The fuel systems of modern car engines are complex systems of mechanisms and assemblies. Among them there are systems that can only be operated by a specialist. However, simpler systems, such as those found, for example, in older VAZ car models, can be more difficult to repair than systems in modern cars. Failure of even the smallest parts of the fuel system can seriously impair the performance of the vehicle. The fuel system check valve is no exception. But, before starting any repair work, you need to find out about the structure and functions of this unit.
Check valve functions
The fuel pumps of modern cars have high performance and, with proper care, provide a continuous supply of fuel, regardless of the load being generated. It is impossible for the engine to operate at idle speed without a fuel system check valve.
Moreover, this unit is present not only in gasoline engines with a carburetor and in injection engines. The check valve for the fuel system of a diesel engine is also an indispensable part of the fuel system of such engines.
The main purpose of this valve is to prevent the build-up of too high pressure in the fuel system, which could result in the fuel hoses breaking. In principle, the purpose of any valve is to allow the movement of different fluids in one main direction. Located in the fuel system, this valve prevents a number of problems that can arise in the system as a result of broken hoses.
For example, if you are driving a car with a diesel engine, then a breakdown of the check valve along the way can cause the fuel system to begin to fill with air.
If the driver stops the engine, while fuel flows into the tank along the working line, then the vacated space is quickly filled with air. In such situations, you will have to turn the engine with the starter for at least fifty seconds.
Reasons for failure of the fuel pressure sensor
There are actually few reasons for the failure of the fuel pressure sensor. This is either damage to the internal parts of the sensor or its wiring. In the first case, this may be mechanical damage to the body, its rusting due to mechanical damage or simple old age. It may also damage any electrical contact inside the sensor. As a rule, it cannot be repaired and must be replaced.
However, more often than not, it is not the sensor itself that is damaged, but its signal wiring or connection connector (the so-called “chip”). In some cases, it is noted that under the influence of vibration, wires fray, their insulation deteriorates, and a short circuit may even occur, which can cause the engine to stall while driving. In this case, it is necessary to perform additional diagnostics and replace the wiring and/or connector that fits onto the sensor.
As for the mechanical fuel pressure control valve, it can simply allow a certain amount of fuel to pass through, which is why there will be low pressure in the system with all the ensuing consequences, in particular, a drop in engine power, “twitching” of the car and other troubles.
The cause of the breakdown may also be a clogged mesh on the regulator. Clogging can be caused by debris getting into the fuel if the fuel filter does not cope with the tasks assigned to it or it is simply clogged and debris from it passes into the fuel line. As for diesel engines, in cold weather the diesel fuel can freeze, and solid paraffin particles form in it. In this case, it makes sense to use diesel fuel defrosters.
Types of valves
- 1 Types of valves
- 2 A little about fuel injection pump
Modern injection pumps use several valves. One of the main ones is injection. Let's consider its functions and tasks.
- One of the tasks of the discharge valve is to prevent the penetration of gases from the engine into the fuel injection pump.
- Thanks to this valve, leakage of the injectors is reduced, and the injection of the injectors is stopped abruptly and instantly.
- It provides improved fuel filling of the pump.
- Creates residual pressure in systems and allows you to reduce it, which makes it possible to more clearly maintain injection phases and better control the process.
- The injection valve adjusts the fuel supply, bringing the performance closer to ideal.
It is customary to distinguish discharge valves by type: cylindrical, combined, mushroom, etc.
