Turbocharging as a means of increasing the power of any engine, be it a gasoline or diesel unit, is rightfully considered the most highly efficient. This system also makes it possible to reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases due to more complete combustion of fuel and reduced fuel consumption. The demand for supercharging in the modern automotive industry is also explained by the fact that it is carried out using the energy of exhaust gases. That is, the efficiency of this unit is beyond doubt. Especially when it comes to diesel engines, characterized by a high compression ratio at a fairly low crankshaft frequency.
An additional limiting factor for the inclusion of this device in the scheme of gasoline power units is the following fact: how the engine turbine operates is not particularly important, but this process is accompanied by a high risk of detonation and a mandatory increase in exhaust gas temperature.
Advantages of a turbocharger.
- An engine equipped with a turbocharger has economic and technical advantages compared to atmospheric (naturally aspirated) pressure
- An engine with a turbocharger has higher weight and power than a naturally aspirated engine.
- An engine with a turbocharger is not as huge as a naturally aspirated one, with the same power
The torque curve of an engine equipped with a turbocharger is better adapted to specific operating conditions. This is, for example, when the driver of a huge and heavy truck changes gears much less often on a mountainous road, plus the driving itself will be “softer”.
We also note that on the basis of naturally aspirated engines, it is possible to produce versions equipped with a turbocharger, which will differ in power.
- The turbocharger included in the engine ensures better fuel combustion. And this confirms the reduction in fuel consumption by trucks over long runs.
- By improving combustion, the turbocharger reduces exhaust emissions
- An engine with a turbocharger operates much more stable than its naturally aspirated counterpart of the same power and produces less noise
- The turbocharger for the engine and the entire combustion system acts as a specific muffler in the exhaust system
Turbocharger repair (turbine repair).
A modern turbocharger is a high-tech device, therefore, repairing turbines is a complex task that requires craftsmen to be attentive, accurate, and have technical skills using high-quality materials.
If you notice any problems with your equipment related to turbine equipment, then you need to immediately consult a specialist or technician and take appropriate measures.
Here the main task of the technician is to identify all the causes contributing to problems with the turbine. Quickly and effectively understand the problems and solve them by ordering turbine repair.
As for the reasons that contribute to the failure of a turbocharger, there can be many of them. For example, significantly high exhaust gas temperature, high shaft speed, and others.
The turbine can also be damaged by ordinary (natural) causes of malfunctions, without placing large loads on the engine:
- Oil deficiency
- Oil contamination by chemical elements
- Dirty air filter
- Turbocharger overheating
- Other objects caught in the volute of a compressor or mechanical turbine
By identifying and eliminating all these reasons, and possible others, turbocharger repair and diagnostics proceed as follows:
- All equipment is disassembled, parts are thoroughly cleaned and washed of grease.
- Defect detection, search for cracks and signs of turbine wear are carried out
- Repair turning and metalwork work is carried out
- New components are installed on the turbocharger
- The shaft rotor and turbine are balanced, then assembled, and diagnostics are carried out for oil leaks
- Upon completion, the snail and cast iron are installed
By carrying out the entire set of measures listed above for the repair of turbochargers, it is possible to repair turbine equipment of any complexity: for cars and trucks, buses, agricultural, construction equipment, etc. The main thing is to carry out repairs in the factory.
High-quality repair of turbines is almost impossible without high-quality special equipment.
Balancing is one of the most important and fundamental points in the repair of a turbocharger; without this operation or poor-quality balancing, the repair can be considered invalid.
Repair of turbines for cars and trucks, minibuses, and special equipment must be carried out by experienced, qualified specialists in the field of hydraulic equipment. Repair of a turbocharger must be accompanied by a warranty card and installation and operating instructions.
Finally, we note that any turbocharger or mechanical turbine requires some maintenance. Namely, you should always monitor the lubrication of all equipment. Because a lack of oil usually leads to severe wear and even failure of spare parts.
