Thermostat - what is it?
A thermostat is a discrete device shaped like a valve. The word comes from the Greek language, translated means “warmth” and “standing”.
The mechanical device is able to respond to the temperature of the antifreeze, maintaining a certain thermal regime of the engine automatically.
It does not show the real value of t at a given time. His role is completely different. The task of the device is to change its state in time. When the engine warms up, the valve is closed and the liquid moves in a small circle. The unit warms up faster, but as soon as the required t is reached, the valve opens and refrigerant flow occurs.
Volkswagen Passat B3
On the VW Passat B3, the thermostat is located on the right side of the engine, when viewed in the direction of travel, and is attached to the pump. Look at the diagram.
As a rule, if they change the pump on a Volkswagen Passat B3, they immediately check the thermostat for serviceability and, if necessary, change it, since the device itself is not so easy to get to.
Design
Thermostats are made primarily of copper and brass. They have a design that includes different elements. These include the small and large cooling circle valve, pipes, springs, ball and pistons.
The standard device has a movable valve. It begins to move after a change in the environment (when cooled or heated). In this he is helped by a thermoelement, inside of which there is a substance with the addition of various components that improve thermal conductivity. Once the coolant reaches a certain temperature, the valve will open due to the expansion of the ceresin. As the engine cools down, it forces the valve to close.
Thermostat is divided into types, i.e. It can be one- or two-valve. The latter type most correctly allows antifreeze to circulate. That is why it began to be used more often.
Cause of breakdowns, solutions
In 99 percent of cases, the cause of the malfunction is the thermocouple. In the first or second case, the wax could have washed out due to breakdown and depressurization of the chamber (or it had dried out due to time). In the third, the manufacturer simply did not supply the thermoelement in full or installed a low-quality spring. But in any case, the only way to solve the problem is to purchase and install a new thermostat. The element is non-separable and can be changed entirely. And its cost is not too high to take repair measures.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of the thermostat is simple. At the moment when the driver, the engine warms up to a certain t. To speed up the process, the coolant comes into play.
After the engine warms up, the valve is activated, the antifreeze circulates in a large circle, performing the cooling function.
It turns out that the operation of the thermostat in a car is based on the chemical properties of the ceresin found inside. At elevated temperatures, the substance melts, thereby expanding and pushing out the pin to open it. As the wax cools, it hardens and thereby causes the valve to close. Melting of the substance occurs almost instantly thanks to special additives in the composition.
Lanos 1.4/1.5
The thermostat in Lanos 1.5 is located on the right side of the unit behind the timing belt cover when viewed in the direction of travel.
To replace it, you have to remove or tilt this casing.
On Lanos 1.4 (ZAZ Tavria) the thermostat is located to the left of the engine, when viewed in the direction of travel. It is located on the block head.
Kinds
Having figured out how a thermostat works in a car, let's look at its types. As technological progress continues, devices are also improved. Today they are divided according to the following parameters:
Design features of valves. Two-stage ones have a valve consisting of 2 “plates”. One opens when the temperature is high, and the second when the temperature is low.
Modern cars are often equipped with electronic (electrical) devices. Their operation is no different from a standard device. The only thing is that they have a housing with a heater.
Number of valves. There are one- and two-valve devices. The role of the first is aimed at regulating the flow of antifreeze to the radiator, the second type controls several coolant flows.
Thermostat design. There are dual types of thermostats, when there are two devices in one device that have different opening temperatures.
Different types of thermostat have different response temperatures, since engines themselves differ in operating temperature.
Presence of the body. There are frameless and framed designs. If the first is installed using a gasket, then the second is placed in the distribution casing.
Also included in the category of varieties are controlled and uncontrolled thermostats. Uncontrolled ones do not allow you to control the operation of the device, while controlled ones make it possible to configure them using the car’s ECU.
How to determine if there is a breakdown?