| Mushroom discharge valve | |
| Most widespread | Diesel systems |
| Valve with suction belt | It is pressed against the socket by a spring and its lifting depends on the limiter |
| Operating principle | During the injection process, fuel presses from below on the valve mushroom, as a result of which it rises and opens access to the injector. When the supply stops, the spring lowers the valve down and then presses it tightly against the seat. When the suction belt enters the guide, the volume of the discharge line increases and the pressure in the system decreases. |
| Cylindrical valves | |
| Form | Cup |
| Weight | The mass of cylindrical valves is less than that of mushroom valves. They allow for a noticeable reduction in the volume of the fitting. |
| Plate valves | |
| Device | They are simple in design, have low mass, and therefore have low inertia. |
| Operating principle | As the pressure increases, both plates rise. When the lower plate rests against the protrusion of the nut, the upper one continues to move upward and allows fuel to access the fitting. |
| Combination valves | |
| Purpose | Combination valves are used to eliminate vibrations in the fuel injection line. |
| Operating principle | The valve consists of two plasti, one of which is loaded with a spring. During the pumping process, plate 1 moves upward and rests against the body with its protrusions. Fuel passes through the hole in the bottom plate, flows around the top plate and enters the fuel injection line. After the fuel pressure is cut off, the upper plate is pressed against the lower plate, decoupling the fuel line and the high-pressure pump. |
| Double valves | |
| Scope of application | Double valves are installed in critical heavy diesel engines. |
| Purpose | The presence of two sequentially located valves ensures greater reliability of the fuel system, as it creates greater tightness of the unit. In addition, if one of them fails due to jamming or solid contaminants getting under the cone, the other continues to independently perform the functions of isolating the pipeline and the pump. |
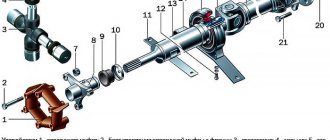
Device and principle of operation
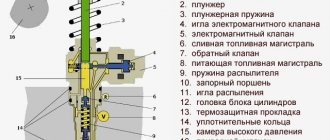
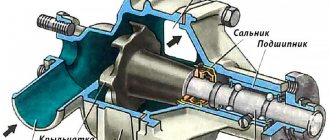
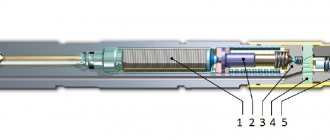
The check valve device is simple. The entire mechanism consists of a spring, a membrane and the valve itself. The ball-type valve is equipped with a special seat, which is made of soft metal and is calibrated as accurately as possible.
The valve body is equipped with three outlets: the first is for the intake manifold, and the others are for fuel removal. Fuel moves freely through the valve in only one direction.
It is not able to flow back into the valve due to the pressure created on it, which is why it closes. The valve opens due to the movement of the spring resulting from the vacuum as the engine speed increases. Excess fuel is returned back to the fuel tank.
The fuel system valve is often confused with the pressure reducing valve. To avoid this, read the vehicle's operating instructions in detail. The pressure reducing valve is used in injection and diesel engines and operates in parallel with the check valve of the fuel system.
The check valve for diesel fuel is no different in operating principle from its “brother” used in gasoline engines; differences can only arise in the location of this unit.
Reference
Many people know that the fuel system valve aggregates:
There is nothing complicated about the mechanical design. This is a ball-type device with a seat, which is made of soft metal, with the most accurate balancing. Fuel flows freely through the fuel valve in one direction. The pressure that is created prevents gasoline or diesel fuel from flowing back into the fuel tank, since the non-demountable structure is locked.
Despite its simplicity, the device can cause a lot of trouble for a novice and an experienced driver. Therefore, it is necessary to know its possible vagaries and ways to eliminate breakdowns. But first of all, understand where the mechanical structure is installed.
“The concept of a fuel system check valve should not be confused with a pressure reducing device.”
What to expect from a non-working check valve
Nothing good. At the very least it is a difficult start. Airing of the diesel power system is a rather problematic breakdown on the road. Injection power systems also do not like air in the system. Troubles begin when we turn off the engine, and the fuel, which must wait for the next start (working pressure must be maintained in the system), goes into the tank along the working line, and air takes its place. Now, in order to start the engine, it is necessary to normalize the pressure in the system and supply fuel to the injectors. To do this, you need to turn the engine with the starter for 40-50 seconds, so starting with half a turn is out of the question.
Strange situations also arise when the check valve is confused with the pressure regulator, which is installed on the fuel rail in most injection engines - 2110, 2114, Kia Sportage 3.