Frequent and main signs of malfunction
– this is black or bluish smoke from the exhaust pipe, reduced engine power, increased engine oil consumption or noise when the turbocharger operates.
On an engine that runs perfectly, is maintained on time and is well maintained, the turbocharger can operate trouble-free for many years. Consequently, there will be no need to think about repairing turbochargers on your equipment for a long time.
The operating principle of a turbocharger (turbine), its design and types.
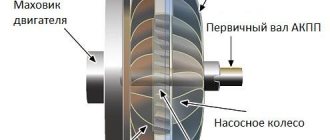
The operating principle of any turbocharger is based on the use of energy from the exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine. The flow of exhaust gases hits the turbine wheel (fixed to the shaft), thereby spinning it and at the same time spinning the compressor wheel, which forces air into the engine cylinders.
Since when using supercharging, air is forced into the cylinders (under pressure), and not only due to the vacuum created by the piston (this vacuum can only take a certain amount of the air-fuel mixture), then a large mixture of air and fuel enters the engine. As a result, during combustion the volume of fuel burned with air increases, the resulting gas occupies a larger volume and, accordingly, a greater force is generated pressing on the piston.
Internal combustion engines equipped with a turbocharger are more efficient, i.e. lower specific effective fuel consumption (grams per kilowatt-hour, g/(kW•h)), and higher liter power (power removed from a unit of engine volume - kW/l), which makes it possible to increase the power of a small engine without increasing engine speed .Due to the increase in the mass of air compressed in the cylinders, the temperature at the end of the compression stroke increases noticeably and the likelihood of detonation arises.
Therefore, the design of engines with a turbocharger provides for a reduced compression ratio, high-octane fuel grades are used, and the system also includes an intermediate charge air cooler (intercooler) - a radiator for cooling the air. A decrease in air temperature is also required to ensure that its density does not decrease due to heating from compression after the turbine, otherwise the efficiency of the entire system will drop significantly.
Turbocharging is especially effective in diesel engines of heavy trucks. It increases power and torque with a slight increase in fuel consumption. The most powerful (relative to engine power) turbochargers are used on diesel locomotive engines. For example, on a diesel engine D 49 with a power of 4000 hp. a turbocharger with a capacity of 1100 hp is installed. The highest (in absolute value) power is possessed by turbocompressors of marine engines, which reaches 7000 hp. .Modern turbochargers can be divided into two main types: 1- with variable nozzle geometry (VNT turbochargers) and 2- without geometry. All of them, in turn, can be mono, twin-scroll (double turbines), etc.
Turbocharging defects and causes of their occurrence
Malfunctions of diesel and gasoline engine turbines are no different from each other. Below are some of them:
- Wear of the shaft bearing journals and sliding bearings. Reasons: low pressure, poor quality or severe contamination of the oil. A sign of this malfunction is the noisy operation of the turbine at any speed.
- Mechanical damage to the impellers. Occurs when there is a large uneven wear between the shaft and the bearings, leading to the impellers beating against the housing. Or when foreign objects get on the impeller blades.
- Clogging of bearing lubrication channels with burnt oil. This is possible when turning off the diesel engine immediately after stopping the car. Because if, after stopping the car, you do not allow the engine to idle for several minutes, overheating of the bearing housing is inevitable. And in the case when the turbine is liquid cooled - when the thermal conductivity of the channels of this system decreases due to the deposition of scale or antifreeze sealant on their surface.
- Oil entering the engine intake manifold from the turbocharger. The reason is increased gaps between the surfaces of the shaft journals and the bearings, together with a clogged oil drain line. This makes itself known by the appearance of blue smoke at high engine speeds. As the crankshaft speed decreases, the exhaust becomes almost colorless.
- Actuator malfunction. Most often this is a jamming of the bypass valve in one of the extreme positions. A sign is insufficient compressor boost or exceeding the permissible impeller speeds.
