The fuel system of a car is one of the key systems in a car. Its malfunction or incorrect operation can lead to expensive repairs or excessive fuel consumption. The fuel system diagram of modern cars consists of five key elements. Diesel and gasoline engine systems are different. Read about the features of their designs below.
Design and main structural elements
By design, the entire fuel system can be divided into the following elements:
- Fuel tank . Tanks come in different configurations and volumes. Equipped with a fuel level sensor, which gives the driver an understanding of the tank’s full level. To fill the fuel, the tank has a neck that can be closed with a lid.
- Fuel lines . They are a set of tubular lines through which fuel travels from the tank to the distribution device.
- Filters . Coarse and fine filters are used. The coarse filter is mounted directly on the fuel tank and consists of a metal grid. This filter prevents large particles of contaminants from entering the fuel system lines. The fine filter is installed directly in the engine compartment in front of the fuel pump. It already catches smaller particles of dirt.
- Fuel pumps . According to the design, two or one fuel pump is installed. Their number depends on the design of the educator mixture. In carburetor types there is only one pump. Diesel engines are equipped with low and high pressure pumps.
- Mixing agent. This element is responsible for mixing fuel with air and injecting the mixture into the engine. In gasoline engines this is a carburetor or an injector.
Power System Options
The main types of fuel for internal combustion engines are gasoline and diesel fuel (“diesel fuel”). Gas (methane) also belongs to the types of modern fuel, but, despite its widespread use, it has not yet become relevant. The type of fuel is one of the criteria for classifying internal combustion engine power systems.
In this regard, power units are distinguished:
- gasoline;
- diesel;
- based on gaseous fuel.
But the most recognized among experts is the typology of engine power systems based on the method of fuel supply and preparation of the fuel-air mixture. Following this classification principle, we distinguish, firstly, the power supply system of a carburetor engine, and secondly, the power supply system with fuel injection (or an injection engine).
Carburetor
The carburetor system is based on the operation of a technically complex device - a carburetor. A carburetor is a device that prepares a mixture of fuel and air in the required proportions. Despite the variety of types, in automotive practice the most widely used is the float suction carburetor, the circuit diagram of which includes:
- float chamber and float;
- atomizer, diffuser and mixing chamber;
- air and throttle valves;
- fuel and air channels with corresponding jets.
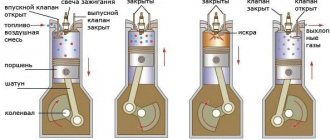
The preparation of the fuel-air mixture in the carburetor is carried out according to a passive scheme. The movement of the piston during the intake stroke (first stroke) creates a rarefied space in the cylinder, into which air rushes, passing through the air filter and through the carburetor. It is here that the formation of a combustible mixture occurs: in the mixing chamber, in the diffuser, the fuel escaping from the atomizer is crushed by the air flow and mixed with it. Finally, through the intake manifold and intake valves, the combustible mixture is supplied to a specific engine cylinder, where at the required moment it is ignited by a spark from the spark plug.
Thus, the power system of a carburetor engine is a predominantly mechanical method of preparing the fuel-air mixture.
Fuel injection
The era of the carburetor is being replaced by the era of the injection engine, the power system of which is based on fuel injection. Its main elements are: an electric fuel pump (located, as a rule, in the fuel tank), injectors (or nozzle), and an internal combustion engine control unit (the so-called “brains”).
Types of engine fuel supply systems
Depending on the design of the car, its year of manufacture and the type of combustible material on which it runs, fuel systems have their own differences.
By fuel type:
- gasoline;
- diesel
This is interesting: 5 differences between an automatic transmission and a robot: advantages and disadvantages of transmissions
The design of these fuel systems is radically different and read about their features below.
Gasoline engines, in turn, are divided into:
- carburetor;
- injectors.
In modern cars, carburetor fuel supplies are almost never found. Most have injectors. But cars produced 10 - 15 years ago were equipped with carburetors, so we will also look at the operating principle of such systems.
Fuel system of carburetor engines
By design, the carburetor consists of a body, a float chamber, valves, jets, and a mixture of the forming chamber. In the carburetor system, there is one fuel pump installed - low pressure. It is installed in the engine compartment, near the carburetor. The pump pumps fuel into the float chamber. This chamber got its name from the float that regulates its filling. If there is more fuel in the chamber than needed, the float raises the needle valve. The needle valve closes the fuel supply to the chamber. If there is a lack of fuel in the chamber, the whole process occurs in reverse.
From the float chamber, fuel is supplied through a nozzle, which is a tube with a small hole, into the mixing chamber. In this chamber, gasoline is mixed with air, which in turn comes from the air intake.