Airing the diesel power system is an extremely complex breakdown on the road
Its job is to equalize the pressure in the fuel rail section, otherwise the injector simply will not receive fuel at the required pressure and will not be able to supply it to the combustion chamber. At the moment when we turn off the ignition, the regulator stops supplying fuel to the injectors, the locking mechanism is activated, thus cutting off part of the fuel line from the fuel pump with a check valve to the fuel rail. And now only the check valve is responsible for the presence of fuel in the system. And it’s easy to check who is to blame in this situation. If the pressure in the fuel rail is normal, and in most cars it should be within 2-3 atm, then the check valve is to blame.
As you can see, one tiny valve can do such things. This once again confirms that there are no small things in the car’s design and there cannot be, and every breakdown is eliminated first with the head, and only then with the hands.
Checking and replacing the fuel pressure regulator
As you can see, a malfunctioning pressure regulator has symptoms very similar to a malfunctioning fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter. At the very beginning, we note that if problems with this element are detected during the inspection, then it is preferable to replace the RTD with a new one. The fact is that replacing individual parts, cleaning attempts and other manipulations often do not allow the device to return to proper functionality. Considering that the price of a fuel pressure regulator is quite affordable, then any repair attempts can be considered impractical.
Read also: Mobile 1 5w30 esp formula
Measurements should show changes in pressure in the system within a certain range. The fuel pressure should increase, being within the range of 0.3 - 0.7 Bar. If this does not happen, then first you can try replacing the vacuum hose, and then repeat the measurements. To check the fuel pressure at the end of the ramp, you will need to unscrew the fitting plug. This plug also has a special ring for sealing. The specified ring should be checked for integrity; the element should remain elastic. If there are defects, then the ring or the entire plug also needs to be changed at once.
- After inspecting the ring, you can unscrew the umbrella from the fitting. Many drivers use a metal wheel valve cap to loosen it. Now the hose and the pressure gauge connected to it need to be connected to the fitting, after which the structure is additionally secured using clamps. Next, the engine can be started and measurements taken. Normally, the indicators should be about 2.9-3.3 kgf per cm2. Afterwards, you can disconnect the hose from the RTD, observing the pressure gauge readings. The pressure indicator should increase from 20 to 70 kPa.
- If the fuel pressure regulator still produces a low or zero reading, then you can think about replacing the device. Changing an RTD is not a difficult task, that is, you can do the replacement yourself in a garage. At the beginning of the procedure, you need to “bleed off” the pressure in the engine power supply system. To solve the problem, you need to unscrew the nut that secures the fuel pipe. Now you can unscrew a couple of bolts that usually attach the regulator to the fuel rail on most fuel-injected cars.
- The next step is to carefully remove the regulator fitting from the hole in the fuel rail and its final dismantling (the fuel pipe must be completely disconnected in advance). The final stage is the installation of a new or known-good element into the ramp, after which the functionality is checked in the manner described above using a pressure gauge. Finally, we would like to add that it is also recommended to additionally lubricate the O-rings with gasoline before installing a new RTD or in case of replacing the said rings.
Characteristic symptoms of a check valve malfunction
This could be: an unexpected change in the speed of the power unit at startup or while driving; The engine can be started by pressing the accelerator pedal. Although before this the power unit was driven by a starter; Unstable engine operation at low or idle speeds; loss of fuel that escapes through the supply or return pipes. In this case, the sealing of the fuel hoses is not broken. In our case, the non-removable mechanical structure can be easily repaired. This is on the one hand. On the other hand, the problem cannot be determined by scanning. Next, let's look at options for checking the device.
How can you check a check valve?
You can find out what condition the fuel valve is in as follows. Using a pressure gauge, check the pressure. It should be within 3 kg per cm2. These are figures for passenger cars. You can find out how the device works by pinching the “return” fuel hoses. If the permanent mechanical structure is in order, the pressure should increase. For your information. This method is only for cars that have rubber hoses installed. Self-diagnosis can be carried out without using a pressure gauge. This concerns the problem of unstable operation of the internal combustion engine (ICE) and poor acceleration. Having pinched the rubber hose that moves the fuel in the opposite direction, you need to pay attention to the operation of the engine. If the speed increases and the engine cylinders operate as planned, then the check valve is faulty.