- Leaks in the joint between the compressor scroll and the intake manifold. The reason may be a violation of the geometry of the turbocharger housing or the gasket becoming unusable. This malfunction reveals itself by the whistling sound of compressed air escaping through the defect.
Removing the turbocharger
- Cool the engine and drain the antifreeze.
- Disconnect the oil lines and cooling pipes from the assembly housing.
- Unscrew the volute flange fasteners. To avoid damaging the edges of bolts or nuts, use only box and socket wrenches.
- Disconnecting the compressor volute flange from the intake manifold is usually not difficult. The turbine scroll flange usually sticks tightly to the exhaust system. To separate this joint, you should use WD-40, and if this does not help, then a wooden mallet.
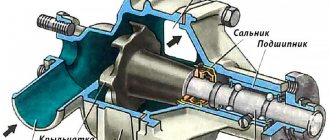
What is a turbine cartridge
An engine turbocharger cartridge is a unit consisting of a bearing housing, liners and a shaft with impellers installed in them. Available for sale, it does not require balancing the shaft with impellers or other preparatory operations and, after removing the preservative grease, is completely ready for installation.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=HGcIrc4S69I
How does it work
It is worth noting that the principle of operation of a turbine on a gasoline engine is the same as on a diesel engine. During operation of the internal combustion engine, exhaust gases are produced. They enter the housing (the hot part of the cochlea), where they move along the blades of the turbine wheel. The latter spins up to incredible speeds - 100 or more thousand revolutions per minute. Since the turbine wheel is rigidly connected to the shaft, torque is transmitted to the second cold part of the turbine. That, in turn, begins to capture oxygen from the atmosphere. It gets inside after it passes through the filter. Next, air under pressure enters the intake manifold, where it mixes with fuel and penetrates the combustion chamber. Heat-resistant steel grades and iron-nickel alloy are used as materials for the turbine housing.
The performance of the compressor depends on its shape and overall dimensions. The larger its diameter, the more air is sucked into the intake manifold. But you cannot constantly increase the size of the compressor. This may result in turbo lag. The small turbine spins up much faster to rated speed. But at its peak it has less productivity. Therefore, the dimensions and shape of the element are selected strictly individually for each internal combustion engine. You cannot install a unit from a gasoline car to a diesel one, and vice versa. Although the turbine operates on the same principle, it will operate differently on different cars.
An important point: to regulate the boost pressure, the design provides a special bypass valve. It is pneumatically driven and controlled by the engine ECU.
Design features of the engine turbine
Structurally, a turbocharger is a very simple mechanism that consists of several basic elements:
- Common body of the assembly and cochlea;
- Sliding bearing;
- Thrust bearing;
- Spacer and thrust bushing.
The turbine housing is made of aluminum alloy, and the shaft is made of steel.
Therefore, if these elements fail, the only correct solution is replacement.
Most turbine damage can be easily diagnosed and repaired. In this case, the work can be entrusted to professionals in their field or you can do everything yourself.
In principle, there is nothing complicated about this (we will look at how to dismantle and repair a turbine in the article).
Lada 21099 turbo PROJECT ORIGIN Logbook DIY turbocharger turbine repair
Before repairing the turbine, it is necessary to carefully inspect it from the outside in order to identify the presence of all components, external defects and deformations.
Then both “snails” are removed from the turbine and the condition of both impellers is visually determined. Quite often, impellers have physical damage that is visible to the naked eye. Such damage immediately indicates that repair of the turbine is inevitable. If the turbine drives oil
Then, all components of the turbine are examined to determine the suitability of each part for restoration. Parts found to be unsuitable must be replaced with new ones.
Repair of turbines of diesel and gasoline engines is basically no different and occurs in several stages:
After this, the parts that have undergone shot blasting are washed again to wash off and completely remove any solid particles that may remain on the parts. Numerous damage to the compressor wheel blades.
