Purpose and design of the VAZ 2107 driveshaft
The driveshaft is a mechanism that connects the gearbox to the rear axle gearbox and is designed to transmit torque. This type of transmission is most widespread on vehicles with rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive.
Cardan device
The VAZ 2107 driveshaft consists of the following elements:
The cardan transmission can be single-shaft or double-shaft. The second option involves the use of an intermediate mechanism, to the back of which a shank with splines is attached to the outside, and a sliding sleeve is fixed to the front through a hinge. In single-shaft structures there is no intermediate section.
The front part of the cardan is attached to the gearbox through a movable coupling with a spline joint. To do this, there is a hole with internal splines at the end of the shaft. The cardan design involves longitudinal movement of these splines at the moment of rotation. The design also includes a suspension bearing attached to the body using a bracket. It is an additional attachment point for the cardan and is designed to limit the amplitude of its movement.
A fork is located between the middle and front element of the propeller shaft. Together with the crosspiece, it transmits torque when the cardan bends. The rear part of the shaft is attached to the rear axle gearbox through a flange. The shank engages with the main gear flange through external splines.
The cardan is unified for all classic VAZ models.
Cross device
The VAZ 2107 crosspiece is designed to align the axes of the cardan and transmit torque when its elements bend. The hinge provides connection for the forks attached to the ends of the mechanism. The main element of the crosspiece is needle bearings, thanks to which the cardan can move. These bearings are inserted into the fork holes and secured with retaining rings. When the joint wears out, the driveshaft begins to knock while driving. A worn crosspiece is always replaced with a new one.
Types of cardan shafts
Cardan shafts are of the following types:
The classic cardan consists of a fork and a cross with needle bearings. Most rear-wheel drive cars are equipped with such shafts. Cardan shafts with CV joints are usually installed on SUVs. This allows the selection to be completely eliminated.
The mechanism with elastic hinges consists of a rubber coupling capable of transmitting torque at angles of no more than 8˚. Since the rubber is quite soft, the cardan provides a smooth start to movement and prevents sudden loads. Such shafts do not require maintenance. The rigid semi-cardan joint has a complex design that involves transmitting torque thanks to the gaps in the spline connection. Such shafts have a number of disadvantages associated with rapid wear and complexity of manufacturing, and are not used in the automotive industry.
CV joint
The imperfection of the design of a classic cardan on crosspieces is manifested in the fact that at large angles vibrations occur and torque is lost. The universal joint can deflect by a maximum of 30–36˚. At such angles, the mechanism may jam or completely fail. Cardan shafts on CV joints, usually consisting of:
The maximum possible angle of inclination of the cardan of this design is 70˚, which is noticeably higher than that of the shaft on the crosses. There are other designs of CV joint cardans.
Gimbal function
In a car, a cardan is needed to transmit torque from the gearbox or transfer case to the axle gearboxes.
The difficulty lies in the fact that the rotation axes of the box and the bridge are in different planes. Therefore, the cardan is not installed clearly in a horizontal plane, but at a slight angle. When you engage the gear and press the gas, the torque transfers to the sliding fork. The movement is transmitted to the cross-shaped joint and then goes to the rear axle gearbox. The designers' task is to minimize torque losses. Since the cardan constantly works when moving and it is necessary to ensure the reliability of its operation, the following compensation methods have been created:
- Composite structure of several pipes. Provides a reliable connection between the gearbox and the axle, which are located in different planes.
- Minimal play in the crosspieces and forks is needed for smooth transmission of torque, which affects the smoothness of the ride.
- Compensation for rear axle movement using a sliding fork.
Ideally, the rotation speed of the transmission shaft should coincide with the movement of the rear axle drive gear. However, in practice this depends on the actual condition of the cardan. It is necessary to monitor the wear of hinges and bushings, support bearings.
VAZ 2107 cardan mount
The VAZ 2107 cardan is attached in several places:
Cardan mounting bolts
To attach the cardan to the VAZ 2107, four bolts measuring M8x1.25x26 with a conical head are used. A self-locking nut with a nylon ring is screwed onto them. If the bolt turns when tightening or unscrewing, it is secured with a screwdriver.