Primary diagnostics of the thermostat is carried out on the car. After starting the engine, check the temperature of the pipes going to the radiator (by hand or with a sensor mounted on a digital multimeter). After warming up the engine, it is necessary to check the degree of heating of the hoses going to the radiator. If the thermostat is working properly, the hoses should heat up evenly. The technique allows you to determine whether the valve stem and disc are jammed. The absence of cracks in the body parts of the regulator is also checked.
Additional testing involves removing the regulator from the machine. Antifreeze is drained from the cooling system; rubber pipes are held on the thermostat housing with screw or spring clamps (depending on the car manufacturer). The dismantled element is needed to be immersed in a container of water, which is installed on a gas or electric stove. To check the degree of heating of the liquid, use a thermometer or electronic thermometer.
When the water warms up to 90°C and above in a working thermostat, the valve should open. The opening process is controlled visually: if the plate remains motionless, the regulator must be replaced with a device with identical performance characteristics. The visual inspection method is not very accurate, since it is impossible to track the relationship between the valve position and the degree of heating. The correct heating of the power unit and maintaining the set temperature depend on this parameter.
Filling options
Having figured out what the thermostat in a car is responsible for, you need to understand the principle of its operation depending on the filler option. There are devices with solid and liquid filler.
A device with a solid filler has a mechanical valve, which is considered an important structural unit of the system. Its role is to distribute antifreeze flows. Control occurs through a temperature-sensitive element. When melting, the wax compresses the chamber, which affects the metal rod. The valve opens or closes the coolant flow.
To improve sensitivity, instead of wax, a mixture of it is added in combination with copper or graphite particles. The thermostat functions more smoothly if the transitions of its state from liquid to solid are carried out correctly.
The principle of operation of the device with a bellows is similar to the previous version. However, the sensitive element here is water and alcohol.
If the engine is cold, then no evaporation occurs, which means there is no pressure. But during heating, the alcohol evaporates, which means the pressure in the cylinder increases and the bellows opens the valve.
Recommendations for use
Domestic cars often experience problems maintaining engine operating temperature. Moreover, this can occur even with a working thermostat. To solve this problem, experts recommend using different thermostats seasonally. For example, in winter, drive with the element at 85 degrees, and in summer - at 75. This way the car will warm up faster in winter and not boil in summer. Also, you will not experience problems with a cold stove.
How to check the thermostat for functionality?
Professional car enthusiasts are mostly interested in something other than what a thermostat in a car is for.
Some people don’t know how to check the device’s functionality. There are two techniques that help to recognize whether the device is functioning correctly or not. The first method does not require removing the device, but a pyrometer is required for operation. The second method is simpler, but the driver will have to remove the part.
Checking without removing the engine is done quite quickly. The body of the device is connected to a radiator hose included in a large coolant circulation circle. It turns out that in working condition the hose remains cold until the coolant is released. To check the device without removing the “engine” you will need a pyrometer. Some people recommend taking measurements by hand. But we do not recommend doing this.
Verification algorithm:
The pyrometer is directed to the radiator hose (upper) and the “engine” is started. Next, you need to study the indicators and draw conclusions from them.
The hose was initially cold for no more than 3 minutes, and then warmed up, which means the thermostat is working correctly, switching the circulation correctly.
The hose heats up for quite a long time, which indicates that it is “stuck” in the open position.
The hose did not heat up at all. The thermostat is broken.
During the test, it is important to monitor the engine temperature to prevent overheating. Otherwise, a large number of parts will break, which is undesirable for drivers.
Before diagnosis, the device is removed and brought into the house. Fill a large saucepan with plain water. The body of the device will indicate at what temperature it switches. It is worth recording this data and then hanging the thermostat over the pan so that it does not touch the walls, but is immersed in water.
The next step is to heat the water, at the same time you need to measure its temperature with a special thermometer. When the water reaches the value at which the thermostat switches, you need to track this moment. If the thermometer shows the correct value, then the device is working properly.
Cost of parts and repairs
Most auto repair shops recommend replacing the thermostat every 3-5 years, without waiting for problems to arise. It is most convenient to do this together with diagnosing the cooling system or replacing the coolant. The cost of this work is low, it all depends on the position of the part under the hood and the car manufacturer.