In addition to visually visible damage to the impellers, the main damage is damage to the support bearings, retaining rings, bushings and the shaft itself. Typically, these damages occur from a lack of oil supply to the working surfaces during turbine operation or the use of non-recommended oils. Increased wear of the shaft journal.
Cause: The quantity or pressure of oil supplied to the TKR is less than required. During repairs, you may have to replace the shaft with a new one. In most cases, the shaft does not change. Significant uneven wear of the shaft journal.
Cause: Dirty oil. During repairs, it is necessary to replace the shaft with a new one. Significant uneven wear of the bearing.
Cause: Dirty oil. During repairs, all bearings are replaced with new ones. Burnt oil in the oil channels of the bearings.
Reason: Engine overheating or sudden engine shutdown, poor quality oil. During repairs, all bearings are replaced with new ones. Start repairing the turbine with your own hands.
Then the turbine shaft is measured for wear. If the wear of the turbine shaft is within the normal range, then it goes to a special turning and grinding machine, where it is ground to repair size. The groove of the locking ring is straightened on a special machine. Then the balancing process occurs. It consists of two stages. First, the turbine shaft is balanced in two planes of the turbine wheel. After this, bushings and a compressor impeller are installed on the shaft and, in this form, it is again sent for balancing. Balancing the turbine on a stand.
There are separate specialized stands for balancing turbines for trucks and cars.
During balancing work, special balancing marks are applied along which the turbine “cartridge” is assembled. In principle, the result is an assembled turbine only without the “snails”.
The cartridge assembled in this way is sent for testing to a balancing stand, where compressed air is supplied to the “cold” impeller and the turbine is spun up to 5,000 rpm.
If all turbine parameters are normal, then “snails” are screwed to the cartridge.
Causes of breakdowns
Turbocharger malfunctions occur for a number of reasons.
Most often, diesel engine and turbine breakdowns occur due to untimely oil changes.
Long-term use of old lubricant or the ingress of water or fuel into it leads to rapid wear of the bearings, blockage of the oil channels or damage to the axle. The faulty element must be replaced. It cannot be repaired. The described consequences result from using too thick oil.
The second most “popular” cause of problems with a turbocharger is a decrease in pressure in the oil hoses caused by improper installation of these elements or the turbine itself. This problem can lead to rapid wear of the rings, shaft journal, and bearings.
It is important to note: running a diesel engine for 5 minutes without oil causes serious and irreparable damage to the power unit. We should also not forget that foreign objects can get into the turbocharger.
Their appearance in an operating turbine leads to breakdowns of the wheel and rotor blades, which reduces the level of pressure generated
Peculiarities of turbine operation
If we compare the action of a turbocharger with a standard air supercharger, which operates solely from the crankshaft drive, the main advantages of the first will be:
- reuse of exhaust gas energy;
- low price;
- energy saving.
The design of the compressor turbine is almost the same when used on diesel and gasoline engines. However, preference is still given to compressors for diesel units.
The peculiarity of a turbocharger lies in its mode of operation. For gasoline engines, the devices are made of heat-resistant materials due to the high temperature of the exhaust gases, which can reach 1000°. A diesel engine has a lower gas temperature, which is why the materials used in the turbocharger are less heat-resistant.
Specifics of self-repair
- It is necessary to have a special repair kit available, which includes hardware, rings, seals and liners.
- We check the fixity of the nominal liners. If there are vibrations, we grind, clean, lubricate with engine oil and balance the shaft.
- We install the retaining rings in special grooves of the cartridge inside the turbine.
- Lubricate the turbocharger liner with special engine oil and fix it in place using a locking ring.
- Install the compressor liner.
- Lubricate and install the bushing.
- We secure the bushing on top with a plate using bolts.
- We install protection against dirt using retaining rings.
- Install the oil removable ring.
- Installing snails.