Elastic coupling
The elastic coupling is an intermediate element for connecting the cardan cross and the secondary shaft of the box. It is made of high-strength rubber to reduce vibration. The clutch is removed in case of mechanical damage for replacement or when repairing the gearbox. When installing an old coupling, you will need a clamp of the appropriate size to tighten it. New flexible couplings are usually sold complete with a clamp, which is removed after installation.
What are the main parts of the VAZ 2107 cardan transmission?
- Parts capable of changing the angle and length of the transmission are the coupling (5), as well as rigid hinges (9.7) and elastic (3). It is called a coupling. The role of the coupling is that it reduces the noise of the connection and angular torque is transmitted. Repair of the driveshaft is required if the coupling material is cracked and crumbled. Simply put, the clutch needs to be replaced.
- The cardan coupling consists of 6 rubber parts (30), with metal spacers (31) between them. These parts are tightly connected into a one-piece unit, so in case of failure, the most correct solution is to replace the coupling.
- The coupling is placed between the flanges (4,2). They are attached to it with 35 bolts.
- Intermediate support (6), which serves to reduce vibrations and various types of beating.
- The front shaft of the VAZ 2107 (5) is a pipe with splines installed by welding. There is a tip (40) at the front. One of the coupling flanges is located on it, and the rear splined end is located on the support bearing (6). The bearing itself is well insulated from dirt by seals. Repair of the driveshaft is necessary if the splines are worn out.
- The rubber pad (12) in which the bearing is located dampens vibration well. On it, the front shaft may move slightly.
- The intermediate cardan support is attached to the bracket (15).
- Important is the safety bracket (27), which prevents the shaft from falling out if the coupling fails. If this bracket was not there, then the cars would overturn at full speed, and such cases have happened before. In this case, repairing the driveshaft is impossible; replacement is required.
- The difference between the rear shaft (8) and the front “neighbor” is that it has a hinge fork at the ends.
- The hinge itself is an important element of the transmission; it consists of a pair of forks (23), one crosspiece (22) and, in a separate figure above, needle-shaped bearings (20) - there are 4 of them, rings (19) and oil seals (21). The bearings are pressed with a fairly large force of about 800 kg into the fork holes. They are non-separable; if they malfunction, they need to be replaced.
- The cross has the required gap, from 0.1 to 0.4 mm. Only within such limits is the crosspiece correctly centered. There are rings in five sizes and five different colors for proper alignment. Repair of the driveshaft most often consists of correcting these gaps and replacing the rings.
Repair of VAZ 2107 cardan
You can dismantle the VAZ 2107 driveshaft for repair or replacement without a ramp or lift. To do this you will need:
Dismantling the cardan
To repair or replace the flexible coupling, the cardan will need to be removed from the vehicle. Its dismantling is carried out in the following order:
Replacing the cardan cross
If there is play in the hinges, the crosspiece is usually replaced with a new one. The fact is that worn needle bearings cannot be repaired. Dismantling the cross after removing the cardan is carried out as follows:
Video: replacing the VAZ 2107 crosspiece
Replacing the outboard bearing
If the bearing or rubber suspension has exhausted its service life, replacement is carried out in the following order:
Video: replacing the suspension bearing on a VAZ 2107
Cardan assembly
Assembly and installation of the driveshaft on the VAZ 2107 is carried out in the reverse order. In this case, you should pay attention to the following important points:
During assembly, it is recommended to lubricate all bolted connections. This will make repair work much easier in the future.
Cardan transmission assembly
Cardan transmission assembly
Repair and operation manual - Transmission VAZ-2101 - VAZ-2107 - Cardan transmission assembly
Cardan transmission assembly
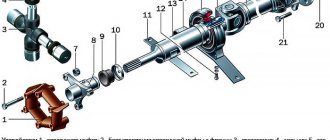
Front driveshaft parts
1 – elastic coupling; 2 – centering sleeve; 3 – elastic coupling flange; 4 – oil seal; 5 – oil seal cage; 6 – cardan shaft; 7 – dust deflector; 8 – bearing; 9 – retaining ring; 10 – nut; 11 – universal joint fork; 12 – dust deflector; 13 – elastic support.