The car market responds to demand with a wide range of both universal ones, designed for almost any engine, and individual copies. Domestic production will be an order of magnitude cheaper than imported analogues. For example, the cost of a Russian unit for a VAZ will be about 300 rubles. While a foreign device has a price of 600 rubles and above.
Possible faults
Any malfunctions in the car system negatively affect its overall performance. As for the thermostat, corrosion is considered the main reason for its malfunction. It covers the pin and cylinder. This results in a pulsating flow of coolant.
Here are a few more signs indicating a malfunctioning valve:
The lower pipe remains warm for a couple of minutes of engine operation.
The engine overheats too quickly, while both pipes have the same t.
When the device is operating, the needle shows a lower temperature. Its readings increase only at the moment when the “engine” stops working.
The device remains in the closed position for too long, it seems to be “stuck”, despite the fact that the temperature shows boiling.
A faulty thermostat can cause a lot of problems. Unfortunately, it is a non-repairable unit. Its price is not too high, but still not everyone wants to buy a new part.
Sometimes a thermostat breaks down not because its moving parts are worn out. This happens when dirt, scale, or a broken o-ring gets under the valves. In this situation, you may not need to completely replace the part. The driver can simply remove the thermostat, treat it with a substance that removes deposits and install it in place. A product for removing scale from water heaters is suitable for the job.
If the valve opens when it gets into boiling water, then the device is functioning. Before returning the part to its place, it is necessary to replace the O-ring and rinse the system with a special solution.
What are the signs of a broken thermostat?
In order to promptly identify a breakdown, you need to clearly know the signs of a faulty thermostat. The sooner the breakdown is identified and repaired, the less load the engine will receive, and the car will not boil or stall on the road. But first, let's study the reasons that can disable this part:
- scale on the rod and corrosive deposits on metal parts often occur due to the use of low-quality antifreeze;
- vibrations lead to destruction of the mechanism, this situation is typical for defective parts in which the rolling was carried out insufficiently well;
- Deformation of the rubber seal can occur as a result of exposure to high temperatures.
The malfunctioning state of the temperature control mechanism can be recognized by the following signs:
- prolonged warm-up of the engine is explained by the open position of the radiator pipe, which constantly cools the antifreeze;
- overheating of the engine indicates a closed radiator pipe;
- an increased duration of engine heating and a sharp increase in temperature with increasing load indicates the middle position of the valves;
- operation of the stove in cold mode, increased fuel consumption, decreased dynamic characteristics of the interior - all these are indirect signs.
Solid-state thermostat design
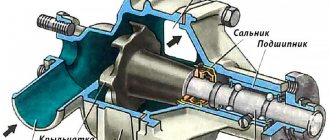
Modern internal combustion engine liquid cooling systems have received the most common version with a single valve, as well as a two-valve thermostat with a solid filler in the vast majority of cases. This element of the internal combustion engine cooling system is a heat-sensitive valve, which is enclosed in a brass frame. The valve also has a plate that is attached to the body. The body itself is a kind of cylinder. A special rod is inserted into this cylinder. The specified rod has one end resting on the upper part of the thermostat frame, and the other end rests on a rubber cavity in the device body. The body and rubber cavity are separated by a heat-sensitive element.
To put it simply, a common two-valve thermostat has a housing, two inlet pipes, an outlet pipe, a main and an additional valve, as well as a coolant temperature-sensitive element. The device is often installed in front of the point where the working fluid enters the centrifugal pump housing and is connected to it with a special outlet pipe. One inlet pipe connects the thermostat to the cylinder head, and the other makes a connection to the lower radiator tank.
The heat-sensitive coolant element consists of a copper cylinder, a rubber diaphragm and a rod. The solid filler is located between the diaphragm and the wall of the balloon. The element is a mixture of copper and granulated wax.
The main requirement for the material is a high coefficient of volumetric expansion. To perform the required functions, fine-crystalline wax or a mixture of copper powder and ceresin is excellent.