You should be extremely careful when reassembling a disassembled turbine. Often a situation arises when the analysis went quite well, but problems arise with the installation. Carefully cleaned of contaminants, washed with a specially selected composition and inspected for deformations (replaced if necessary), the turbine parts are very carefully installed into the intended grooves until they are fully seated.
The peculiarity of the turbine structure is that the small number of elements determines its relative durability. Its components are easily broken and in most cases require replacement, but even if absolutely all parts fail, the turbine is capable of performing operational actions. However, this fact should not be taken as a guide to action, since an incorrectly functioning turbine provides truly fantastic oil consumption.
The indicated sequence of operations is common for all types of turbochargers; depending on the model, some actions may vary. In the event of a serious malfunction, it is recommended to replace the damaged turbine.
Conclusion:
To save money, it makes sense to learn how to repair the turbine yourself, especially considering that the time required does not exceed several hours.
Vote, did you like the article?
Do-it-yourself turbocharger repair, causes of malfunctions and instructions
Just ten years ago, a car turbocharger moved from the category of a special chic inherent only in selected cars to the category of a necessary part for every car. It serves to increase engine power and helps reduce fuel consumption. These parameters are becoming increasingly popular when choosing a car. Therefore, today every driver needs to know the structure of a turbocharger and be able to understand what its malfunctions are in order to navigate and diagnose the breakdown of his car in time. In addition to the design of the turbocharger, you should also know the features of your car model; for this you should read the repair and operating instructions for your car, for example, the repair instructions for GAZ 3110 and Chevrolet Lanos.
Mobile: 8 (926) 120-33-55
Write to us on WhatsApp
0
What are turbines and what are they for?
The main task of turbines is to increase the power of a car engine. With the help of a turbine you can significantly increase the power of a car.
The principle of operation of a turbocharger is simple: through the exhaust manifold, exhaust gases enter the turbine housing in which a turbine wheel is installed, which is driven. A compressor wheel is installed on the same axis with the turbine wheel, which in turn compresses the air and drops it into the engine intake manifold. From all this it follows that the turbine speed is very high and directly depends on the engine power; the turbine rotation speed reaches 150,000 rpm or more.
When using a turbine, high-pressure air enters the engine, which allows the vehicle's power to increase in relation to engine volume and fuel quantity. High-pressure turbochargers are the most efficient. The difference in design from conventional turbines is that high-pressure turbines have a valve that eliminates excess pressure at high speeds. Most turbochargers are also equipped with an intercooler.
The main task of the intercooler is to cool the air. Since the turbine operates at high speeds, the air in it heats up, thereby reducing the oxygen content and air density. The intercooler copes with this problem. One of the problems of turbines has always been a slight delay in reaction (inertia), but now these shortcomings have been practically eliminated. With the advent of two parallel turbines, one designed to operate at high speeds and the other at low speeds, turbine inertia was significantly reduced.
Also, turbines appeared in which it became possible to change the angle of inclination of the rotor, which in turn also makes it possible to combat problems associated with delays in response. Inertia is well reduced in turbochargers with ceramic rotor blades, due to the fact that their weight is less than that of standard analogues.
Turbocharger device.
- Turbine with impeller.
- Air centrifugal pump.
- Compressor.
- A rigid axis that connects them.
- Bearings, rings, valves, seals and other small parts.
These malfunctions do not always relate to problems with the turbocharger; sometimes it can be something else, for example, you need to repair the muffler yourself.
Exhaust gases escape from the engine and enter the turbine impeller. It converts their energy from kinetic to mechanical, and the pump through the air filter supplies fresh air to the compressor, which compresses it and sends it to the engine. This entire process helps increase engine power by 20-50%, increasing efficiency and fuel burning rate.
What are the types of turbocharger malfunctions and how to recognize them?
- Your engine suddenly seems to lose power.
- Black or dark blue smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe.
- Oil consumption has increased.
- The sound of the engine and turbocharger has changed.