Cardan joint assembly
1 – universal joint fork; 2 – retaining ring; 3 – bearing housing; 4 – oil seal; 5 – spike of the cross; 6 – bearing needle; 7 – caliber 41.8734.4092; A, B, C, D – probe petals having a thickness of 1.53; 1.56; 1.59; 1.62
EXECUTION ORDER
1. Assemble the cardan shafts in the reverse order of disassembly, taking into account the following instructions: – apply FIOL-1 lubricant to the splined joints; – when connecting parts, align the marks made on the detachable parts before disassembling; – after assembling the spline connection, pressing the oil seal 0.3–0.5 mm with an axial load, crimp the clip onto the groove of the fork; – tighten the nut securing the front propeller shaft fork with a torque wrench and caulk it.
2. When assembling the intermediate support, press in the bearing with a mandrel (1 – mandrel A.70045, 2 – bearing, 3 – elastic support) and install a retaining spring ring in the groove of the support.
3. Place dust deflector 7 on the rear end of the front propeller shaft (see Fig. Details of the front driveshaft).
4. Using a mandrel (1 – mandrel A.74035, 2 – elastic support; 3 – rear part of the front driveshaft), press in the support with the bearing and put on the second dust deflector 12 (see Fig. Details of the front driveshaft), press the fork 11 of the front driveshaft onto the shaft propeller shaft and secure it with the nut as described above.
5. Assemble the cardan joint in the following order. After removing the old thickened grease, fill the cavities in the spider spikes and lubricate the inner surface of the bearing housings with FIOL-2U grease (0.4–0.6 g for each bearing). Lubricate the spikes of the cross with a thin layer to prevent the formation of an air cushion during assembly. Insert the spider tenons into the fork.
6. Place the bearing housings with needles on the spider spikes and press them into the fork holes with a force of 7840 N (800 kgf). Install the retaining rings in the grooves of the fork in their original places, according to the marks. Then check the axial free play of the spider, which should be 0.01–0.04 mm. If the free play is greater than specified, replace one thinner snap ring with a thicker one.
7. When replacing parts of the universal joint, select retaining rings with caliber 41.7834.4092, which has four blades of different thicknesses (1.53 mm; 1.56 mm; 1.59 mm; 1.62 mm). To do this, install retaining ring 2 (see Fig. Cardan joint assembly) with a thickness of 1.56 mm.
8. When pressing bearings, when the cross rests against the bearing housing (in this case there are no gaps), use a feeler gauge to determine the distance between the bearing housing and the end of the annular groove. Depending on the measured distance, taking into account the axial clearance of 0.01–0.04 mm, insert a second circlip of appropriate thickness.
Warning Retaining rings are supplied in spare parts in five sizes (thickness, mm), each of which has a specific color: 1.50 – unpainted; 1.53 – dark brown; 1.56 – blue; 1.59 – black; 1.62 – yellow.
9. Having installed the retaining rings, hit the forks with a hammer with a plastic striker. Under the influence of impact and elastically compressed oil seals, the gap between the bottom of the bearing and the retaining ring is knocked out, and gaps appear between the bearing housings and the ends of the crosspiece studs. After assembly, check the ease of rotation of the hinge forks and the balancing of the cardan drive.
Quote
Balancing the VAZ 2107 driveshaft
If vibration occurs due to an imbalance in the driveshaft, it will need to be balanced. It is problematic to do this on your own, so they usually turn to a car service. Balance the cardan as follows.
The results obtained make it possible to balance the cardan by welding weights into the places established according to the measurement results. After this, the balance is checked again.
Video: balancing the cardan
Craftsmen have figured out how to balance the VAZ 2107 cardan with their own hands. The procedure is as follows:
Obviously, it will not be possible to achieve high balancing accuracy using the traditional method.
Repairing a VAZ 2107 driveline transmission is not particularly difficult even for inexperienced car owners. All you need is desire, free time, a minimum set of plumbing tools and careful adherence to the instructions of specialists.
Source
Cardan balancing
An imbalance can occur for several reasons:
- Presence of gaps
- Manufacturing defects
- Mechanical damage during operation
- Shaft deformation
- Wear
To perform ideal balancing of the cardan, you need to contact a service station that specializes in such work. The length of the cardan exceeds the diameter and for perfect balancing you will need high-precision equipment. This kind of work cannot be done in a garage. You can only remove the source of strong vibration. There is no need to remove the driveshaft. The cardan area is divided into small sections, and weights are attached to each of them in turn. After this, you should take a test drive to check for vibration. The weights must be moved along the sections of the cardan until the vibration noticeably decreases.
