cooling” in the system due to the fact that it is leaking from under the pulley.
So, let’s consider what consequences a motorist should prepare for if a unit is not repaired in a timely manner:
- Constant fluid leaks reduce the level of coolant in the system, which first leads to constant operation of the thermostat and topping up fluid, and then to overheating.
- In turn, overheating is fraught with serious consequences, such as damage to the internal elements of the cylinder head. The worst option is the deflection and deformation of the cylinder head plane, which entails other terrible consequences.
- Also, constant overheating causes cracks to appear in the body of the cylinder head and cylinder block, which are quite difficult to eliminate.
- The worst consequence is that after the cylinder head is deformed, the coolant can go inside the combustion chambers, and this is a water hammer, the consequence of which is a complete and irrevocable overhaul of the power unit or replacement of the engine altogether. This can seriously hit the owner's pocket.
Based on the above, repairs to the cooling system water pump should be carried out on time, when the first signs of a malfunction are detected. If this is not done, the consequences can be disastrous for the engine and the vehicle owner.
Purpose of the pump
The water pump ensures continuous circulation of antifreeze in the cooling jacket of the internal combustion engine. Under the pressure created by the pump, the coolant, heated by the rubbing parts of the engine, enters the central radiator.
Pump for VAZ 2110, new, in packaging
There it cools down, and then goes back into the cooling jacket. If this antifreeze cycle is interrupted for just 5 minutes, the engine will definitely overheat. In essence, a water pump is an ordinary centrifugal pump that creates excess pressure using a steel impeller that rotates at high speed.
Purpose and location of the element
The coolant is unable to circulate through the radiator and engine water jacket on its own. To encourage it to move, the system uses a pumping device - a pump, whose impeller (impeller) is rotated by a belt drive from the crankshaft. Depending on the design of the vehicle, the pump is located in the following places:
- In front-wheel drive cars, the element is located on the right side of the engine (if viewed in the direction of travel). Since the pump is part of the timing belt drive, protected by a cover, it cannot be seen from the outside.
- On vehicles equipped with rear-wheel drive, the pump is located at the front of the power unit and is driven by the timing belt or alternator drive.
A pump built into the engine design is needed for effective cooling of the block and cylinder head by creating forced circulation. Thanks to it, the flow of antifreeze passes through 2 radiators - the main one and the cabin one, where it gives off the lion's share of the heat.
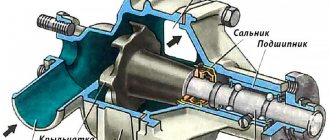
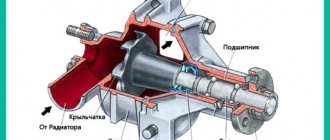
Water pump design
Cooling pumps installed on the vast majority of passenger cars have a similar design. There is a pump housing, it contains a central shaft on which a steel impeller is attached. The shaft is suspended on two bearings, next to which there is an oil seal that prevents coolant from leaking out of the housing. There is a hole in the housing cover. Through this hole, the end of the central shaft is brought out, where a toothed pulley is installed on it. A timing belt is put on this pulley, which ensures the rotation of the shaft with the impeller.
Most water pumps on modern cars have a similar design.
However, not all passenger cars have the water pump shaft rotated by the timing belt. On some engines, the pump may be equipped with its own drive. But this design is gradually becoming a thing of the past, and automakers are increasingly giving preference to a single timing belt that rotates both the camshaft and the water pump shaft. Because this design is simpler and, most importantly, cheaper.
Signs of a pump malfunction
During the operation of the car, the water pump wears out naturally. The two parts that experience the greatest load are the bearing and the oil seal, and they most often fail. The impeller and pulley break much less often. Problems appear like this:
- Antifreeze stains appear at the permanent location of the car.
- The end wall of the motor and nearby units are splashed with coolant. If the mechanism is protected by a casing, antifreeze drips in the lower part become noticeable.
- When the engine is running, a hum or crackling sound is heard from the pump.
- The power unit stalls while driving, and the coolant temperature rises to the maximum.
Spots appearing under the car should always alert the driver . If the engine compartment is dry and there is a noticeable leak on the asphalt, remove the protective cover of the gas distribution mechanism. If you find dampness in the pump area, perform a simple diagnosis: loosen the drive belt and pump the pumping device pulley by hand. Noticeable shaft play is a clear sign that it is time to change the engine cooling system pump.
If you are able to hear a noise made by a broken pump bearing, immediately have it checked for play. The test method is identical: you need to get to the pulley, loosen the tension on the belt drive and rock it by hand.
When the engine stalls while driving and the sensor shows a temperature of more than 120 °C, it means the worst has already happened. The pump shaft is jammed and the timing belt has broken or jumped off. We can only hope that the engine valves do not meet the pistons and become bent.
If the generator drive belt breaks, the engine will not stall, but the battery charging indicator will turn on, and the temperature will inevitably rise (after all, the pump has stopped pumping liquid). Immediately turn off the engine and take measures to evacuate the car to a garage or service center.
Turning the pump on and off
Since the pump is connected to the camshaft through the timing belt, it begins to rotate simultaneously with it, that is, immediately after the engine starts. The pump also stops simultaneously with the motor
Features of additional water pumps
It is important to note that the above rule does not apply to additional water pumps that drivers install on cars themselves (usually this is done in order to improve the performance of the heater).
Pumps from BOSCH are installed to improve heating of the car interior
The additional pump can be turned on and off whenever the driver wants it, because it is almost always equipped with a special relay with a shutdown button.