All this indicates that it’s time to make sure you have a turbocharger repair kit and check the serviceability of not only the turbocharger, but also, first of all, the car’s engine and all its attachments. Do not neglect this advice, because a well-maintained and properly functioning engine ensures trouble-free operation of the turbocharger for many years.
Let us say right away that not a single specialist will advise you to disassemble and repair the turbocharger yourself. The reasons for this are compelling and it will suffice to name at least one of them. For example, the slightest grain of sand entering a unit can damage it. But there is another opinion - if someone does it, then I can do it too! If you decide to disassemble and repair the turbocharger yourself, prepare a minimum turbocharger repair kit: liners of several sizes, a full set of all kinds of seals, rings, washers, screws, screws and spare liners. Be extremely careful and remember that taking something apart is easier than putting it back together. If possible, mark all the fastening points of the parts and their position relative to each other.
So, we begin repairing turbochargers in our own workshop.
- We remove the turbine and free it from all screws. We also unscrew the screws securing the snails.
- We check both impellers: turbine and compressor. They cannot be repaired, but will have to be replaced in case of malfunction.
- You can try to grind the shaft on which the compressor and turbine are mounted. Then you will need to replace the bearings with others that fit in size.
- To remove the compressor wheel, you will need pliers with sliding lips. And you must take into account that the compressor shaft has a left-hand thread!
- It is very difficult to check whether the shaft play is acceptable in a regular workshop. But here we take a risk, hoping for luck and the opportunity to go to the workshop later.
- Using a universal puller, we try to remove the compressor wheel from the shaft.
- Shaft bushings are very often the cause of backlash.
- We clean and rinse all parts with special products. During assembly, some components and parts are forcibly lubricated with oil, which is used when operating the car. The list of such details varies in each specific case.
- Don't forget to congratulate yourself after you managed to assemble the turbocharger! And if he still works, it’s time for you to think about changing your profession. There is a good salary at the service station...
Before you decide to disassemble and reassemble a turbocharger in less than ideal conditions, without having experience in such work, carefully weigh the pros and cons again.
A professional workshop has the opportunity to diagnose all components and parts of any turbocharger at all stages of repair, including before and after disassembly and assembly. And conditions of cleanliness have been created there, which cannot be achieved in a home workshop even if one wants to. After all, you don’t have a special unit in your garage - a high-pressure washing machine, for example? What about the balancing stand? As you understand, we strongly do not recommend repairing the turbocharger yourself and insist on it!
Steam turbine
Its operating principle is slightly different. The steam that is generated in the boiler flows under pressure onto the turbine impeller. The latter rotates, thereby generating mechanical energy. Typically, such a turbine is connected to a generator and is used in power plants. Thanks to mechanical energy, the generator produces electricity. The power of such units can reach 1000 MW.
However, this indicator significantly depends on the difference in steam pressure at the inlet and outlet. Also, similar turbines are used to drive a feed pump on ships and vessels with a nuclear installation. As for warships, a gas turbine is used. The principle of its operation is as follows. Gas enters through the compressor nozzle into the low pressure area. At the same time, it expands and accelerates. The gas flow then moves the turbine blades. The latter transmit forces to the shaft through discs. This creates useful torque.
Signs of trouble
Manufacturing a turbine is a rather labor-intensive process, despite the apparent simplicity of its design. Manufacturers of the unit have to measure its dimensions to fractions of a millimeter.
Before repairing diesel engine turbines, it is necessary to carry out preliminary diagnostics.
Any errors during the restoration of the TCR lead to a sharp increase in the cost of work due to the high cost of the unit. To identify faults and eliminate them, you will need the help of an experienced specialist. However, you can diagnose the motor yourself. The following signs of turbine malfunction may indicate problems with the engine:
- Exhaust gases have acquired a black, bluish or bluish tint.
- The motor began to make a lot of noise in different operating modes.
- The engine temperature regularly reaches high levels (overheating is observed).
- The power plant began to consume noticeably more fuel and oil.