Installing a new or repaired cardan is similar to removal, but in reverse order.
Replacing the driveshaft: when is it necessary and how to do it?
Issues discussed in the material:
Owners of front-wheel drive cars are completely uninterested in such a topic as replacing a driveshaft. However, if you have an all-wheel drive car or with rear-wheel drive, then it is better to know as much as possible about this unit. The importance of a properly functioning driveshaft for reliable vehicle operation cannot be overestimated. This is one of the key elements of car design.
How does a driveshaft work?
The driveshaft or driveshaft is a transmission element. Through this unit, rotation is transmitted from the gearbox to the rear or front axle gearbox. At the same time, the driveshaft is designed quite simply and has changed very little over the hundred-year history of the automotive industry. Any all-wheel drive includes a cardan.
The cardan shaft (CV) consists of several parts:
HF can consist of several segments - three or more. The size and weight of the vehicle directly affect the corresponding performance of the driveshaft. The single-section shaft will consist of a central part and tips equipped with crosses.
What is a cardan shaft
The cardan is a mechanism that transmits rotation from the gearbox to the rear axle gearbox.
The task is complicated by the fact that these two mechanisms are located in different planes relative to each other. All car models whose rear wheels are driven are equipped with cardans. The transmission driveshaft is installed along the vehicle's exhaust system and looks like a long beam running from the gearbox to the rear axle. It is equipped with at least two cross joints (one on each side), and in units with a slight offset of the axes - one.
A similar transmission is also used in the steering system of a car. The hinge connects the steering column with the steering mechanism located in a different plane.
In agricultural machinery, such a device is used to connect additional equipment to the tractor power take-off shaft.
A description of the operating principle of a cardan-type transmission was compiled by the Italian engineer and philosopher G. Cardano. In the automotive industry, this scheme was successfully used by the industrialist Louis Renault on a modification of the De Dion-Bouton car (1898).
Basic driveshaft faults
Defects that occur in the cardan may have various external signs. Among the most characteristic are shocks under the bottom of the car, vibration and hum, especially strong during acceleration. The nature of the symptoms can tell you a lot about which parts will need to be replaced.
A number of simple faults can be easily repaired with your own hands. To successfully complete the procedure, you must have at least minimal knowledge of the HF device, as well as have a set of tools. If the problem is serious, then it is better to entrust its solution to professional services. Independent intervention in this case can lead the cardan to a condition beyond repair.
1. Blows, kicks when turning on the gearbox
If starting from a stop is accompanied by metallic impacts, and vibration is felt during acceleration:
2. Constant or periodic creaking
When you press the accelerator pedal, a squeaking or squeaking noise may occur. It is recommended to carefully study its features, first of all, determine whether the extraneous sound occurs constantly or periodically. For example, when the car warms up, the squeak goes away or remains.
3. Constant hum, howl or whistle, increasing with speed
A hum, noise or whistle of a constant nature, only increasing as the car accelerates, indicates a malfunction of the intermediate support bearing. This means that the lubricant in it has already dried out, and moisture has penetrated into it, causing corrosion.
In this case, it is impossible to do without a thorough diagnosis of the intermediate support. If the results confirm that the bearing is faulty, it must be replaced with a new part as soon as possible.
A situation is likely when the bearing jams. In this case, it rotates in the seat where it is pressed into at the factory. If this happens, then simply replacing the bearing cannot solve the problem. It is necessary to either restore the seating surface or replace this part as well.
We recommend
4. Oil leaks at the junction of the cardan and the gearbox
5. Ringing in the cardan pipe
6. Ringing from the driveshaft
The most likely cause of the ringing is poor fastening of the intermediate support mud deflector. You need to position it in the center and weld it in four places.
7. Scraping or shuffling sound while driving
During rotation, the driveshaft touches parts of the car body. Most often, the driveshaft is interfered with by the gearbox housing or exhaust system parts.