Pump operating principle
When the engine is started and the liquid pump begins to operate, then the rotation of the impeller from the drive (in most cases provided by a belt from the crankshaft pulley) creates a vacuum at the pump inlet. Thanks to this, the coolant that is in the radiator and expansion tank is supplied to the pump. Next, the liquid ends up inside the pump and hits the impeller. After it passes over the impeller blades, centrifugal force will throw the coolant out of the pump. From there, the liquid will enter the cooling jacket of the power unit cylinder block. If we trace in more detail the path of coolant in the system after starting the internal combustion engine, we get the following:
- The liquid located in the lower radiator reservoir passes through a channel in the center of the liquid pump housing into the pump.
- The rotation of the impeller creates a centrifugal force that literally throws the coolant towards the walls of the pump housing. Since pressure created by the pump has appeared in the system, this pressure ensures that coolant is pumped through a special channel into the distribution tube, which is located in the cylinder head of the engine.
- Through the hole in this tube, the coolant will first end up in the pipes near the heated exhaust valves.
The specified pattern of fluid movement in this sequence ensures immediate and priority cooling of precisely those parts of the power unit that heat up the most. The liquid then follows along the engine jacket, cooling the remaining heat-loaded elements of the motor.
If the main thermostat valve is closed, then the coolant passes through the cooling jacket and enters the bypass channel, through which it is returned back to the centrifugal liquid pump. If the thermostat is open, then as the fluid moves in a large circle, it flows back into the pump from the lower radiator tank. The liquid supply is realized through the lower supply pipe.
Systems with additional pump
There are engine cooling systems in which two coolant pumps can be installed at once. If the main pump is responsible for the main function, then the additional pump can perform one of a number of functions depending on the design of the engine itself:
- Providing additional engine cooling, which is important for countries with high year-round outdoor temperatures.
- An additional centrifugal pump allows the operation of an autonomous heater, which can be included in the overall circuit of the power plant cooling system;
- Cooling of exhaust gases in the exhaust gas recirculation system;
- Another pump can be used to cool the turbocharger on engines that are equipped with supercharging;
- A second pump can be installed to pump coolant after the engine is stopped. This solution is used to avoid overheating of the power plant after stopping the engine and deactivating the main mechanical pump.
In the vast majority of cases, the additional coolant pump is equipped with an electric drive. An additional pump is an element that is controlled by the internal combustion engine control system. The device is controlled by a command from the electronic control unit of the vehicle's power unit. It turns out that turning the pump on and off is controlled by the ECU.
Switchable pump
It is worth noting some centrifugal coolant pumps, which are switchable devices and are installed on certain engine models, among them there are engines with a turbine. Such switchable pumps are capable of providing the fastest possible engine warm-up during a cold start. This result becomes possible due to the fact that the coolant circulation in the engine jacket is turned off until the temperature of the power unit reaches 30°C. The coolant itself is constantly in the engine, but without movement. This allows the engine and the fluid in it to warm up much faster, which is very important when the engine is operating at low temperatures. Another advantage of using a switchable pump is that it reduces the load on a cold engine when warming up, which leads to an increase in its service life and a decrease in fuel consumption.
The supply of coolant in such pumps is interrupted by a damper, which is an annular diaphragm. It is this that blocks the fluid supply channel from the pump. It is noteworthy that the impeller in the pump continues to rotate. The specified diaphragm is connected to the membrane using special levers. The membrane moves when vacuum begins to act on it. A channel intended for this purpose connects the space in front of the diaphragm with the intake manifold, which is the source of vacuum.
This vacuum line is closed by a control valve, which is included in the overall engine control system. When the valve opens, a vacuum begins to affect the membrane and it moves, thereby neutralizing the effect of the rotating impeller of a liquid centrifugal pump. If the valve closes, the membrane will return to its original position under the action of the spring, and the diaphragm will release the impeller and the pump will begin to operate as usual.
Popular makes and models
For domestic and imported cars, car dealerships sell different models of water pumps. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Manufacturers of water pumps for foreign cars
One of the most common manufacturers of car pumps is the Spanish company Dolz. By the way, Dolz has been producing technical devices for equipping vehicles since 1934. All models of water pumps are required to undergo certification, and therefore are considered reliable and high-quality in operation.
The product has a high price, but the build quality allows you to save on further operation
The Hepu company (Germany) manufactures water pumps for almost all brands of cars - from Porsche to Fiat. The concern's product line includes many models of pumps, and in the production of each product special attention is paid to the introduction of the most advanced technologies.
BGA is a UK manufacturer of pumps and other automotive components. The company is very strict about quality control of its products, so each pump lasts for many years.
Manufacturers of water pumps for Russian cars
The Belarusian enterprise Fenox produces cheap mechanisms of average quality. Each product has a factory passport and warranty.
The Russian company sells pumps for the domestic automobile industry complete with a sealing gasket. This part is easy to change. Products from this company can be purchased at almost any auto store.
Another Russian company Luzar specializes exclusively in the production of water pumps. The impeller is made of aluminum alloy, which ensures the lightness of the mechanism. In addition, the kit includes not only a seal, but also additional fasteners.
Luzar is one of the most popular manufacturers of water pumps in Russia
Thus, the car pump is the element on which high-quality engine cooling depends. It is worth paying attention to the choice of a new element and repairing the old one, if necessary.
Replacing the water pump of a Volkswagen Polo yourself: how to do it quickly and efficiently
Replacing the pump on a Daewoo Nexia: replacement procedure and recommendations for drivers