- The appearance of clear pops while the engine is running, a whistle or a dull hum.
- Reduced vehicle dynamics due to decreased traction levels. At low speeds the power unit is unstable.
- Oil smell appears.
Turbine types
At the moment, there are several popular types of compressors:
- Separated. It has two nozzles for each pair of cylinders and two exhaust gas inlets. The first nozzle is designed for quick response, the second is for maximum performance. The design has separated exhaust channels. This was done to prevent the channels from blocking when releasing exhaust gases.
- Compressor with variable nozzle. It is also known as a variable geometry turbine. Used on engines marked TDI from Volkswagen. Here the design has 9 movable blades. They can regulate the flow of exhaust gases that go to the turbine. The angle of inclination of the blades is adjustable, which allows you to match the pressure of the injected air and the speed of gas movement with the engine speed.
For greater performance, two compressors can be installed on the vehicle. Such systems are labeled “Twin-turbo”.
These mechanisms are installed sequentially. In this case, the first turbine operates at low speeds, and the second at high speeds. On V-shaped engines, superchargers are installed in parallel (one turbine for each row). As practice shows, installing two small compressors is much more effective than using one large one.
Design features
To understand possible failures, one should also recall the design of the turbine used with diesel engines. The turbocharging system includes:
- Compressor impeller.
- Supercharger impeller.
- Support shaft.
- Bearing assembly.
- Lubrication fitting.
- Boost pressure control regulator.
When the turbine operates, the air heats up, which leads to an increase in its density. Therefore, it is necessary to turn on the cooler (intercooler) to return the parameters to normal.
Sliding bearings receive the greatest impact in operation, taking into account the high rotation speed. Therefore, the importance of maintenance in terms of timely oil changes is very high. By the way, engine oil for a diesel engine with a turbine should be selected only taking into account the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Other reasons that disrupt the normal operation of the turbine include a sharp start on a cold engine, stopping the engine after an intense rhythm without waiting to idle.
Turbine purpose and resource
The operation of a turbocharger is aimed at increasing the flow of supplied air into the combustion chamber.
This leads to more complete and rapid combustion of fuel, resulting in greater efficiency from the engine at the required operating conditions. Designers do not have to increase the engine displacement and carry out complex technical upgrades. Turbocharging is used both on diesel engines and gasoline units. In this case, diesel engines demonstrate greater efficiency. This is due to the high compression ratio of the diesel fuel unit and the lower number of revolutions during operation. Recently, a gas turbine engine, which has already been developed for tractors and trucks, has been called promising.
Given the high repair costs, owners strive to keep the turbocharger operational for as long as possible. Increasing the service life is directly related to understanding the operating features of the turbine supercharger. The impeller starts working from the first seconds of starting the engine, and stops a few seconds after the crankshaft stops. At low engine speeds, the exhaust gas pressure does not allow the turbine to spin. Switching on occurs with increasing speed, and the engine seems to get a second wind.
Initially, the service life of the supercharger is not inferior to that of the engine itself. Premature turbine failure is associated with high temperature loads and high rotation speeds.
Design and principle of operation of the turbine
The schematic diagram of the turbocharging system underwent many changes during its development. At the moment, it can be considered as modernized and simplified as possible, which ensures stable operation with a low probability of malfunctions.
Turbocharger,
which is the main component of the power increasing system, is an impeller with blades that rotates at a speed comparable only to that of a dental drill - at least 100,000 rpm. This allows it to function as a compressor, pumping large volumes of air into a special chamber. During this procedure, the air is compressed and therefore automatically heated - this is the main disadvantage of how the turbine works.
Intercooler.
In an effort to solve this issue, car designers thought of a lot of ways to cool the air during its transition to the power unit. As a result, the so-called intercooler was invented, the name of which speaks for itself - it should perform the function of intermediately lowering the temperature of the substance passing through it. In order to ensure this process, the device contains a refrigerant, which allows the effect of a heat exchanger to be used. However, in some models there is no coolant, and the matter is limited only to air exchange. Despite the rather complex design, the intercooler is capable of not only reducing the likelihood of engine detonation by an order of magnitude, but also increasing the power rating of the unit by up to 20%.