The fuel supply is regulated by the throttle valve, which is connected by a cable to the gas pedal in the car. From the carburetor, the mixture is supplied to the engine using reverse thrust from the cylinder-piston group. In other words, the piston sucks in the fuel mixture.
There are three types of fuel mixture:
- Enriched . This mixture contains an increased amount of fuel and a reduced volume of air. This in turn leads to excessive fuel consumption. This mixture is used when starting a car engine. This is regulated using the so-called “suction”. After warming up the engine, the mixture must be returned to normal and the “suction” removed.
- Normal . The mixture contains the right amount of fuel and air. This is, in other words, the golden mean.
- Depleted . In this mixture there is more air than necessary, and less fuel. This entails a reduction in consumption and power. The car will have difficulty climbing hills, especially when loaded. The speed will become significantly slower.
The quality of the mixture on the carburetor is adjusted with a bolt. In general, it is worth saying that the carburetor has an idle speed and mixture quality screw. It is the mixture quality screw that regulates its composition.
If you don’t understand how to regulate, then it’s better to entrust this matter to a professional. This work is very precise and requires skills.
This is interesting: How to turn off a faulty car alarm? 3 main ways
One of the most common problems with carburetor types of systems is self-adjustment. There are situations when the problem is not in the settings at all, but, for example, in a broken needle valve. Due to the overflow of the float chamber, the flow rate increases, and car enthusiasts begin to turn the screws of the educator mixture. It doesn't lead to anything.
Features of the fuel injection system
The difference between the injection type engine and the carburetor type is as follows. The fuel pump creates high pressure and supplies fuel to the fuel rail, and from it through the injectors to the engine. The control unit regulates the fuel supply, its quantity and quality.
It is possible to make any adjustments only through a special computer. In addition, the control unit will not give a signal to supply fuel if at least one sensor in the car fails. The panel will display an error with the name. By the name of the error, you can decipher which sensor has failed.
Diesel engine fuel system diagram
A diesel engine has a different fuel system than a gasoline engine. Ignition of the fuel mixture occurs due to air compression and heating. In such systems, spark plugs are not used to detonate the mixture. Diesel engines use spark plugs, but incandescent ones. They serve to heat the fuel system during startup. They are not needed during work.
The diesel system has two fuel pumps. One of them is high pressure, and the other is low. The low pressure pump pumps fuel from the tank. The high pressure pump creates the required pressure in the system during injection. The role of a distributor is performed by nozzles; they dose the quantity of the mixture and determine its quality. There is a special stand to check injector wear.
A feature of the diesel engine is the lack of regulation of mixture quality. This is especially true in winter at low temperatures. Also in winter, diesel starts to freeze. To prevent this from happening, additives are used.
Car fuel system operation
All the elements considered work in the following sequence... at the moment the engine starts, and on some cars at the moment the driver's door is opened, the fuel pump begins to work, creating the necessary operating pressure in the fuel system necessary to supply fuel to the engine.
As the fuel filter or filter system passes through the engine, the fuel is cleaned of various mechanical impurities. The air enters the combustion chamber or carburetor through an air filter, where it is also cleaned.
Depending on the design of the engine, the fuel-air mixture can be prepared both directly inside the combustion chamber of the engine cylinder, and before entering the cylinder, for example, in a carburetor. A combined method of preparing the fuel-air mixture is also possible.
After the fuel-air mixture is ready and enters the combustion chamber, it ignites. To continue to operate the engine, a constant supply of new portions of fuel is required, for which the fuel system is responsible.
Car device
Fuel equipment of diesel engines
Working on heavy fuel with compression ignition has its own specifics associated with the difficulties of fine atomization and high diesel compression. Therefore, fuel equipment has little in common with gasoline engines.
Separate injection pump and pump injectors
The high pressure required for high-quality injection into highly compressed hot air is created by injection pumps. According to the classical scheme, fuel is supplied to its plungers, that is, piston pairs made with minimal clearances, by a booster pump after thorough cleaning. The plungers are driven into translational motion via the cam shaft from the engine. The same pump performs dosing by turning the plungers through a gear rack connected to the pedal, and determines the injection moment due to synchronization with the gas distribution shafts and the presence of additional automatic regulators.
Each plunger pair is connected by a high-pressure fuel line to injectors, which are simple spring-loaded valves led into the combustion chambers. To simplify the design, so-called pump injectors are sometimes used, combining the functions of high-pressure fuel injection pumps and nozzles due to power drive from the camshaft cams. They have their own plungers and valves.
Main rail injection type Common Rail
The principle of electronic control of injectors connected to a common high-pressure line has become more advanced. Each of them has an electrohydraulic or piezoelectric valve that opens and closes at the command of the electronic unit. The role of the fuel injection pump is reduced only to maintaining the required pressure in the ramp, which, using this principle, could be increased to 2000 atmospheres or more. This made it possible to more accurately control the engine and comply with new toxicity standards.