Types of cardan shafts
The type of cardan transmission depends on the purpose. The layout is developed at the design stage. The choice of why a driveshaft of a particular design is needed is determined by the technical characteristics of the car. In some cases, it is necessary to install a multi-shaft mechanism with several hinges.
Asynchronous
The asynchronous circuit is used in many cars with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive.
Feature - during the movement, unequal angular velocities are formed. This is due to the connection of the two forks using a cross at a right angle. The secondary shaft lags behind the main shaft 2 times and overtakes the main one 2 times. To compensate, additional universal joints of unequal speeds are installed. They are mounted at the ends of the shaft. With this scheme, the angle between the pipes can be changed by up to 20°. Disadvantage: due to the complexity, frequent maintenance and repairs are required.
Synchronous
The solution to the problem of asynchronous models was CV joints - constant velocity joints.
They have different designs. Pegout and Renault cars have a Tripod installed. In it, torque is transmitted through 3 spherical rollers. They slide in the grooves of the driven shaft fork. A special feature of synchronous cardans is the ability to work at deflection angles of up to 70°. Vibration is reduced and the maintenance-free service life is increased. Disadvantages - there is a possibility of damage to the anthers off-road.
Flexible and rigid half-cardan transmission
This is one of the types of driveshafts designed to compensate for angular turns and slight changes in the distance between the gearbox and the rear axle while driving.
The elastic link is made of rubber-fabric material or rubber. Compensation for changes in angle occurs due to compression or stretching of this element. A rigid universal joint is rarely installed in cars. The reason is a low degree of reliability, increased noise during operation. The design is used to compensate for installation defects.
How to check the condition of the driveshaft
The first signs of a malfunction in the cardan are noise and increased vibration. Secondary “symptoms” are oil leakage at the junction of the shaft with the gearbox, and a knocking noise occurs when shifting gears. An overpass or inspection hole is required for inspection. You need free access to all elements and good lighting.
Which nodes need to be checked:
- Fastenings. Checking the presence of the locking washer and the degree of its tightening on the nut of the intermediate support and flange connection. A possible defect is the appearance of play and vibration.
- Condition of the elastic coupling. Possible loss of integrity and mechanical damage. They affect the degree of compensation for displacements of the propeller shaft elements. Check - slowly rotate the cardan clockwise and back. There should be no play.
- The appearance of gaps between the sliding fork and the shaft. The reason is wear of parts. To control, you need to rotate the shaft with the coupling. If “beating” occurs or there is play, the sliding fork needs to be replaced.
- Hinges. It is convenient to check using a slotted screwdriver. It is inserted into the eyes of the forks. A sign of a malfunction - there is play when moving.
- Hanging bearing. If the bearing is beating while the shaft is swinging, this indicates that it needs to be replaced.
It is recommended to balance the cardan on a bench.
To do this, special balancer plates are installed on the shaft. After work, their condition is checked. An alternative method is turning. Important: you can try to balance the cardan at home. But this does not guarantee complete elimination of defects.
What determines the price of replacing a driveshaft at a service station?
It is permissible to independently replace the universal joint if you already have at least minimal experience in troubleshooting automobile faults. Otherwise, you can make the problem worse. Even in such a simple unit as a driveshaft, breakdowns are not uncommon due to the fault of inexperienced repairmen. Therefore, it is best to carry out preventive inspections and repairs at a service station.
Often, car service specialists find it difficult to name the price of repairs right away. They first need to conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the malfunction. Then decide on a list of replacement parts and calculate the cost of spare parts. Then find out the time costs for repair work. After calculating all costs, the amount of the service for the car owner is announced.
Also, the make and model of the vehicle affects the cost of repairing the HF, and the design features of the car are also important. There is price differentiation on a geographical basis. In large cities with a population of over a million, especially in the capital and St. Petersburg, replacing a driveshaft will cost more than in places remote from the center.
It is not uncommon for service station specialists to discover other problems during the diagnostic process, the existence of which the car owner was not even aware of. Moreover, it happens that the elimination of this malfunction must be done promptly in order to maintain the functionality of the car. In this case, new repairs are not carried out until it is agreed upon with the customer or owner of the machine.