Wax was used in the design due to its ability to expand significantly under the influence of heat and change from solid to liquid and back. This wax or paraffin, which is used in the construction of car thermostats, is artificial and differs from the material we are used to. This wax has a number of specific properties that it acquires after undergoing the distillation process.
Principle of operation
When the engine starts, the thermostat is in a closed state at this moment and blocks the access of coolant to the large circle. The coolant circulates along a route that causes it to leave the cylinder block and return immediately. This feature of the cooling system ensures the most efficient heating of the power unit and its subsequent reaching the optimal temperature for its operation under load in the shortest possible time.
When the heating of the coolant reaches a temperature threshold of 80-90°C, then the thermostat begins to open. This happens because the solid element in the device body begins to melt at this temperature. There is a natural increase in the volume of the thermoelement. An increase in volume initiates movement of the thermostat housing along the rod. The rod itself is not capable of moving, since it is rigidly fixed structurally to the upper frame. The valve disc overcomes the force of the return spring and begins to open. This allows the coolant to pass through a fully or partially open valve and begin circulating through the radiator. The cooling efficiency of the coolant in the radiator increases significantly.
At the maximum permissible increase in coolant temperature, the thermostat is fully open, allowing the coolant to pass through the radiator in full. The thermostat opens fully at a temperature of about 95-105°C. When a car engine operates in various modes that are constantly changing, there is a constant change in the degree of opening of the thermostat.
If we consider the operating principle of a two-valve thermostat, taking into account the more familiar concepts of coolant movement in a “large” and “small” circle, then we get the following. Let's imagine that the temperature of the coolant in the system has exceeded 80 degrees Celsius. The solid filler of the thermostat begins to melt and increases in volume, then presses on the rod, which comes out of the cylinder. The balloon begins to move upward, thereby closing the additional valve of the device. The access of coolant to the small circle is closed.
When the coolant reaches a temperature of about 94 degrees, the additional valve will close completely. The main valve still remains open and the coolant circulates freely in a large circle, which implies its movement through the cooling radiator channels.
In the event that there is a decrease in coolant temperature below 80 degrees, the volume of the filler is reduced, and the main thermostat valve begins to gradually close. The fluid flow in the radiator decreases. At the same time, an additional valve begins to open in parallel, which allows the coolant to circulate in a small circle.
The ability to open fully or partially allows you to most efficiently and flexibly maintain optimal temperature indicators for the operation of the internal combustion engine in various load modes. Additionally, the thermostat allows you to reduce the physical wear of parts and components of the power unit, as well as reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases. The most common and high-quality manufacturers of thermostats are Gates, Wahler and Vernet.
How it works
Let's see what this device actually looks like. In fact, from a visual point of view, the thermostat is a special valve, which in some situations is placed in the car engine housing. According to the design itself, they come in two types: unframed and framed.
The housing structure is built into the motor housing and has several terminals (at least two). However, there are exceptions to this point - some two-level devices. These devices are made from some special materials: aluminum, brass and plastic coating. The two terminals that are located as close to each other as possible are called a small circuit in technical language. This circuit controls the temperature of the antifreeze inside the engine and prevents it from directly entering the radiator. All of the above allows the car to warm up as quickly as possible, which ensures that the thermostat opens more quickly. In Russian cars, the following temperature indicators are often found at which our device opens: 81-86 degrees.
By default, the ability to manually control the temperature at which the device will open or close is impossible, but the car enthusiast has the opportunity to go to a specialized service station and order this service there. You will find this function useful in your car.
Regarding the open-frame design: it is built into the engine housing of the car in a specially designated place. This is its main difference from the hull design.
Why is a thermostatic valve needed?
The valve solves two problems: maintains the room temperature at a comfortable level and saves energy.
But in order for it to really cope with such functions, you need to understand in what cases the device is appropriate and how to install it correctly.
If in the middle of winter there is a need to open the windows so that the temperature in the room drops to an acceptable level, a thermostat is definitely needed. But it won’t help when the radiators are barely warm—it will probably make it even colder.