Injector
The injection engine is a modern internal combustion engine design. It significantly exceeds carburetor power systems for gasoline engines in all respects. An injector is a device that provides fuel injection into the engine. This design allows for high engine power. At the same time, the toxicity of exhaust gases is significantly reduced.
Injection engines are characterized by stable operation. The car demonstrates improved dynamics when accelerating. In this case, the amount of gasoline that the vehicle requires to move will be significantly lower than that of a carburetor power system.
Fuel with an injection system burns more efficiently and completely. At the same time, the process control system is fully automated. There is no need to manually configure the unit. The injector and carburetor differ significantly in design and operating principle.
The fuel injection system for a gasoline engine includes special injectors. They inject gasoline under pressure. It is then mixed with air. This system allows you to save fuel consumption and increase engine power. It increases to 15% when compared with carburetor types of internal combustion engines.
The injection engine pump is not mechanical, as was the case in carburetor designs, but electric. It provides the required pressure when injecting gasoline. In this case, the system supplies fuel to the desired cylinder at a certain time. The entire process is controlled by an on-board computer. Using sensors, it evaluates the amount and temperature of air, engine and other indicators. After analyzing the collected information, the computer makes a decision on fuel injection.
Injector device
The power supply system of a gasoline engine with fuel injection has a specific device. To carry out maintenance of such a motor yourself, you need to understand the principle of its operation and design.
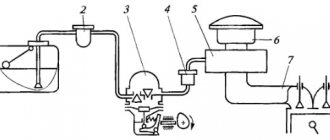
The injection system contains several mandatory elements (the diagram is presented below).
It includes an electronic control unit (on-board computer) (2), an electric pump (3), and injectors (7). There is also a fuel rail (6) and a pressure regulator (8). The system must be monitored by temperature sensors (5). All of these components interact with each other according to a certain pattern. The system also contains a gas tank (1) and a gasoline filter (4).
To understand the operating principle of the presented power system, you need to consider the interaction of the presented elements using an example. New cars are often equipped with an injection system with injection distributed over several injection points. When the engine starts, fuel flows to the fuel pump. It is located in the fuel tank in the fuel. Next, the fuel enters the line under a certain pressure.
Nozzles are installed in the ramp. Gasoline is supplied through it. There is a sensor in the rail that regulates fuel pressure. It determines the air pressure in the injectors and at the intake. The system sensors transmit information to the on-board computer about the state of the system. It synchronizes the process of supplying mixture components, adjusting their quantity for each cylinder.
Knowing how the injection process works, you can independently carry out maintenance of the gasoline engine power system.
Method for preparing the fuel mixture
The operation of the gasoline engine power system, depending on the features of its design, can differ significantly. However, regardless of how it is structured, a number of requirements are put forward to the components and mechanisms.
The fuel supply system must be sealed. Otherwise, failures appear in various parts of it. This will lead to improper operation of the motor and its rapid destruction. The system must also produce accurate fuel dosage. It must be reliable and ensure normal operating conditions of the engine in any conditions.
Another important requirement that is put forward today for the fuel mixture preparation system is ease of maintenance. For this purpose, the design has a certain configuration. This allows the vehicle owner to independently carry out maintenance if necessary.
Today, the power supply system of a gasoline engine differs in the method of preparing the fuel mixture. It can be of two types. In the first case, a carburetor is used to prepare the mixture. It mixes a certain amount of air with gasoline. The second method of preparing fuel is forced injection of gasoline into the intake manifold. This process occurs through injectors. These are special nozzles. This type of engine is called injection.
Both systems presented provide the correct proportion of gasoline and air. Fuel, when dosed correctly, burns completely and very quickly. This indicator is largely influenced by the amount of both ingredients. A normal ratio is considered to be 1 kg of gasoline and 14.8 kg of air. If deviations occur, we can talk about a lean or rich mixture. In this case, the conditions for proper operation of the motor deteriorate. It is important that the system ensures normal quality of the fuel supplied to the internal combustion engine.
The procedure takes place in 4 steps. There are also two-stroke gasoline engines, but they are not used for automotive vehicles.
Fuel return line (“return”)
Fuel systems
As a rule, the fuel pump has a constant capacity, that is, it pumps fuel from the tank into the ramp under constant pressure . The engine operates in different modes, consuming different amounts of fuel, depending on its load. Thus, it becomes necessary to control the pressure and amount of fuel in the fuel rail.
This is done by the fuel pressure regulator, which drains excess fuel back into the tank through the fuel return line , the so-called “return”. Currently, there are two types of fuel systems, differing in the presence or absence of a fuel return line (return line).