OPERATING FEATURES OF THE CARDAN TRANSMISSION
A feature of this hinge is uneven rotation. When the angle of position of the drive shaft relative to the driven one changes, the latter accelerates or slows down at certain points, that is, the angular velocity increases or decreases. Moreover, as the angle increases, the speed of advance or lag of the driven shaft from the drive shaft increases, so this transmission of rotation is cyclic in nature. A significant angle (more than 20 degrees) between the shafts increases the load on the hinge components, which can lead to failure.
Let's look at the principle of operation of a cardan joint using an example when the drive shaft is positioned strictly horizontally, and the driven shaft is positioned at an angle downwards (standard position of the cardan joint). The initial position of the inner hinge fork is also horizontal. When transmitting rotation due to the angled position, the downward portion of the fork accelerates relative to the drive shaft. Maximum advance is achieved at the bottom point.
At the same time, part of the driven shaft fork, which began to move upward during rotation, slows down and lags behind the driving one in rotation speed. The maximum lag is at the highest point.
Due to these features of the operation of the joint of unequal angular velocities, rotation is transmitted unevenly.
To reduce the unevenness of rotation speeds and loads, the design of the cardan transmission uses two hinges - at the ends of the hollow shaft. Moreover, for maximum smoothing, the internal forks are located in the same plane.
Due to the use of two hinges, the position angles of the shafts and, accordingly, the unevenness of rotation speeds are reduced.
Due to the uneven rotation between the shafts, the cardan transmission is not used in the transmission design of front-wheel drive vehicles. On such models, the unequal velocity joint is replaced by a constant velocity joint, in which transmission is carried out evenly regardless of the angle between the shafts.
We recommend: Symptoms of a faulty coolant temperature sensor
Which company driveshaft is better to install: opinions of car owners
“I have experience using different driveshafts on CV joints from a wide range of manufacturers. None of them deserve the title of a reliable product. The main weak points are separators and anthers. Last month I replaced the old shaft with a KARDAnovsky one. I immediately noticed the absence of vibration on the crosspieces. Now I don’t worry about the integrity of the anthers either. The fear of stopping somewhere with a completely disabled car has gone away.”
“In December I installed SiM on the rear axle. I had to choose where to replace it, since there was no money for both bridges. Just before the new year, I received a shaft from KARDAN JSC, on which the boot was damaged. Carried out maintenance, lubrication, and changed the boot. I installed it on the front. I didn't notice any problems in the city. But when driving along the highway at speeds from 80 to 100, vibration appeared.
I couldn't stand it for more than a week, I bought SiM again. The difference between these plants is that KARDAN JSC only carries out large-unit assembly, while SiM has established a full production cycle. It was possible to replace it only after the New Year holidays. After which everything became perfect. I’m still driving, let’s see how long these driveshafts can withstand.”
“My factory cardans were from Hammer and Sickle. But the mileage is 85 thousand, and oil leaks have been noticed on the CV joint of the rear CV. Suspicion fell on the boot, but inspection showed its integrity. The reason for the leaks was different. A nut came loose from the gearbox, which led to an oil leak into the CV joint. In addition, the driveshaft itself has already shown play.
The CV joints underwent preventive maintenance with replacement of lubricant and anthers. Then I gave the cardans to a friend, for whom they still work. I bought Belcard for myself. However, they did not like the work. Either there was a defect, or the quality of the company’s products was poor, but at some speeds vibration appeared. I replaced them with new driveshafts from SiM.”
“It all depends on the operating conditions. When driving on asphalt, and if the suspension is stock, it is better to use Sim on both axles. Under more severe conditions, it is optimal to use a shaft from Belkard. Let me explain with my example. I use the car in a mixed cycle. Suspension lift. At the front I have a CV joint. This choice is made because the front axle does not change angles during operation, and this driveshaft is less prone to vibration. The rear axle works with a reinforced cross "belcard".
Technical application on cardan shafts.
1.Safety:
Cardan (drive) shafts must be manufactured in strict compliance with assembly technology, followed by dynamic balancing of the shaft.
The operating parameters underlying the driveshaft design include torque, deflection angle, rotation speed, overall shaft length, length compensation, operating conditions (ambient temperature). It is important to avoid exceeding the load on the cardan drive in order to maintain its working condition.