Other diagnostic methods
You can also check the fuel system check valve by monitoring the pressure level when the return hose is pinched, in which case it should increase. Unfortunately, this method is not suitable for all cars, since many of them have short hoses or are completely replaced with metal ones.
If the engine picks up speed poorly and starts to stall, you can check it without a pressure gauge. To do this, you also need to clamp the return hose and observe the operation of the engine. If at this moment the required power is gained and all cylinders are functioning, it is necessary to replace the fuel system check valve.
Despite its apparent simplicity, the fuel system of a car is a complex mechanism, and work with it should only be done with special skills. Having at least minimal experience and knowledge of all the design features, you can independently deal with most of the problems.
Diagnostics and troubleshooting of check valve operation
So, you suspect that the vehicle's performance has decreased due to a malfunction of the fuel system check valve, and there are some signs of its malfunction. In order to find out whether this is so, several methods are used.
Most often, the pressure level is checked. An adequate pressure level should be about 3 kg/cm2 (for passenger cars). At the same time, the pressure level should not drop sharply when the engine is stopped. Otherwise, this will also be a sign of a faulty check valve.
As mentioned above, hose compression is sometimes used. But this method is not always suitable, since only a rubber elastic hose can be compressed.
Be sure to determine the reason why the fuel system is filling with air. If it is functioning correctly, a small amount of liquid should remain in the chamber awaiting the next engine start. If the valve is missing or worn out, air appears instead of this fluid. Starting the engine in such conditions will be disproportionately difficult.
So, as a result of measuring the pressure with a pressure gauge inserted into the rail, you concluded that after stopping the engine it began to drop significantly. In this case, either there is a defect in the fuel line, or the valve itself is faulty. If the result at the outlet of the fuel pump is different, then the valve is faulty.
To fix the problem, select a high-quality check valve from a spare parts store that fits the cross-sectional dimensions. If you select a valve with the wrong cross-sectional dimensions, it may begin to “slip.” Before purchasing, check the operation of the valve on site, if possible. The check valve must be cut into the line at any suitable location.
For example, this can be done between the fuel pump and the filter. After this, test the functionality of your car by driving it up a hill at an angle. If the car shows no signs of loss of power, then the valve has failed.
Sometimes there is no need to replace the valve, but the fuel pump itself needs to be replaced. However, this procedure is much more expensive. An alternative option is to install an additional valve. When choosing a valve, keep in mind that models for Russian cars often differ in cross-section from foreign cars.
There is also a folk method for troubleshooting, but it is only suitable if the valve is clogged. You need to hit the valve a couple of times with a hammer. The impact force must be calculated to avoid mechanical damage. With this effect, foreign bodies trapped in the valve can be crushed or even fly out of the valve. But most often it is much easier to replace the valve with a new one.
How to check the serviceability of the fuel pressure sensor
There are two ways to check the serviceability of the fuel pressure regulator: with or without dismantling the fuel rail along with the regulator. The first method is more complex, but with its help you can check not only the operation of the pressure regulator, but also other elements of the fuel system. In addition, such a check requires a special stand, which is available only in specialized auto repair shops, in particular, at official representatives of a particular automaker. Although some car enthusiasts assemble similar homemade ones in their garage.
Checking old-style sensors
The old-style fuel pressure regulators mentioned above could be checked by simply pressing the fuel “return” for a short time. This method is old and therefore suitable for older cars. This check must be performed “cold”, when the engine has not yet warmed up. It is best to do this within approximately one minute after starting the engine. Relevant for gasoline engines.
The main action in this case is to pinch the fuel return hose using pliers for a few seconds. If, at the same time, the throbbing and poorly functioning engine regains speed and begins to operate normally, it means that the fuel pressure regulator has failed. However, remember that you should not pinch the hose for a long time, as this can cause wear on the fuel pump to the point of failure or tearing off any clamp at the place where the fuel hoses are attached. However, this method is only suitable for those cars that use long rubber hoses in the return fuel line. And on many modern foreign cars these elements are made of metal, so it is impossible to mechanically compress them.