- Fuel supply system with return line . Fuel that is not injected by the injector is excess fuel and it returns back to the tank through the regulator, which is located on the fuel rail, and the return line. In this way, constant pressure is maintained in the fuel manifold.
- Fuel system without return line . The fuel pressure regulator in such systems is usually installed in the submersible fuel pump module. Excess fuel supplied by the pump is returned back to the tank through a short return line. In this case, only the amount of fuel that is injected by the injectors is supplied to the fuel rail. This system has the following advantages: lower cost and less heating of the fuel in the tank.
Sources
- https://autodromo.ru/articles/toplivnaya-sistema-avtomobilya-sistema-podachi-topliva-ustroystvo-naznachenie-princip
- https://ZnanieAvto.ru/toplivo/sistema-pitaniya-dvigatelya-avtomobilya.html
- https://topdetal.ru/stati/kakie_byvayut_vidy_sistem_pitaniya_dvigatelya/
- https://TechAutoPort.ru/dvigatel/toplivnaya-sistema/toplivnye-sistemy-benzinovyh-i-dizelnyh-dvigateley.html
[collapse]
Malfunctions and service
During the operation of the vehicle, the vehicle's fuel system experiences loads that lead to its unstable operation or failure. The following faults are considered the most common.
Insufficient supply (or lack of supply) of fuel to the engine cylinders
Poor quality fuel, long service life, and environmental exposure lead to contamination and clogging of fuel lines, tank, filters (air and fuel) and technological openings of the combustible mixture preparation device, as well as breakdown of the fuel pump. The system will require repairs, which will consist of timely replacement of filter elements, periodic (every two to three years) cleaning of the fuel tank, carburetor or injector nozzles and replacement or repair of the pump.
Engine power loss
A malfunction of the fuel system in this case is determined by a violation of the regulation of the quality and quantity of the combustible mixture entering the cylinders. Troubleshooting involves the need to diagnose the combustible mixture preparation device.
Fuel leak
A fuel leak is a very dangerous phenomenon and is absolutely unacceptable. This malfunction is included in the “List of malfunctions...” with which the vehicle is prohibited from moving. The causes of the problems lie in the loss of tightness of the components and assemblies of the fuel system. Troubleshooting involves either replacing damaged system elements or tightening the fuel line fastenings.
Thus, the power system is an important element of the internal combustion engine of a modern car and is responsible for the timely and uninterrupted supply of fuel to the power unit.
I like3I don't like
What else is worth reading
VAZ 2109 generator device
The design of the chassis of the VAZ 2109
Intake manifold device
Fuel pump
Power system operating modes
Depending on the goals and road conditions, the driver can use different driving modes. They also correspond to certain operating modes of the power supply system, each of which has a special quality fuel-air mixture.
- The mixture will be rich when starting a cold engine. At the same time, air consumption is minimal. In this mode, the possibility of movement is categorically excluded. Otherwise, this will lead to increased fuel consumption and wear of power unit parts.
- The composition of the mixture will be enriched when using the “idling” mode, which is used when coasting or running the engine in a warm state.
- The mixture will be leaner when driving with partial loads (for example, on a flat road at medium speed in high gear).
- The mixture composition will be enriched at full load when the vehicle is moving at high speed.
- The mixture will be rich, close to rich, when driving under conditions of sharp acceleration (for example, when overtaking).
The choice of operating conditions for the power system, therefore, must be justified by the need to move in a certain mode.
Carburetor system maintenance
Maintenance and repair of gasoline engine power system devices can be done with your own hands. To do this you need to perform a number of manipulations. They boil down to checking the fastenings of the fuel lines and the tightness of all components. The condition of the exhaust gas system, throttle actuator thrust, and carburetor air damper is also assessed. In addition, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the crankshaft limiter.
If necessary, it is necessary to clean the pipelines and replace seals. A feature of carburetor maintenance is the need to tune it in spring and autumn.
In some cases, the cause of deterioration in the performance of a carburetor engine may be faults in other components. Before starting maintenance of the fuel supply system, you need to check other components of the mechanisms.
Malfunctions in the power supply system of a carburetor-type gasoline engine can be checked with the engine running and turned off.
If the engine is turned off, you can assess the amount of gasoline in the tank, as well as the condition of the rubber seals under the filler cap. The fastening of the gas tank, fuel line and all its elements is also assessed. Other elements of the system should also be checked for fastener strength.
Then you need to start the engine. The absence of leaks at the joints is checked. You should also evaluate the condition of the fine filters and sedimentation tank. The carburetor needs to be adjusted correctly. In accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, the ratio of air and gasoline is selected.