Only qualified personnel are allowed to install and dismantle the shaft. Also during maintenance (changing grease in the universal joints, replacing crosspieces), replacing individual parts of the shaft (replacing fasteners, balancing the cardan drive, replacing crosspieces, flanges, painting the cardan, etc.). During any repair work, the shaft must be at rest. Products must be certified.
2.Transportation and storage of cardan shafts:
Cardan shafts are supplied ready for installation according to performance parameters, balanced.
In order not to disrupt the quality of balancing of cardan shafts, it is necessary to avoid falls and impacts during transportation and storage. All balancing plates must be present on the shaft; if the absence of a balancing weight is detected, it is necessary to dynamically balance the shaft.
Belts must be used when loading and unloading cardan shafts. The belts must be securely fastened in the eyes (forks, flanges) of the shaft; the driveshaft must not roll or overhang to one side.
For safe transportation, a horizontal position is preferable. It is also recommended to store the cardans in a horizontal position to prevent the possibility of tipping over.
It is recommended to store cardans on wooden pallets, not in damp or damp areas. Cardan shafts must be folded so that they are clearly visible; during long-term storage, open parts (without paintwork) must be regularly checked for corrosion, and if necessary, covered with protective agents, for example, wax.
3.Installation of cardan shafts:
To ensure high-quality installation of the cardan shaft, the mating components must be thoroughly cleaned of corrosion, anti-corrosion agents, wax, paint, and dirt that has fallen on the end centering parts of the flanges.
All flange surfaces must be inspected for damage and dents.
In shafts with length compensation (the presence of a movable spline), check the correct position of the forks, the direction is indicated by opposite arrows or clamp brackets.
Do not separate the driveshaft so as not to confuse the correct position of the assembly, as this may adversely affect their balancing.
Do not rotate driveshafts using mounting arms or pry bars at the joint where the spider is located, this may cause damage to bearings and seals, as well as grease nipples.
Shafts that have been stored for more than six months must be re-lubricated before installation.
As a connecting element for flange connections, it is recommended to use hexagonal bolts DIN931, with a strength class of 10.9, and hexagonal nuts DIN980, with a strength class of 10.9. This fastener can withstand severe loads and vibrations and is ideal for securing drive shafts.
The tightening torque of the bolts must be observed (see table 1). Tighten the bolts diagonally using a torque wrench.
Table 1
| Bolt | M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 |
| Tightening torque (Nm) | 14 | 35 | 69 | 120 | 190 | 295 |
4.Maintenance of cardan shafts:
Cardan shafts can be divided into 2 types: - without maintenance (standard assembly), - with maintenance, the presence of grease on the crosspieces, spline connection (special order of the cardan).
If the shaft is serviceable, then the moving parts must be lubricated periodically. Lubrication intervals (see Table 2) depend on specific operating conditions. During servicing, old grease and other foreign matter that may have gotten into the bearings and splines must be removed by pushing with new lubricant. Clean the grease nipple of the spider from dirt, continue to lubricate until new grease comes out from under all 4 bearings, do not exceed the maximum grease pressure of 15 bar, use lithium-based grease.
table 2
| Using a cardan drive | Lubrication interval |
| Commercial vehicle | 30,000 km or after 1 year |
| Dump trucks and construction equipment | 10,000 km or every 200 hours |
| Agricultural machinery | 200 hours or after 1 month |
| Industrial equipment | 500 owls or after 1 month |
Under high external influences (temperature, dirt, moisture, etc.), it is recommended to shorten the lubrication intervals indicated above.
It is recommended to perform maintenance at least once a year. It is necessary to check all bolted connections on the flange clamps and connecting flanges, if necessary, tighten them using a torque wrench.
If extraneous noise and vibration are detected during shaft operation, repair work should be carried out (restoring the cardan drive).
If any faults are found during the above checks, the driveshaft must be immediately removed and repaired by a specialist workshop or sent to specially trained personnel for repair.
Kardan-Valtechno offers solutions in the selection of spare parts for repairing cardans. We supply cardan shafts, crosspieces, support bearings, flanges for European trucks and special equipment. We accept orders for the production of non-standard cardans according to customer drawings. We select crosspieces and cardans according to size, diagram, part number, VIN number of the car. Regional supplies of spare parts throughout Russia.