The principle of operation of the turbine in diesel and gasoline engines is absolutely identical, the only difference is the degree of boost. To increase the power of diesel units, more pressure is required, for this reason they are equipped with larger superchargers. Accordingly, in naturally aspirated engines they are smaller in size - if this rule is violated, fuel detonation may begin in the combustion chambers.
Pressure regulator
. It is also one of the main components of the system and, by and large, works as a bypass valve that regulates the energy of the exhaust gases. After all, operating a turbine without such a limiter leads to the fact that at some point the air pressure becomes excessive, which leads to detonation. Therefore, the regulating mechanism will ensure optimal air pressure by removing part of the exhaust gases from the turbocharger impeller. This valve can have either a pneumatic or an electric drive, but in any case its activation occurs from an electronic pressure sensor.
In addition, some models of superchargers also have a safety valve that protects the unit from pressure surges. And such upward fluctuations very often occur during sharp closing of the throttle valve, when the need for air for complete combustion of fuel instantly decreases. To relieve excess pressure, the safety valve releases air into the atmosphere through a special valve or bypasses it to the compressor inlet.
Turbocharger repair
To eliminate an actuator defect, complete disassembly of the engine turbocharger is usually not required. If the malfunction is more complex - jamming of the actuator valve, then its elimination will require complete disassembly of the unit. To repair the turbocharger yourself, do the following:
- Wash the housing and inspect the assembly to determine the malfunction.
- Use marks to mark the position of the turbine scroll relative to the compressor scroll.
- Remove both volutes from the bearing housing.
- Disassemble the “cartridge”. To do this, unscrew the fastenings of the impellers and remove them. Please note that the threads for fixing at the ends of the shaft are always left-handed. The fit of the impeller hubs on the shaft is conical. Therefore, for removal it is often necessary to use a universal puller.
- Correct a slight violation of the geometry of the blades by bending them. After this, as well as after replacing the impellers, the shaft with impellers must be balanced.
- If the geometry of the shaft bearing journals is violated, grind them on a cylindrical grinding machine if the wear does not exceed the maximum permissible values. If the maximum permissible wear is exceeded, replace the shaft.
- Change the shells in the bearing housing. Make sure that the oil supply holes in the housing and liners line up.
- Treat the inner surface of the liners with a reamer. Its size should be 0.04 mm larger than the diameter of the shaft support journals.
- Blow and wash the bearing housing cavity.
- Lubricate the bearing journals with oil and assemble the cartridge.
- Attach the snails.
- If, when installing a turbocharger, you find that the old gaskets have become unusable, you can make them yourself. To seal the connection through which exhaust gases pass, metal asbestos must be used. For the rest, paronite or pressed gaskets are suitable. When installing, the latter should be lightly lubricated with ordinary silicone sealant.
Repairing a turbine cartridge requires access to equipment and tools not found in a typical garage. If you don't have one, you will have to pay for the services of specialists who will perform the necessary operations. Therefore, it is most profitable to repair the engine turbocharger yourself. If you want a guaranteed good result, it is best to replace the cartridge with a new one.
Overload protection repair
To check the serviceability of the actuator, start the engine and remove the hose from the pipe that supplies pressure to the actuator diaphragm. If the actuator valve has not changed its position, then the malfunction is obvious. Repair of a mechanical actuator most often involves replacing the device control diaphragm or otherwise eliminating leaks in the control pneumatic drive. If the jamming of the diesel actuator valve is caused by dirt deposits, then cleaning is enough to repair it.
Troubleshooting the electromechanical engine turbocharging actuator may require checking the electrical part of the device. Most often, defects such as oxidized connection contacts and a break in the wires near the crimping point are encountered.