Checking with a multimeter
Checking the electronic fuel pressure sensor installed on the ramp requires checking that there is power to it. To do this, you need to remove the “chip” from it and, using an electronic multimeter set to voltage measurement mode, check the corresponding values. The black probe is installed on any “minus”, and the red one is installed on the leg on the “chip”. If everything is working properly, then the multimeter screen should read 5 Volts DC. The next step of checking is that the red probe is installed on the “plus” of the battery (or the nearest point where you can take the voltage), and the black probe is installed on the negative leg on the “chip”. In good condition, the value should be -12.3 Volts (or simply 12 Volts). If everything is so, then the sensor wiring is intact. You can return the “chip” to its seat on the sensor.
The next step is to check the signal level from the sensor. To do this, the black wire of the multimeter must be placed on the negative terminal of the battery, and the red wire on the third signal wire (usually located in the middle). Next, you need to start the engine and let it run at idle speed (minimum). In this case, the output voltage should also be minimal. As stated above, this value will be approximately 1.3 Volts. When you press the accelerator pedal (increase engine speed), the corresponding value will increase up to 4.5...5 Volts (at maximum speed). This change can be tracked over time. If the voltage changes, the regulator is working properly. If the voltage value does not change, it needs to be changed to a new one.
However, after checking the “chip”, you also need to check the wire that goes directly to the electronic control unit. This can also be done using a multimeter. If, as the engine speed changes, the corresponding value changes dynamically, then the pressure regulator is working. In very rare cases, situations are possible when the ECU itself becomes a problem, in particular, so-called “glitches” in its software.
Checking with a pressure gauge
Currently, to check the serviceability of the fuel pressure regulator, a pressure gauge is used - a device for measuring pressure in the fuel system (and not only). A pressure gauge is connected between the fuel hose and the fitting. You must first disconnect the vacuum hose.
The operating pressure of a gasoline engine will be about 2.5...3 atmospheres; before measuring, this value must be further clarified in the manual or on the Internet. When re-gassing, the pressure drops slightly (by a few tenths of an atmosphere). After this, the valve should maintain pressure in the system for some time, which can be observed by the readings of the pressure gauge. Next, using pliers, you need to pinch the return fuel line, which helps to increase the pressure to 2.5...3.5 atmospheres.
Checking the pressure regulator of the Common Rail injection pump
First of all, you need to check the resistance value of the control inductive coil. The exact data should be taken from additional reference literature, however in most cases the corresponding value will be around 8 ohms. The resistance value is measured with the same electronic multimeter, but switched to the appropriate operating mode. If the measured value differs significantly in one direction or another, the sensor is obviously faulty and needs to be replaced.
For more detailed diagnostics, additional expensive equipment is used, which is used only in car services, since the average car owner simply does not need it. With its help, not only the tightness of the regulator valve is checked, but also the linearity of its control. If everything is clear about the tightness, then the linearity of the control ensures its smooth closing/opening, which facilitates the normal flow of diesel fuel through the main line to the return line. If mechanical jamming occurs, then the control characteristic will be nonlinear. To build it, special hardware and software are used.
In most cases, repairing the fuel pressure sensor itself is hardly possible, so it is simply replaced with a new one. However, for many cars the cost of this unit is quite high (even for domestic VAZs and their budget analogues). Therefore, before replacing this unit, you need to make sure that it is the fuel pressure sensor that has failed, otherwise it will be a waste of a lot of money.
Conclusion
The fuel pressure regulator is a simple, but important component of the fuel system, which directly affects the operation of the engine. This applies to both gasoline and diesel engines. It is worth considering that when it fails, the engine begins to operate in a less than optimal mode, which creates an air-fuel mixture with the wrong composition, and the fuel pump begins to wear out, which leads to a decrease in its overall service life. Therefore, if you suspect a failure of the fuel pressure sensor, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics as quickly as possible in order to return the engine to optimal operating parameters.
Today we’ll talk about the fuel pressure regulator, a mechanical device that is undeservedly deprived of attention.