In the second case, it is better to try to regulate the temperature in the room differently: change the volume of coolant in each radiator, adjust the operation of the boiler (for a large area), select the optimal circulation pump or adjust the operation of the existing one.
The price of a thermostat ranges from several hundred rubles (200-600), so re-equipment of the heating system will not be expensive. But there are also expensive models
As a temporary measure, control valves can be used. But it is not recommended to use ball valves for these purposes.
Checking the thermostat and common faults
Thermostat malfunctions are most often associated with wear or corrosion. This may cause the valve to become stuck in the open, closed, or partially open positions. Signs of a constantly open thermostat, as well as a stuck in intermediate position situation, appear only at low temperatures (cold weather), when the engine warm-up becomes too long. A permanently closed position is a more serious problem and causes the engine to overheat, which can lead to permanent damage.
How to check if the thermostat is working properly
Also, the thermostat may be initially of poor quality, which often manifests itself as untimely opening. Early firing increases fuel consumption because the engine will take longer to reach operating temperature. When the valve on a large circuit operates later, engine wear increases.
The main way to check the thermostat involves removing it from the engine:
- The thermostat is dismantled and placed first in a container with hot (boiling) water. If the valve does not open or opens too slowly, it will require replacement. If the valve has tripped, perform a reverse check by placing it in cold water and monitoring the closing process.
Car thermostats cannot be repaired and require replacement if faults are detected. You should also know that different brands have different opening and closing temperature characteristics. Therefore, to ensure optimal engine operation, it is necessary to install models recommended by the car manufacturer.
Design and operating features of the device
Let's look at how a thermostatic valve works and on what principle it works.
How does a thermal valve work?
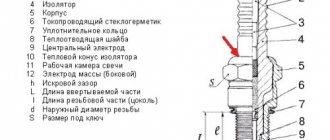
The device consists of two main working elements - a valve and a thermostatic head. The first is most often made of brass, sometimes nickel-plated, its lower part blocks the pipe, and its upper part continues the pressure rod and spring.
Valves are also available in bronze (nickel-plated or chrome-plated), as well as stainless steel. The latter are rare and expensive.
What happens inside the valve? The head device contains a sensitive element. It is located in a cavity with gas or liquid (bellows).
Heating provokes expansion in this environment, the element is pushed forward, pressing on the rod, spring, and later on the valve. The force of pressure determines the degree of overlap.
The figure shows a device with liquid in a bellows. Gas thermostats react faster to temperature changes (5-10 minutes), but are also more expensive. There is no significant difference from this during operation
An additional part of the thermostat is a plug or handle with a scale. Some devices have electronic controls.
Operating principle of the device
Let's take a closer look at the working principle of battery thermostatic valves. The mechanics of their action looks schematically like this: when the temperature of the coolant or the environment changes, the gas or liquid in the head reacts to these fluctuations.
The sensing element acts on the pressure rod, and it goes up or down. When the rod moves down, the valve blocks the flow of coolant, which stops the flow of heat and slows down the circulation rate. No heat enters the battery, so the room temperature does not rise.
And here it is important to distinguish a thermostatic valve from a control valve. The latter can reduce the valve capacity and thus regulate the temperature of the batteries.
When turning the knob or entering a digital value on the panel, the user sets the initial pressure value in the thermal head, to which it “adjusts” during operation
The control valve does not have a thermal head. The thermostat is open or closed, it is controlled by a thermal head, it does not change the volume of coolant, but only turns its supply on and off
Let's look at the operating principle of a thermal valve using an example. So, set the device to the recommended temperature of 20 degrees. This is usually a three or the largest point on the regulator scale.
What happens inside the device? If the surrounding air heats the head to 21 degrees, i.e. increases the set temperature by 1 degree, it presses the rod, the flow of coolant into the battery is completely blocked by the valve.
The radiator does not heat up and the room temperature begins to drop. When the ambient temperature drops to 19 degrees, the thermal valve will open and the battery will begin to heat up.